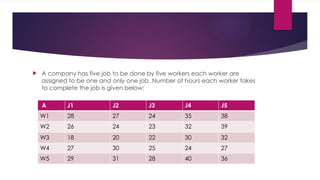
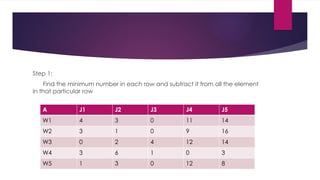
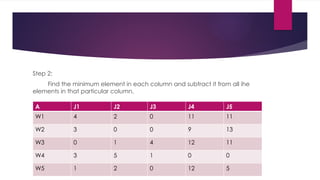
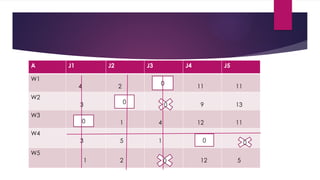
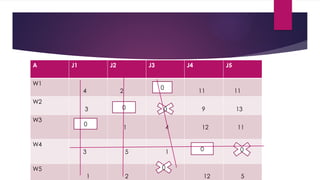
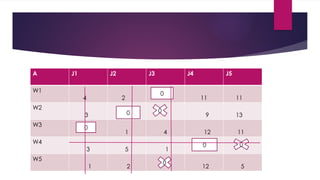
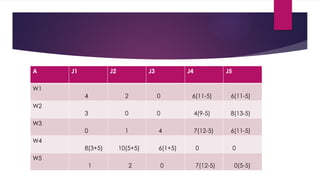
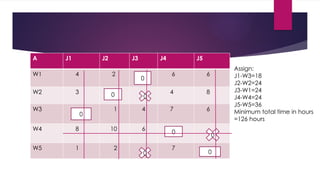
assignment problem in ppt power point presentation in it. again pick the problem of the case study. and solve the problem by step by step.
and the step1 is used to minimize the smallest element in the row and subtracted it from all the element in it. and the step2 is used to minimize the smallest element in the column and subtracted it from all the element in it. and step 1 and step 2 rea remarkable