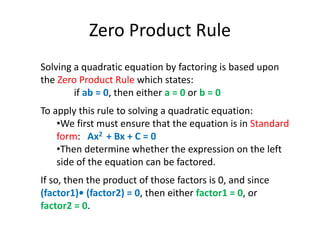
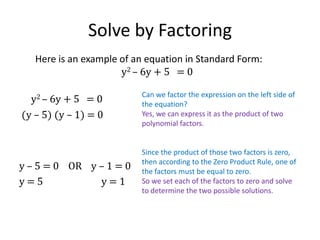
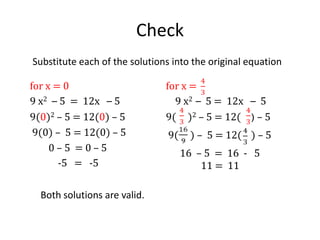
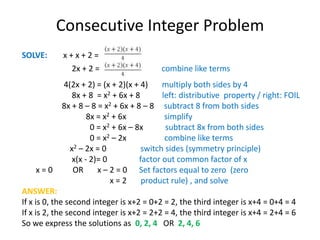
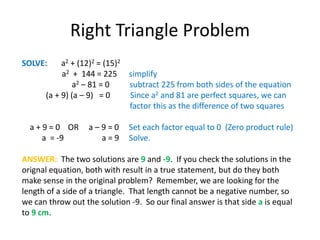
The document discusses solving quadratic equations by factoring. It provides examples of factoring quadratic expressions to find the solutions to the equations. These include using the zero product rule, factoring a common factor, and factoring a perfect square. It also provides two word problems involving consecutive integers and the Pythagorean theorem and shows how to set up and solve the quadratic equations derived from the word problems.