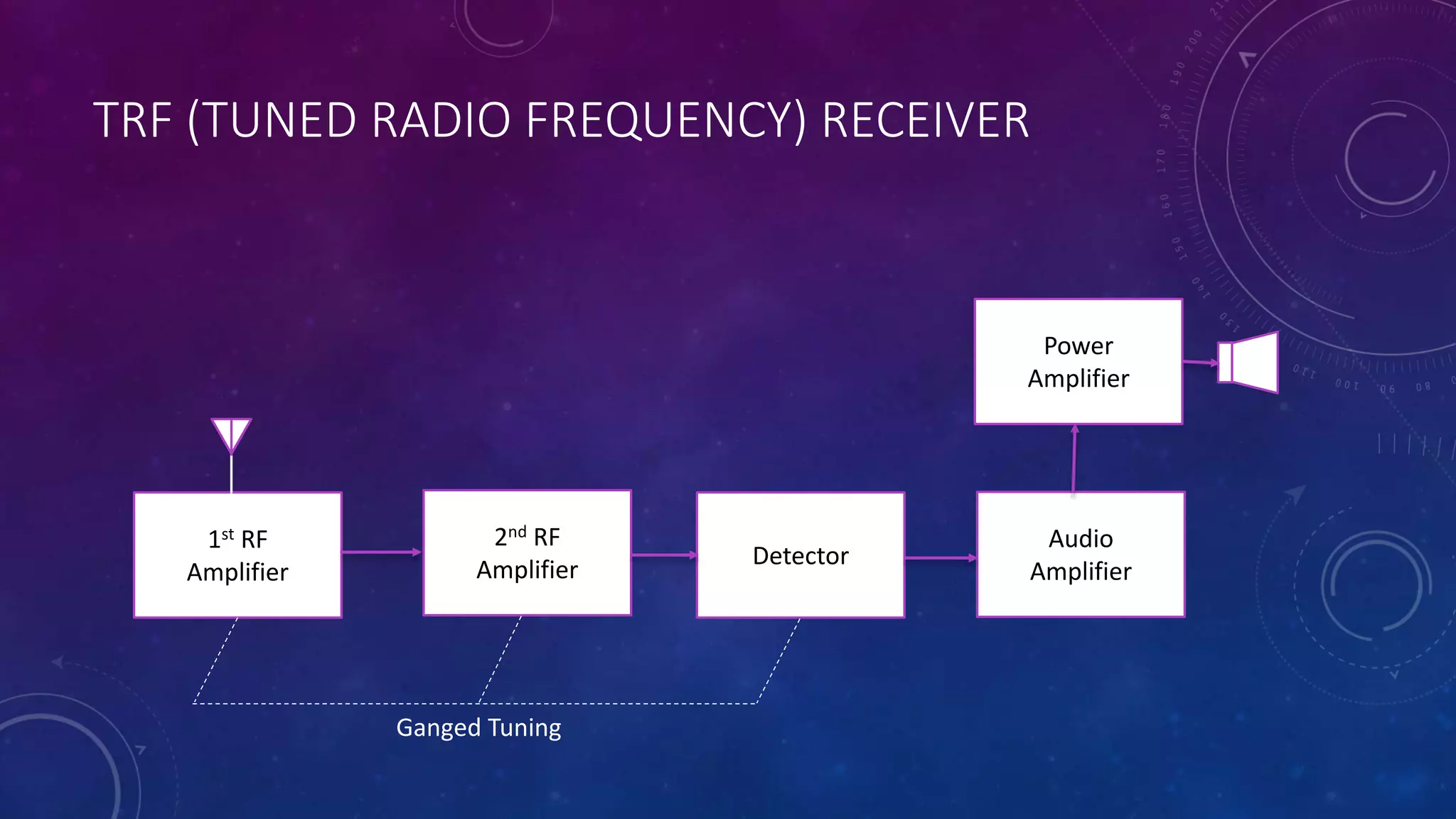
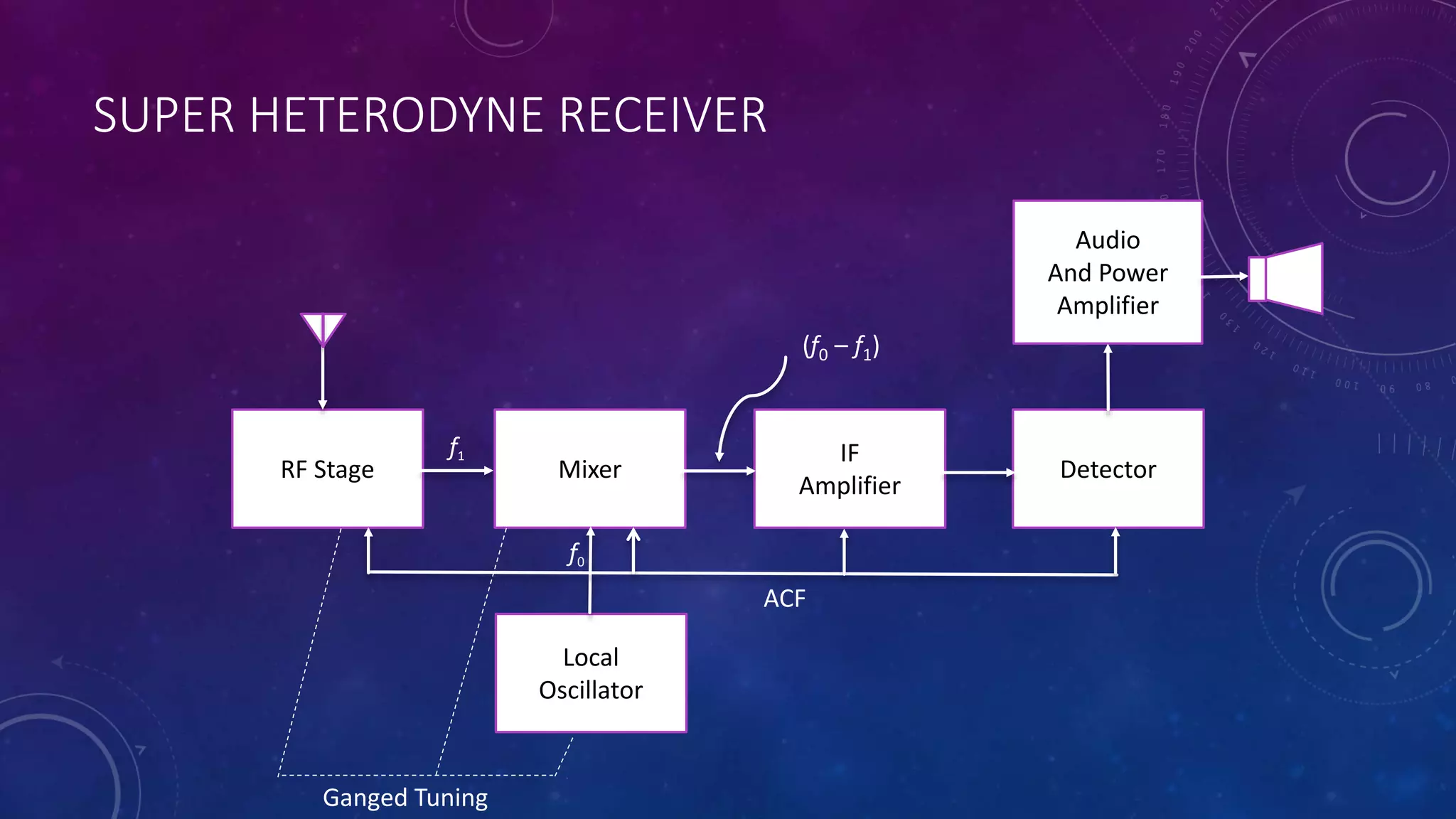
Receivers are devices that receive radio signals at their destination. There are two main types of receivers: tuned radio frequency (TRF) receivers and superheterodyne receivers. TRF receivers were once widely used but are now limited to fixed frequency applications due to issues with selectivity and instability at higher frequencies. Superheterodyne receivers mix the incoming radio signal with a local oscillator signal to convert it to a lower intermediate frequency, addressing the issues with TRF receivers and providing more uniform gain and selectivity across frequencies.