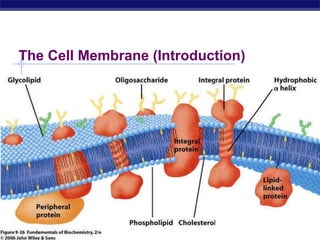
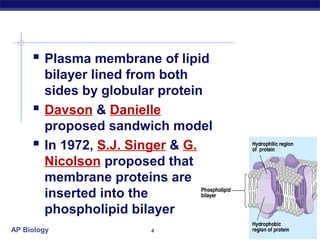
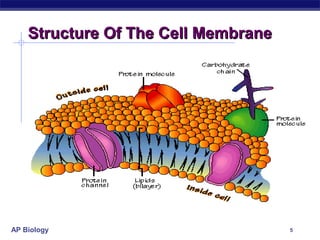
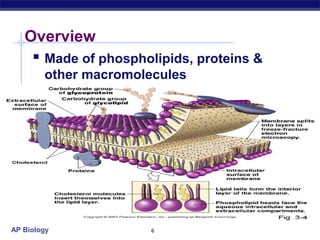
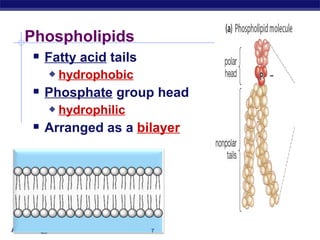
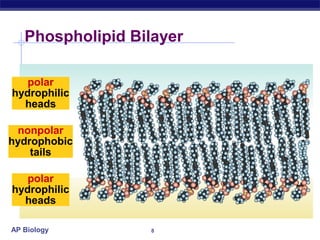
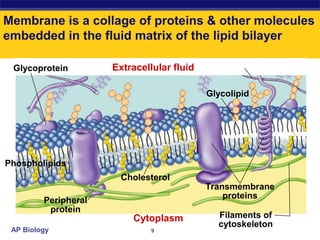
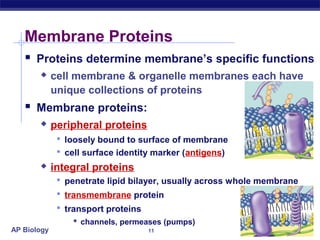
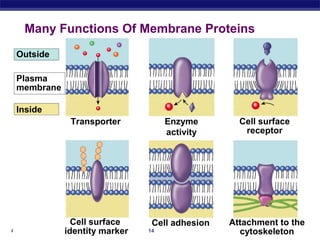
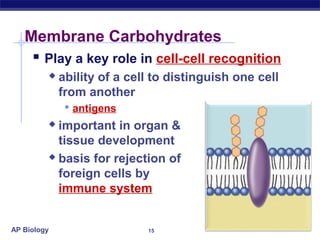
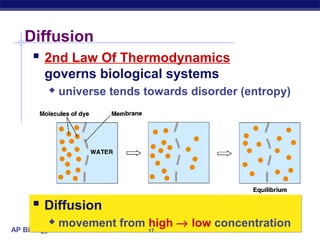
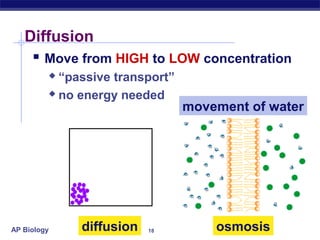
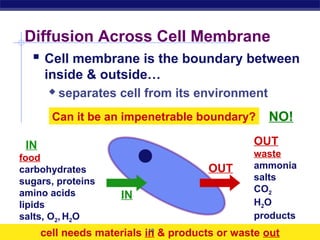
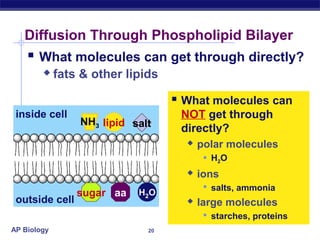
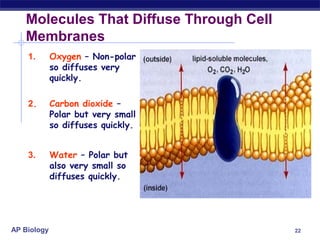
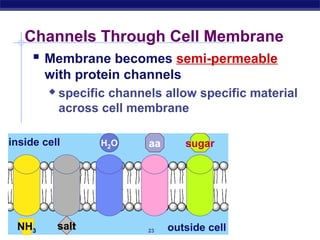
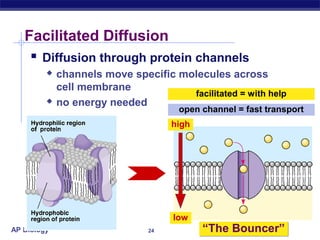
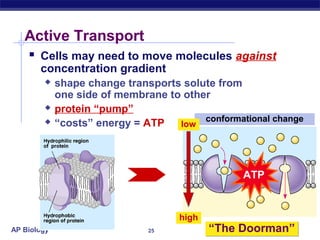
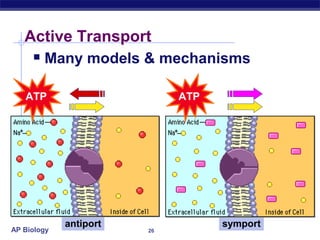
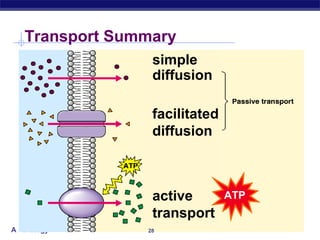
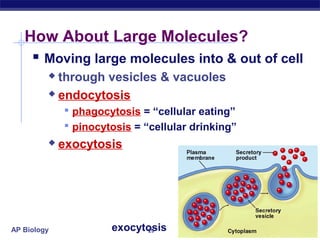
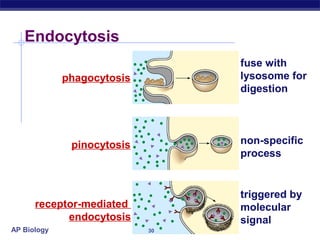
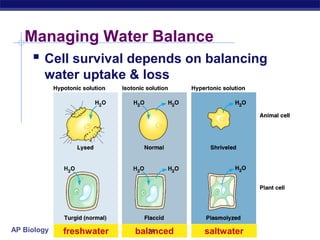
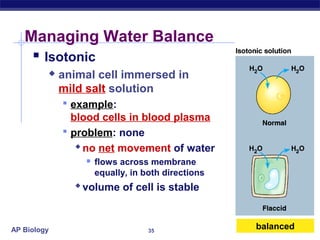
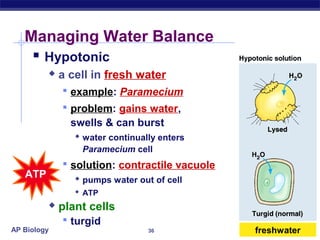
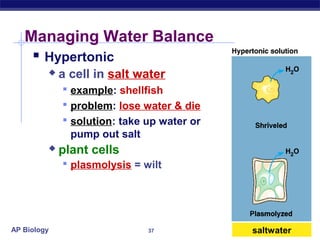
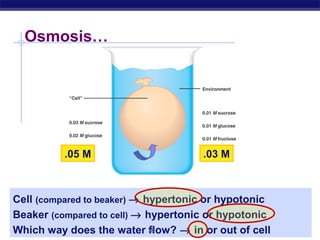
The cell membrane is a thin barrier that separates the living cell from its nonliving surroundings and controls what enters and exits the cell. It is made up of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins and carbohydrates. Membrane proteins and carbohydrates perform important functions like transport, acting as enzymes or receptors, and attaching to the cytoskeleton. There are three main types of transport across the membrane - passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport. Passive diffusion moves molecules down their concentration gradient without energy, while active transport moves molecules against their gradient by using ATP.