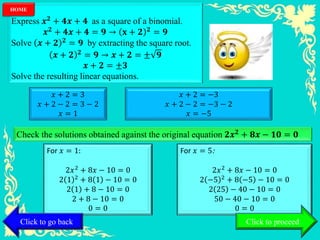
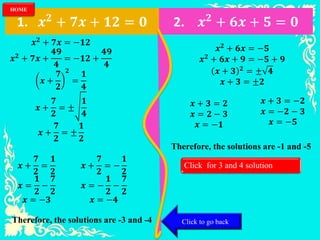
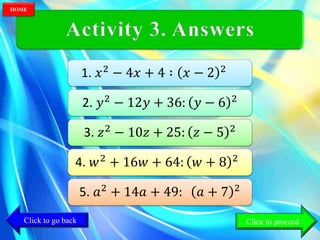This document provides instruction on solving quadratic equations by completing the square. It begins by defining a quadratic equation and explaining why the coefficient of the quadratic term cannot be zero. It then presents the steps to solve a quadratic equation by completing the square, which involves transforming the equation into the form (x - h)2 = k. An example problem is worked through to demonstrate the process.