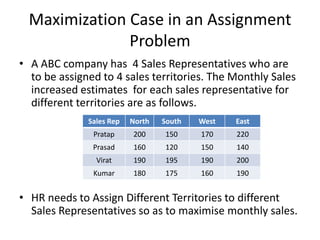
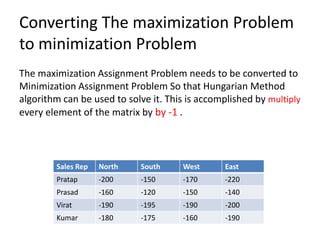
The document discusses applying linear programming to solve employee assignment problems. It describes the assignment problem as assigning personnel to tasks to optimize resources like time and cost. It provides an example of assigning 5 candidates to 4 work jobs to minimize the total time. It defines decision variables and constraints, formulates the objective function to minimize total time, and explains how to solve it using the Hungarian method algorithm. The algorithm involves subtracting row/column minimums, drawing lines to cover all zeros, checking for optimality, and adjusting uneovered elements iteratively until optimal. It also discusses converting a maximization assignment problem to minimization to use the Hungarian method.