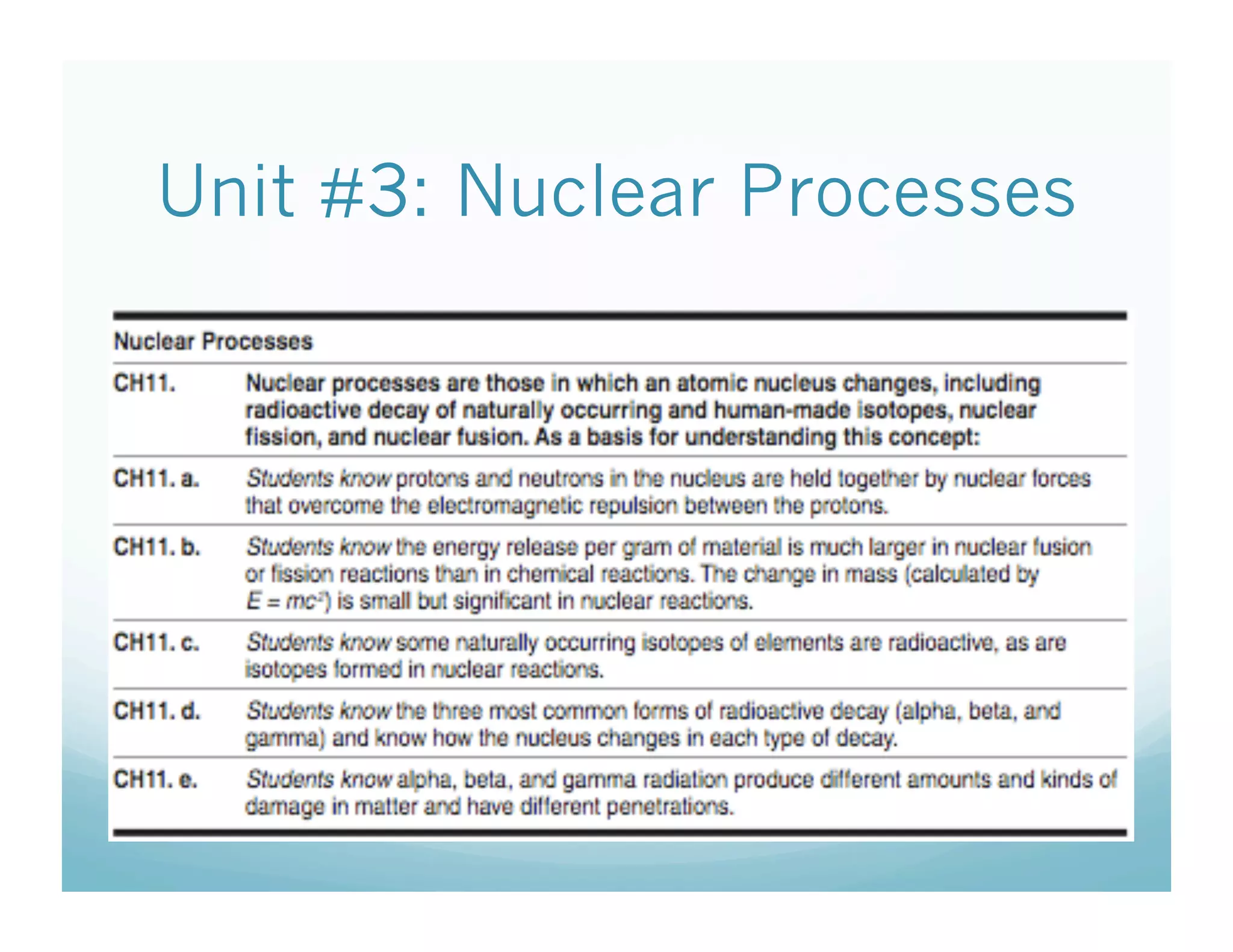
The document discusses radioactive decay and the three main types: alpha, beta, and gamma decay. It defines each type of particle in terms of its symbol, description, and penetrating power. The key points are that alpha particles have low penetration and are equivalent to helium nuclei, beta particles are equivalent to electrons or positrons and have medium penetration, and gamma rays are high-energy electromagnetic radiation with high penetration.