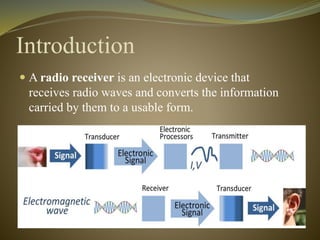
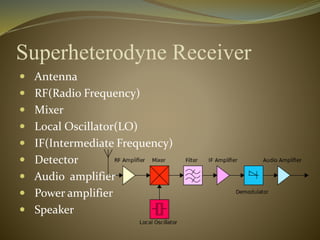
This document discusses the history and types of radio receivers. It describes how the earliest radio receiver was created in 1896 by Alexander Popov and was based on Maxwell's discovery of electromagnetic waves. There are three main types of receivers discussed - crystal radios, tuned radio frequency receivers, and superheterodyne receivers. Crystal radios require no power source beyond the radio waves themselves, while tuned radio frequency receivers have individually tuned amplifier stages and superheterodyne receivers mix signals to extract an intermediate frequency. The document also covers frequency ranges, sensitivity, selectivity and how radio waves propagate.