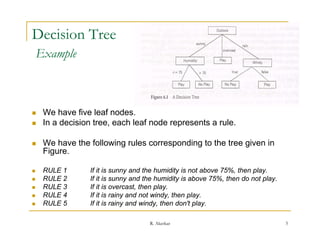
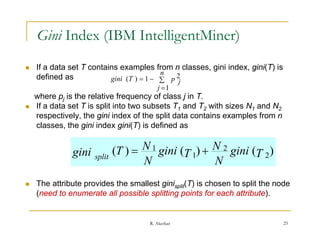
This document provides an overview of decision trees, including:
- Decision trees classify records by sorting them down the tree from root to leaf node, where each leaf represents a classification outcome.
- Trees are constructed top-down by selecting the most informative attribute to split on at each node, usually based on information gain.
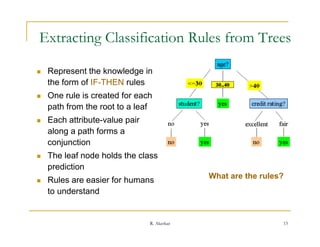
- Trees can handle both numerical and categorical data and produce classification rules from paths in the tree.
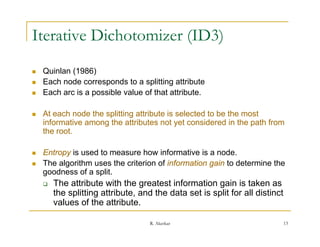
- Examples of decision tree algorithms like ID3 that use information gain to select the best splitting attribute are described. The concepts of entropy and information gain are defined for selecting splits.












![Entropy
Entropy measures the homogeneity (purity) of a set of examples.
It gives the information content of the set in terms of the class labels of
the examples.
Consider that you have a set of examples, S with two classes, P and N. Let
the set have p instances for the class P and n instances for the class N.
So the total number of instances we have is t = p + n. The view [p, n] can
be seen as a class distribution of S.
The entropy for S is defined as
Entropy(S) = - (p/t).log2(p/t) - (n/t).log2(n/t)
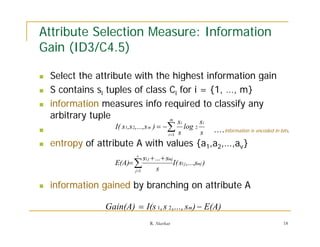
Example: Let a set of examples consists of 9 instances for class positive,
and 5 instances for class negative.
Answer: p = 9 and n = 5.
So Entropy(S) = - (9/14).log2(9/14) - (5/14).log2(5/14)
= -(0.64286)(-0.6375) - (0.35714)(-1.48557)
= (0.40982) + (0.53056)
= 0.940
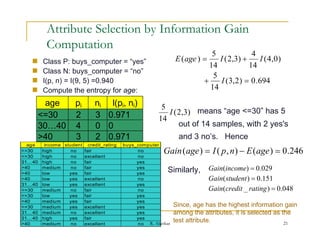
R. Akerkar 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/decisiontree-110906040745-phpapp01/85/Decision-tree-19-320.jpg)
![Entropy
y
The entropy for a completely pure set is 0 and is 1 for a set with
equal occurrences f both th classes.
l for b th the l
i.e. Entropy[14,0] = - (14/14).log2(14/14) - (0/14).log2(0/14)
= -1.log2(1) - 0 l 2(0)
1 l 2(1) 0.log2(0)
= -1.0 - 0
=0
i.e. Entropy[7,7] = - (7/14).log2(7/14) - (7/14).log2(7/14)
= - (0.5).log2(0.5) - (0.5).log2(0.5)
= - (0.5).(-1) - (0.5).(-1)
= 0.5 + 0.5
=1
R. Akerkar 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/decisiontree-110906040745-phpapp01/85/Decision-tree-20-320.jpg)



![Solution 2
SPLIT: Age <= 50
----------------------
| High | Low | Total
--------------------
S1 (left) | 8 | 11 | 19
S2 (right) | 11 | 10 | 21
--------------------
For S1: P(high) = 8/19 = 0.42 and P(low) = 11/19 = 0.58
For S2: P(high) = 11/21 = 0.52 and P(low) = 10/21 = 0.48
Gini(S1) = 1-[0.42x0.42 + 0.58x0.58] = 1-[0.18+0.34] = 1-0.52 = 0.48
Gini(S2) = 1-[0.52x0.52 + 0.48x0.48] = 1-[0.27+0.23] = 1-0.5 = 0.5
Gini-Split(Age<=50) = 19/40 x 0.48 + 21/40 x 0.5 = 0.23 + 0.26 = 0.49
SPLIT: Salary <= 65K
<
----------------------
| High | Low | Total
--------------------
S1 (top) | 18 | 5 | 23
S2 (bottom) | 1 | 16 | 17
--------------------
For S1: P(high) = 18/23 = 0.78 and P(low) = 5/23 = 0.22
For S2: P(high) = 1/17 = 0.06 and P(low) = 16/17 = 0.94
Gini(S1) = 1-[0.78x0.78 + 0.22x0.22] = 1-[0.61+0.05] = 1-0.66 = 0.34
Gini(S2) = 1-[0.06x0.06 + 0 94x0 94] = 1-[0 004+0 884] = 1-0 89 = 0 11
1-[0 06x0 06 0.94x0.94] 1-[0.004+0.884] 1-0.89 0.11
Gini-Split(Age<=50) = 23/40 x 0.34 + 17/40 x 0.11 = 0.20 + 0.05 = 0.25
R. Akerkar 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/decisiontree-110906040745-phpapp01/85/Decision-tree-27-320.jpg)

![Solution 3
Intuitively Salary <= 65K is a better split point since it produces
relatively ``pure'' partitions as opposed to Age <= 50 which
pure'' 50,
results in more mixed partitions (i.e., just look at the distribution
of Highs and Lows in S1 and S2).
More formally, let us consider the properties of the Gini index.
If a partition is totally pure, i.e., has all elements from the same
class, then gini(S) = 1-[1x1+0x0] = 1-1 = 0 (for two classes).
On the other hand if the classes are totally mixed, i.e., both
classes have equal probability then
gini(S) = 1 - [0 5x0 5 + 0 5x0 5] = 1 [0 25+0 25] = 0 5
[0.5x0.5 0.5x0.5] 1-[0.25+0.25] 0.5.
In other words the closer the gini value is to 0, the better the
partition is. Since Salary has lower gini it is a better split.
is split
R. Akerkar 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/decisiontree-110906040745-phpapp01/85/Decision-tree-29-320.jpg)
