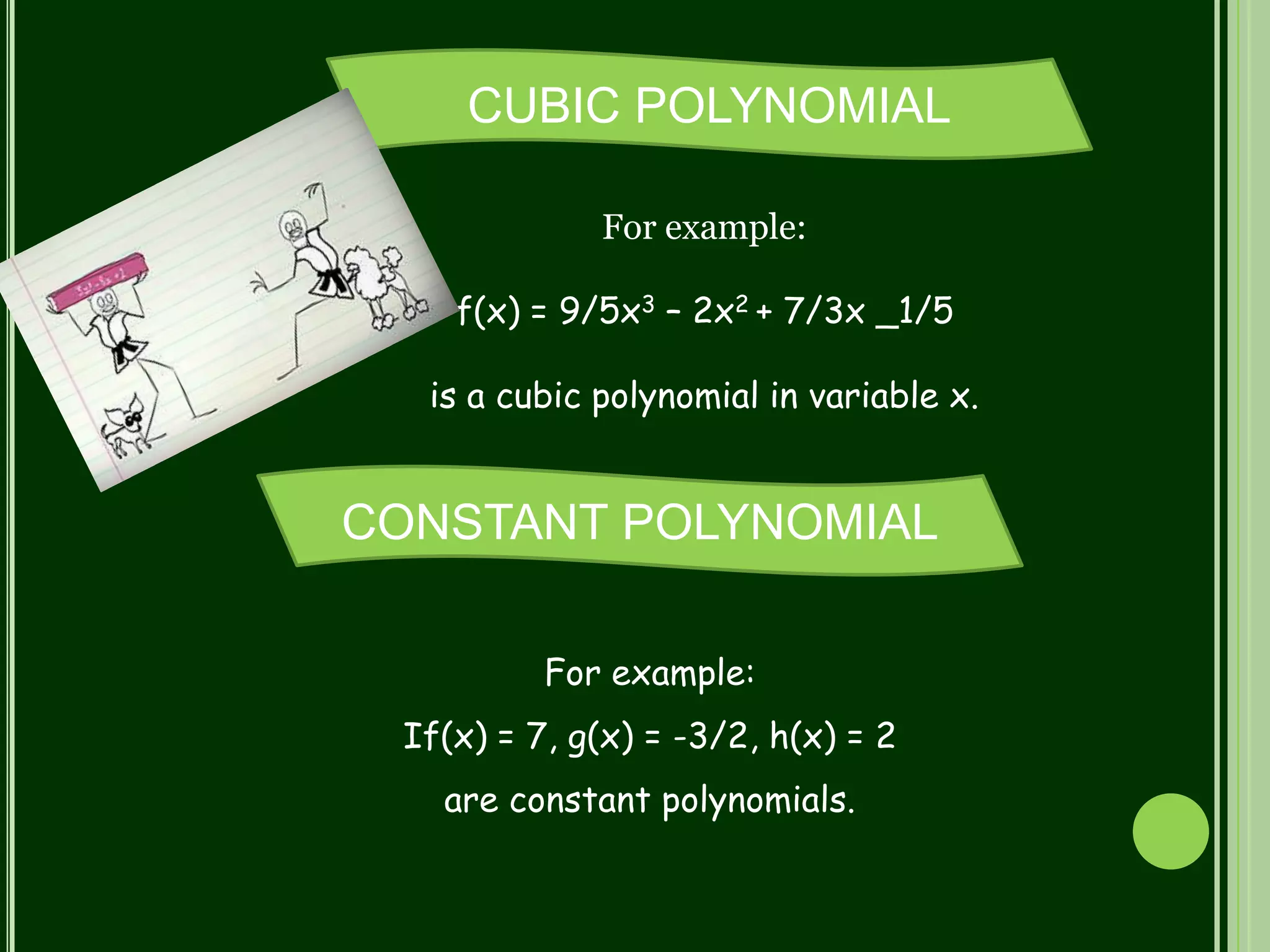
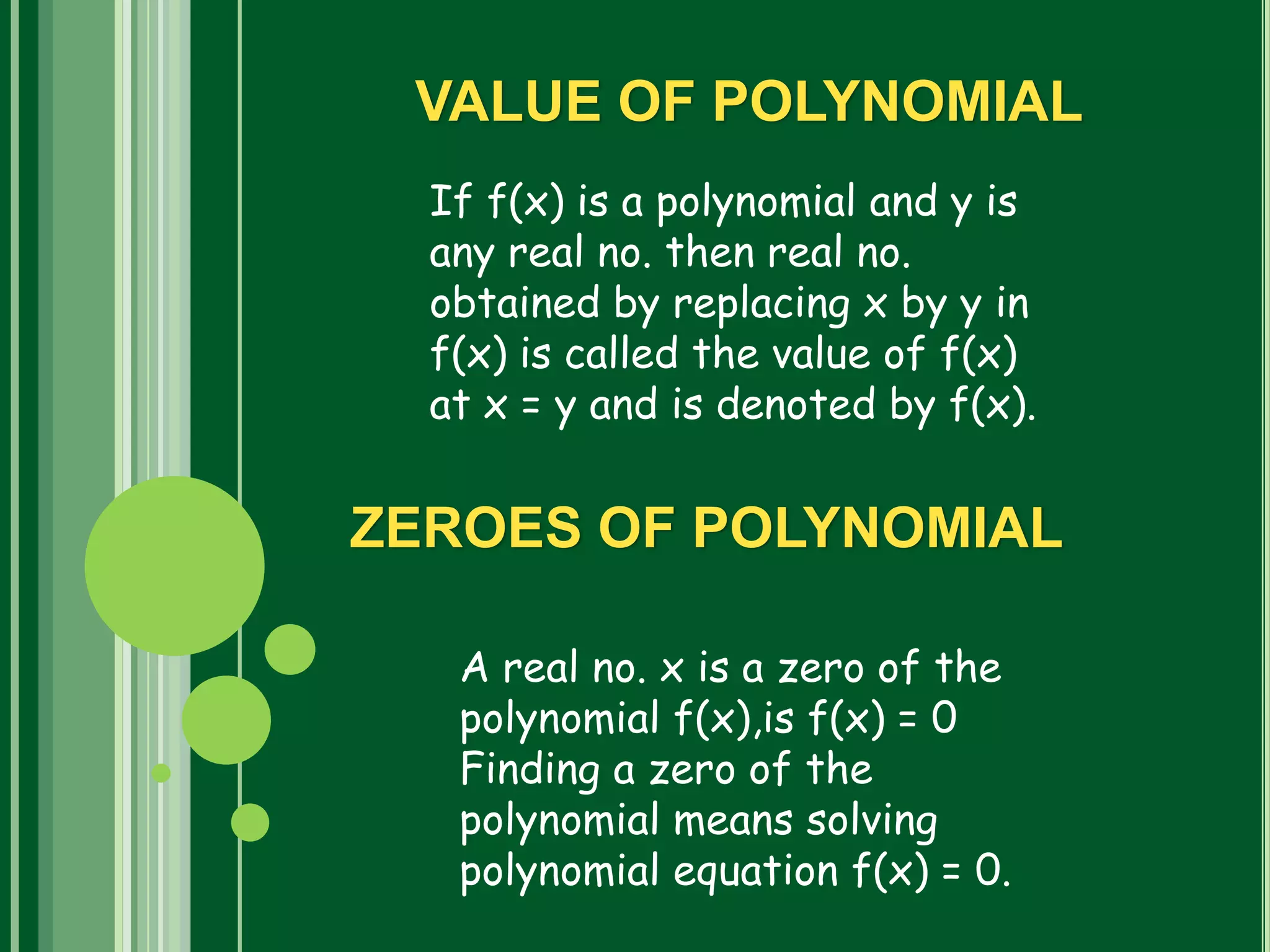
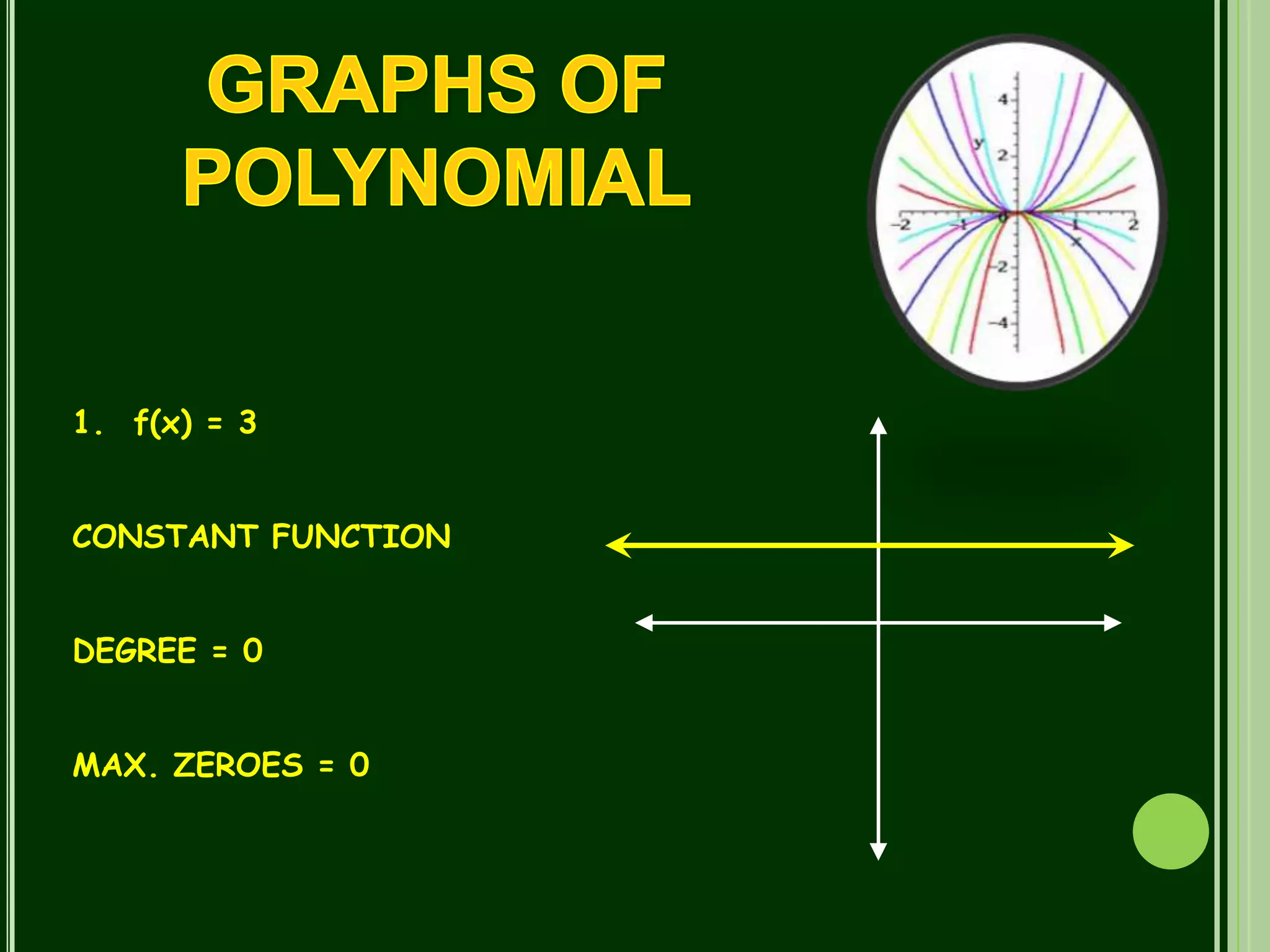
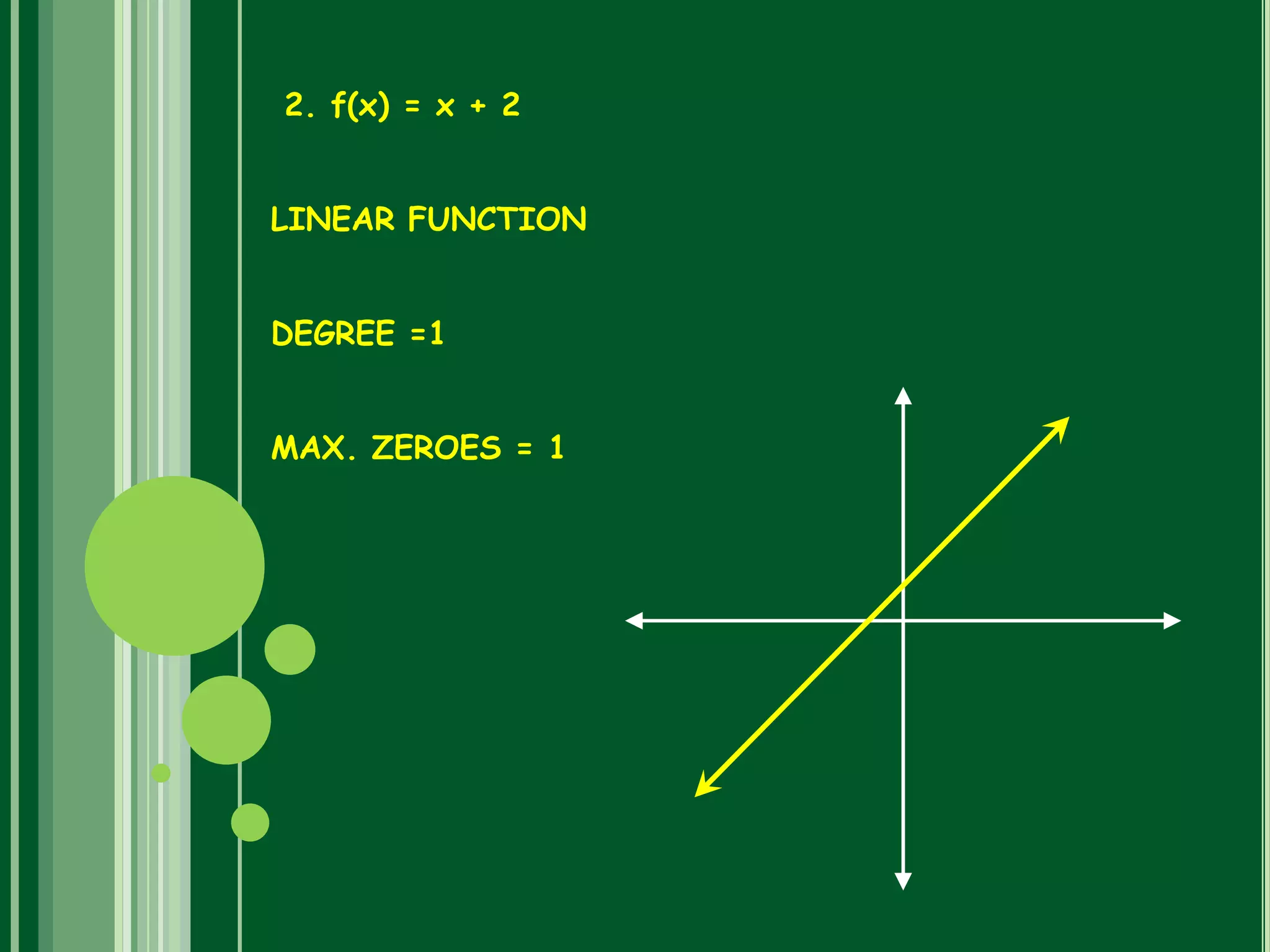
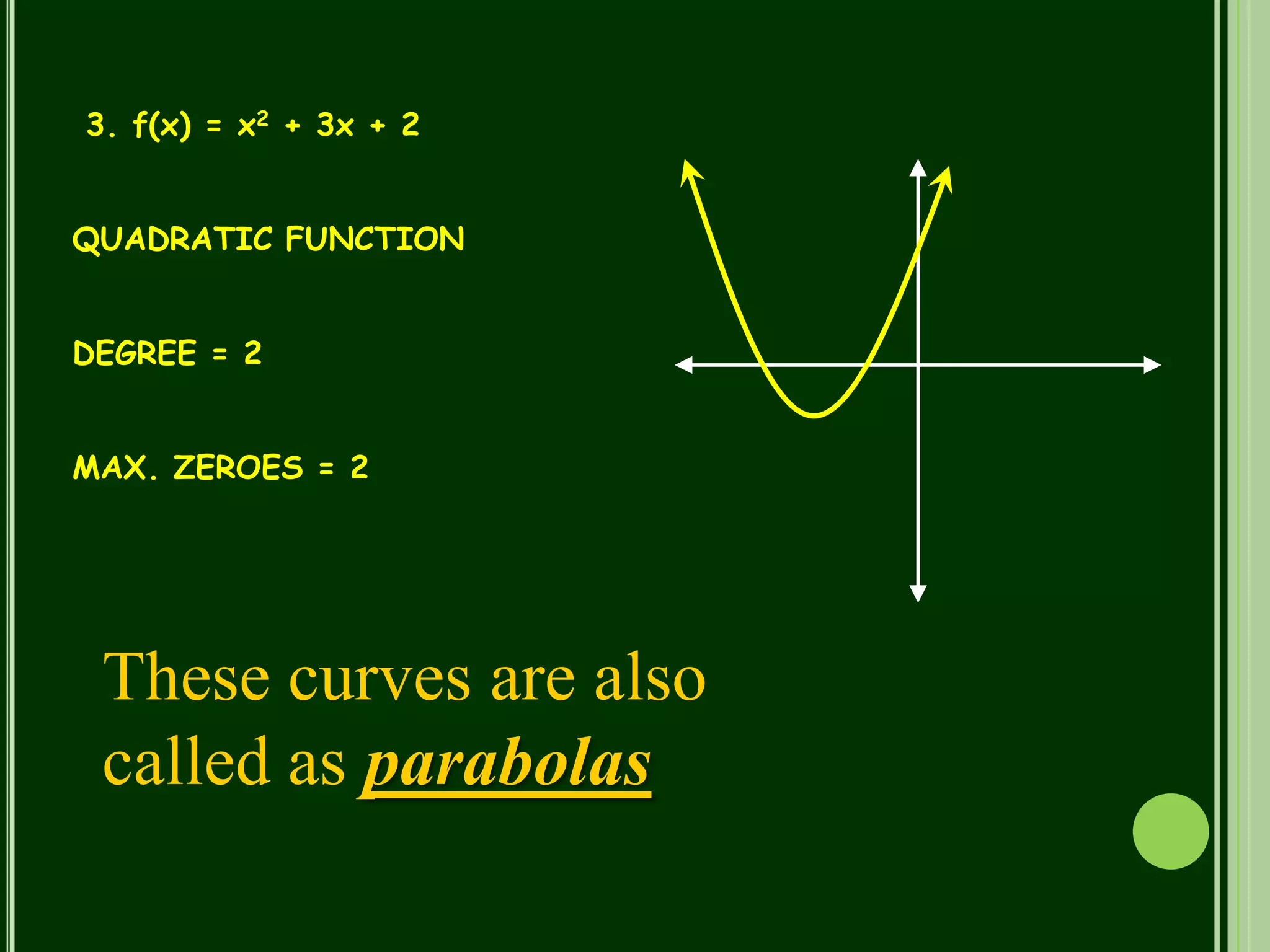
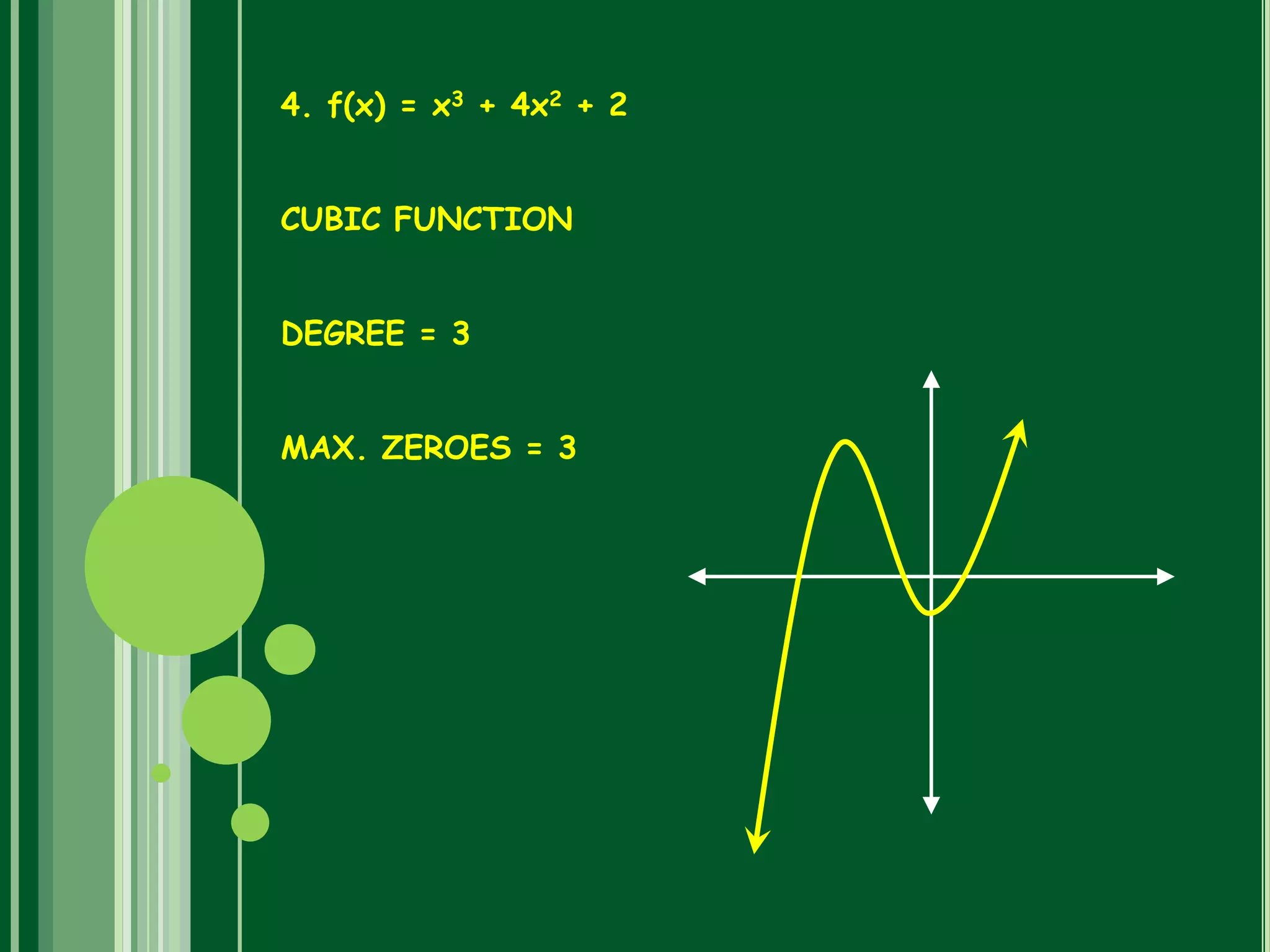
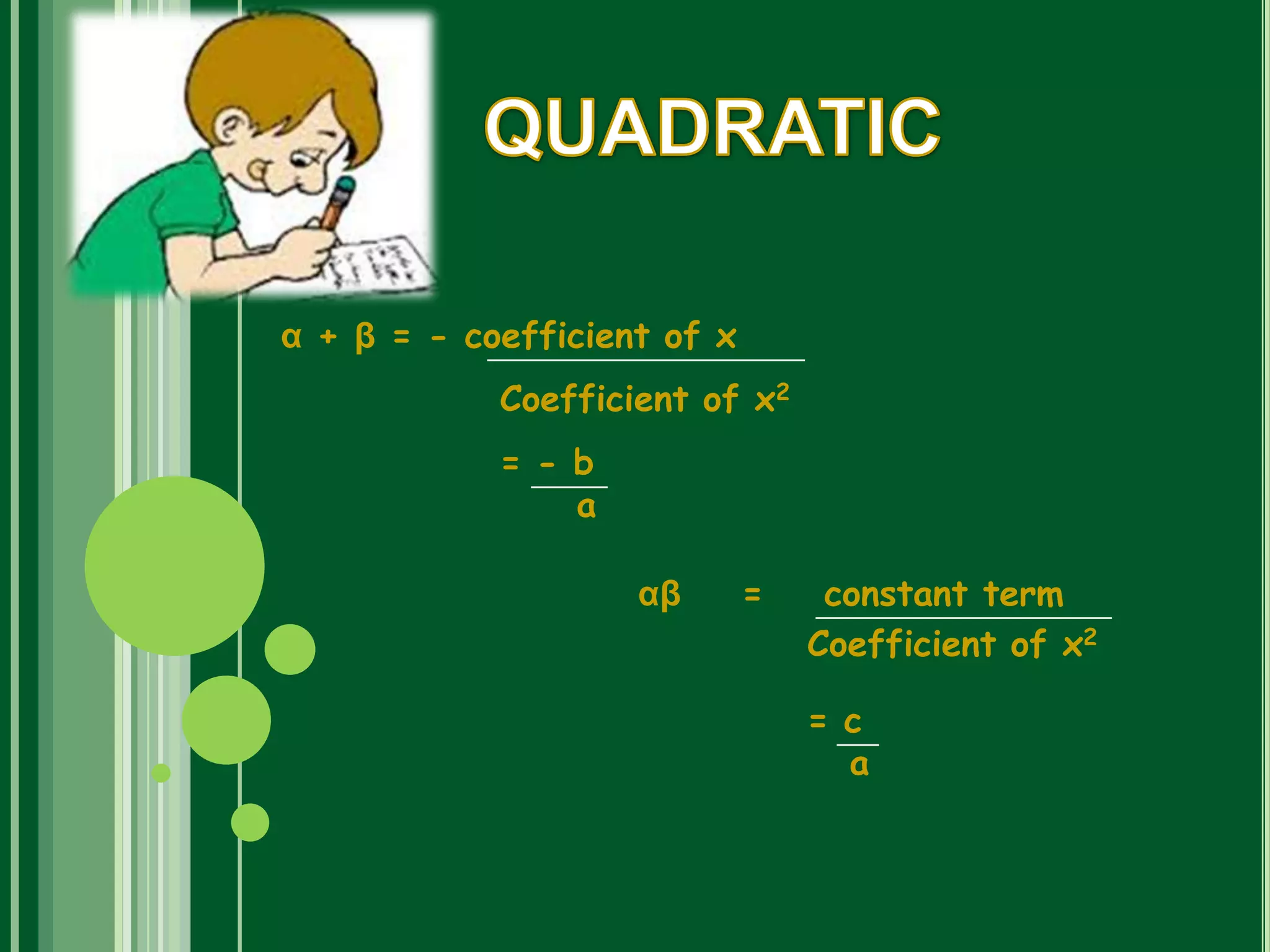
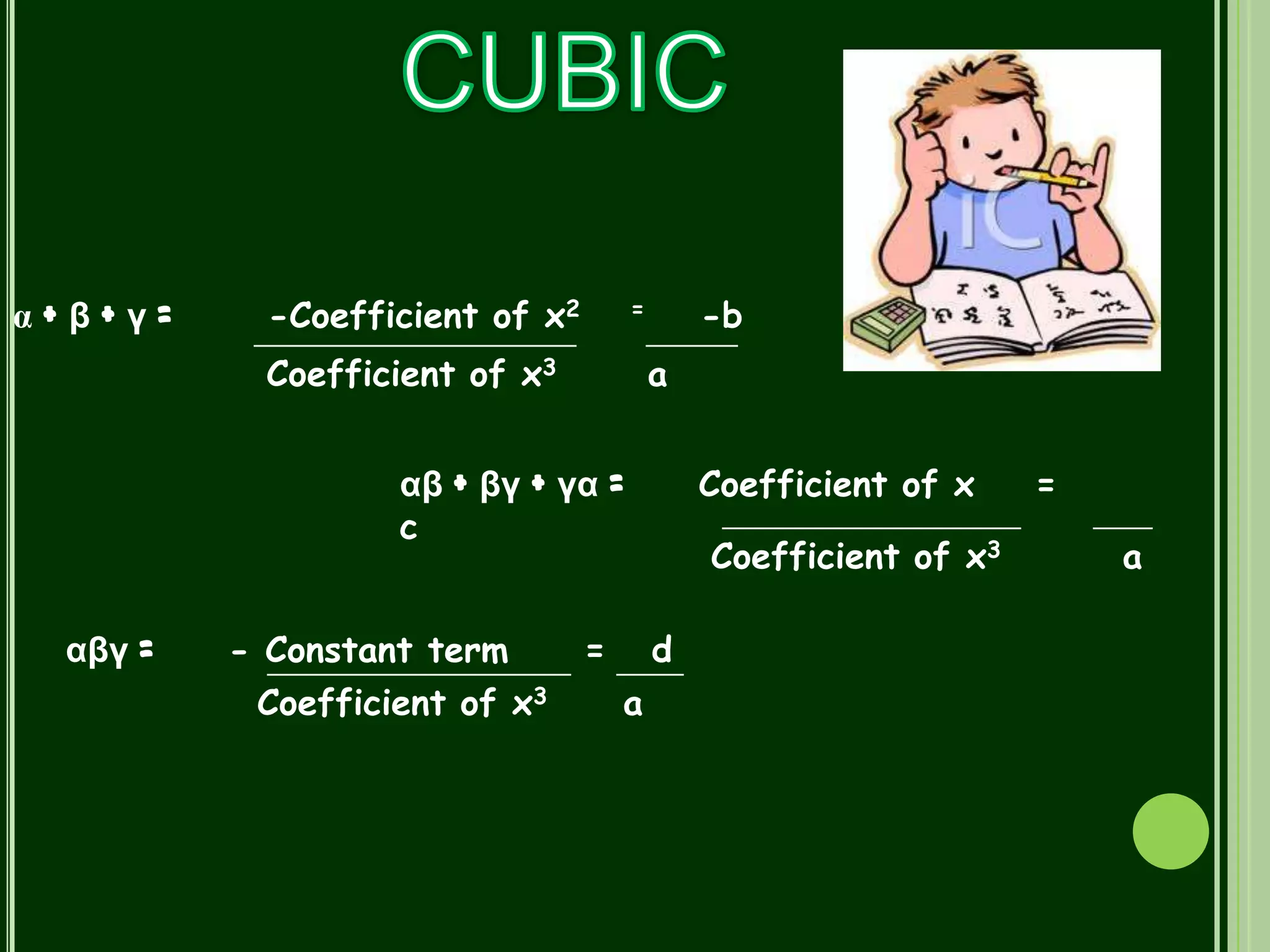
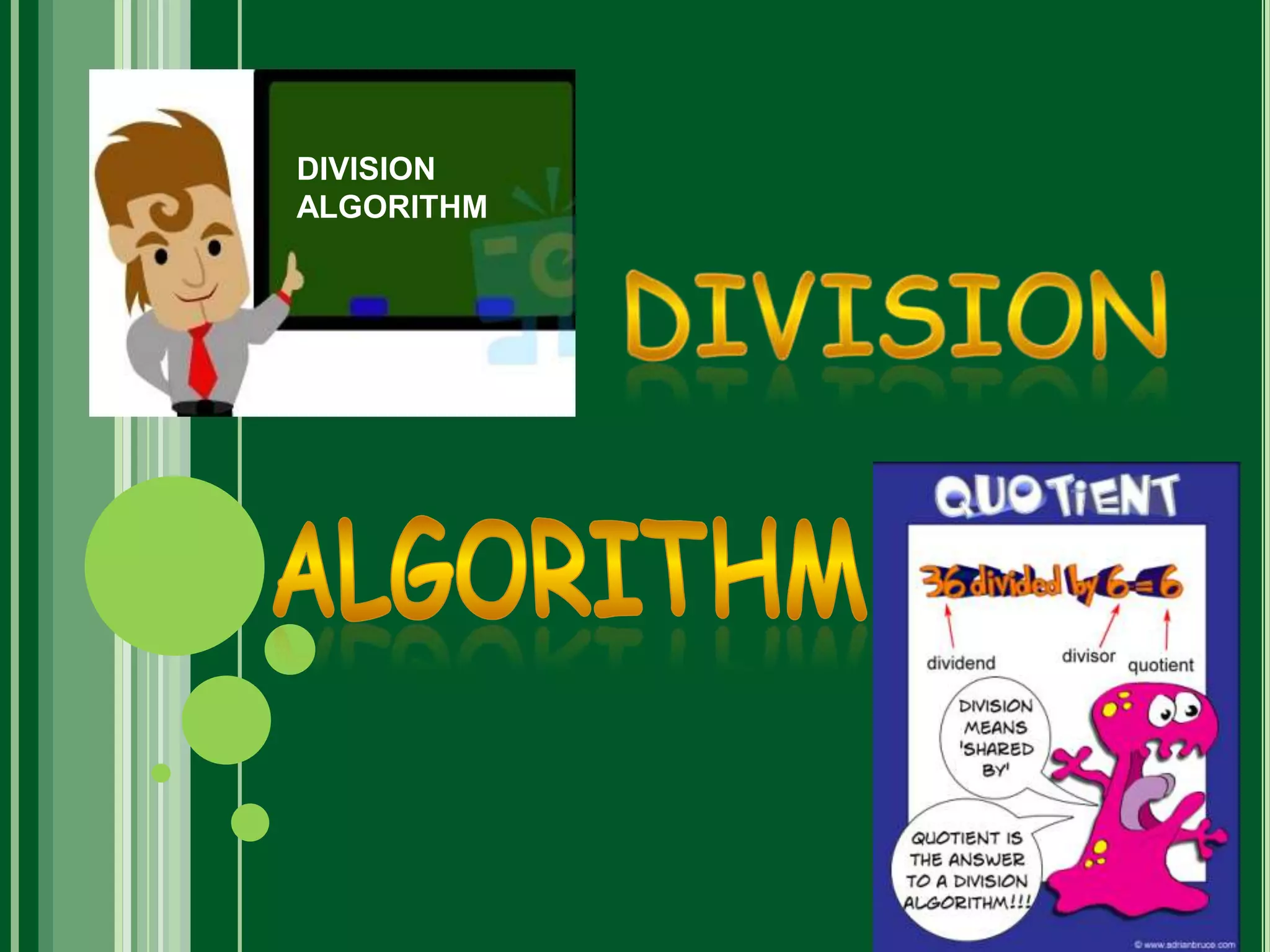
Polynomials are mathematical expressions constructed from variables and constants using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponents of whole numbers. They appear in many areas of mathematics and science. Polynomials can be used to form equations that model problems in various domains. They also define polynomial functions that are used in fields like physics, chemistry, economics, and social sciences. Polynomials are classified based on their degree, with linear polynomials having degree 1 and quadratic polynomials degree 2. The maximum number of zeroes a polynomial can have is equal to its degree.