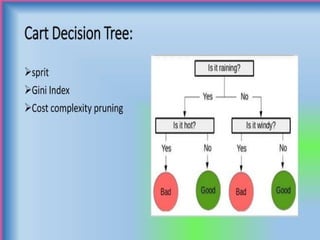
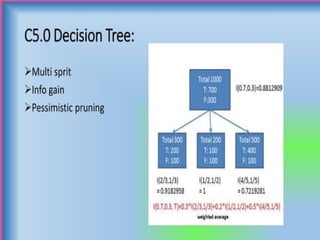
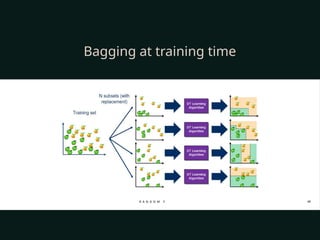
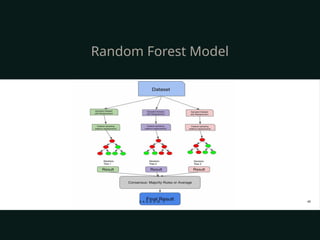
The document discusses supervised and unsupervised machine learning techniques, focusing on unsupervised models like K-means clustering and hierarchical clustering, as well as the Random Forest algorithm. Random Forest is an ensemble learning method that utilizes bagging and feature bagging to create a more accurate model through multiple decision trees. It highlights the advantages, such as versatility and ease of understanding, alongside disadvantages like increased model complexity with more trees.















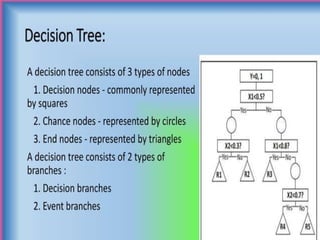


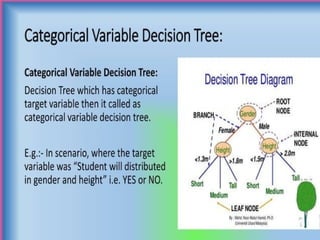

![[Size < 2000?]
/
Yes (<=2000) No (>2000)
/
[Bedrooms < 3?] [Lot Size < 5000 sq.ft?]
/ /
Yes (<=3) No (>3) Yes (<5000) No (>5000)
/ /
[Year < 1990?] [Price: $400K] [Price: $450K] [Price:$550K]
/
Yes No
/
[Price: $300K] [Price: $350K]
Continuous Variable Decision Tree](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/supervisedandunsupervisedlearningalgorithm-240925063749-5a5e5784/85/Supervised-and-Unsupervised-Learning-pptx-24-320.jpg)