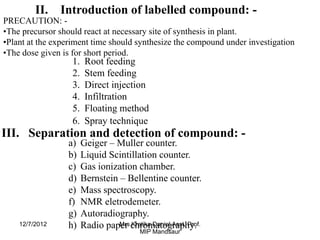
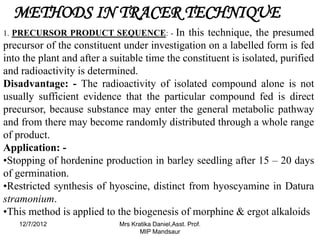
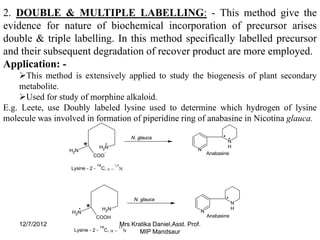
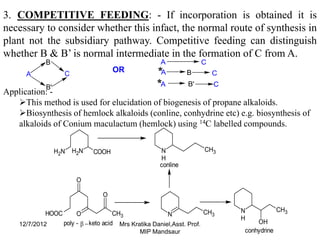
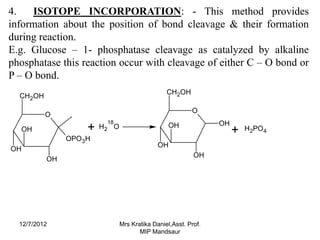
The document discusses the tracer technique, which involves incorporating radioactive isotopes into plant metabolites to trace biosynthetic pathways. It defines the technique and explains that radioactive isotopes like carbon-14 and hydrogen-3 are commonly used. The summary describes some key applications of the technique, like tracing the pathway from phenylalanine to the cyanogenic glycoside prunasin, and determining the location and quantity of compounds containing a radioactive tracer like glucose. It also lists some requirements for the technique, such as using a sufficient starting concentration of the tracer and ensuring it is involved in the relevant synthesis reactions.



![• The labelled compound can be prepared by use of
two types of isotopes.
» Radioactive isotopes.
» Stable isotopes.
• Radioactive isotopes: - [e.g. 1H, 14C, 24Na, 42K, 35S,
35P, 131I decay with emission of radiation]
– For biological investigation – carbon & hydrogen.
– For metabolic studies – S, P, and alkali and alkaline earth
metals are used.
– For studies on protein, alkaloids, and amino acid – labelled
nitrogen atom give more specific information.
– 3H compound is commercially available.
• Stable isotopes: - [e.g. 2H, 13C, 15N, 18O]
– Used for labelling compounds as possible intermediates in
biosynthetic pathways.
– Usual method of detection are: – MASS spectroscopy [15N,
18O]
– NMR spectroscopy [2H, 13C]
12/7/2012 Mrs Kratika Daniel,Asst. Prof.
MIP Mandsaur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tracertechnique-121207032024-phpapp02/85/Tracer-technique-4-320.jpg)