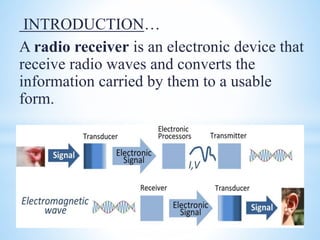
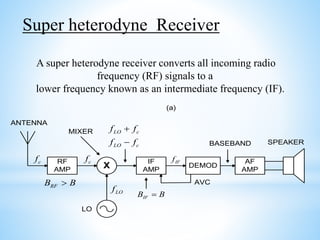
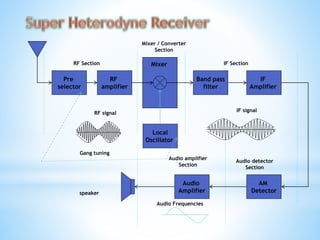
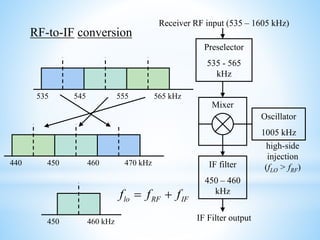
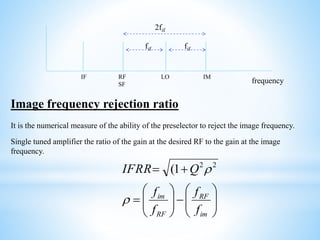
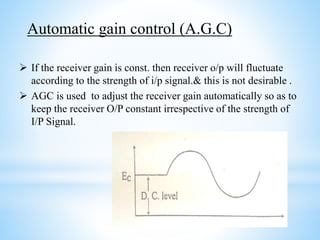
A radio receiver uses radio waves to convert information into a usable form. It selects the desired signal, amplifies it, and demodulates it. A superheterodyne receiver converts incoming radio frequencies to a lower intermediate frequency. It has five sections - RF, mixer/converter, IF, audio detector, and audio amplifier. The intermediate frequency remains constant, providing high selectivity and sensitivity across the tuning range. The superheterodyne concept is used in most modern receivers due to its performance advantages.