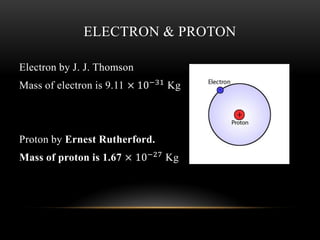
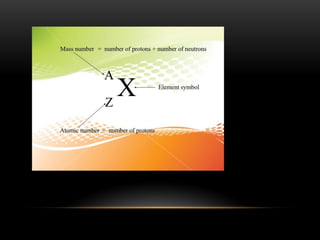
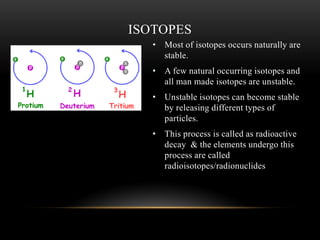
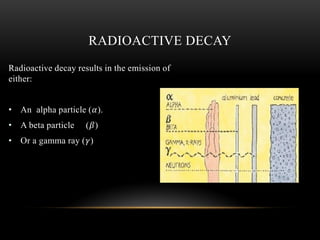
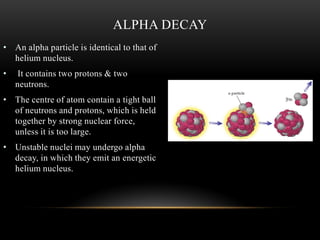
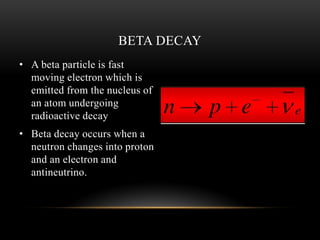
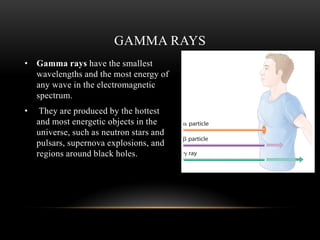
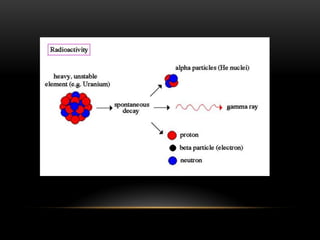
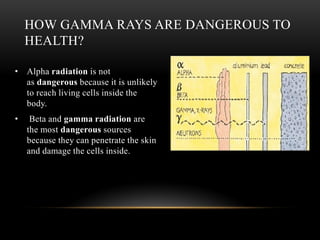
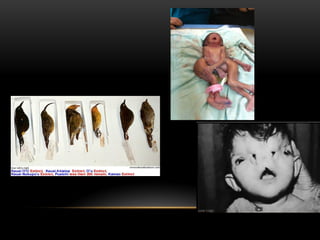
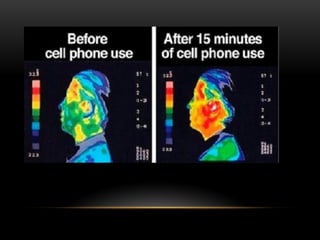
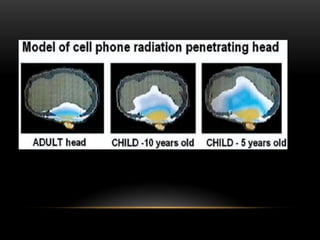
The document discusses nuclear physics, focusing on the properties and interactions of atomic nuclei, including types of radiation (alpha, beta, gamma) and their applications. It explains radioactive decay, the instability of isotopes, and their implications for nuclear power and medicine. Additionally, it highlights the health risks associated with different types of radiation, particularly gamma rays, while noting the limited availability and challenges of using uranium as a power source.