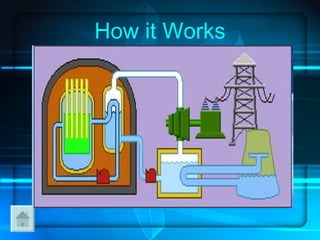
Nuclear power plants generate electricity through nuclear fission. They have several advantages like producing no greenhouse gases, but also pose risks like nuclear waste and accidents. A nuclear power plant has several key parts including a nuclear reactor to produce heat from uranium fission and machines to convert this heat into electricity.