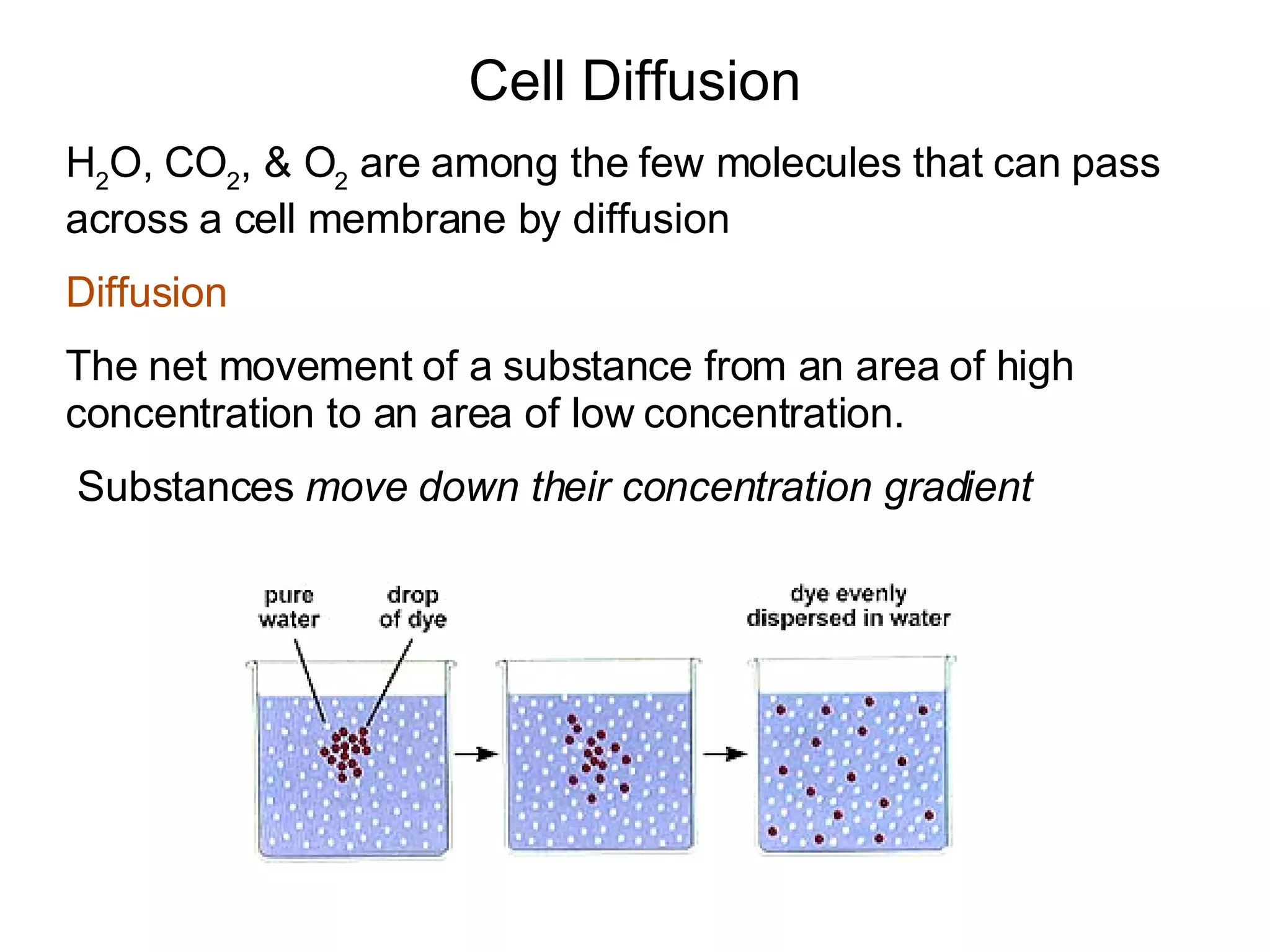
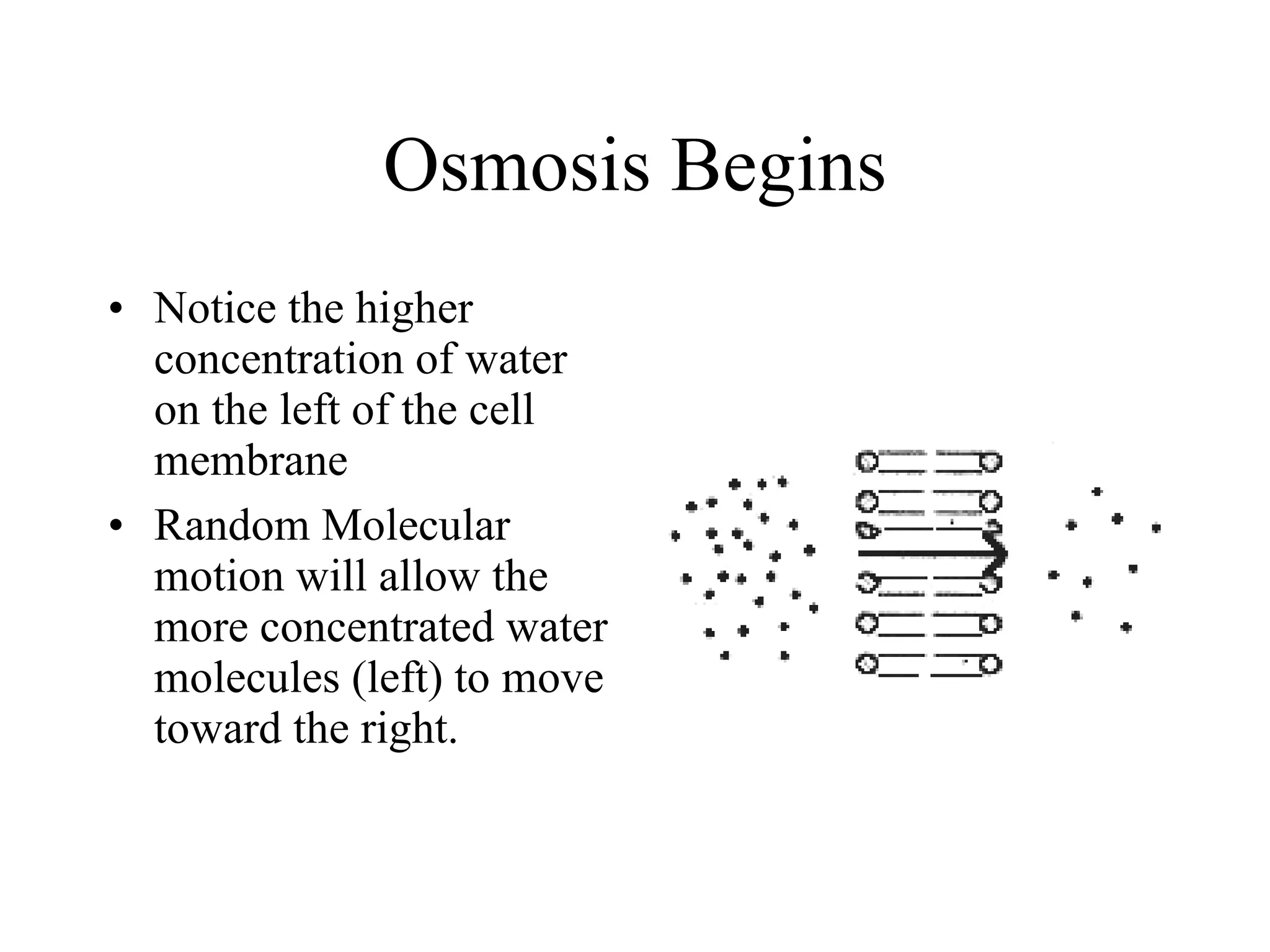
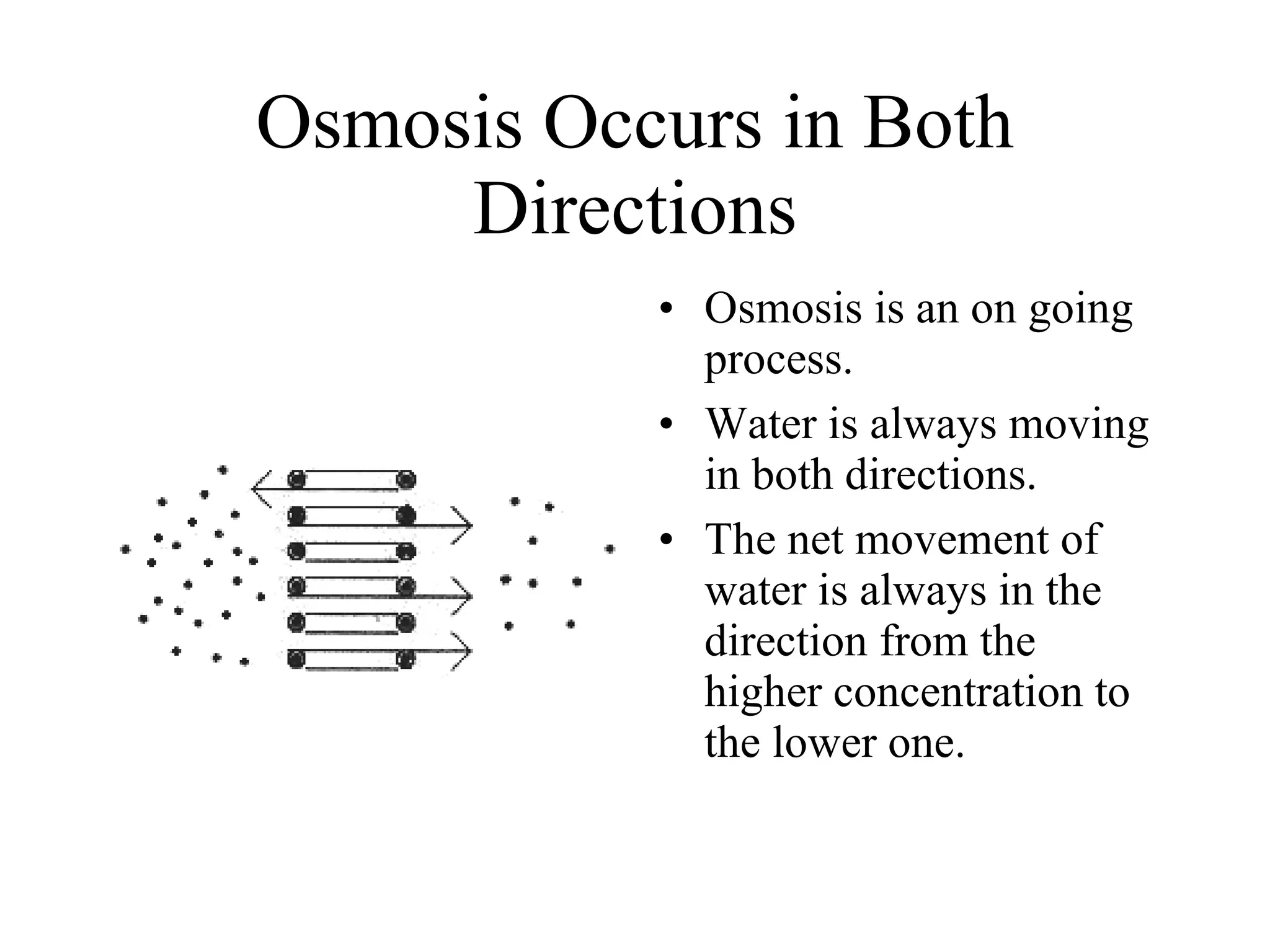
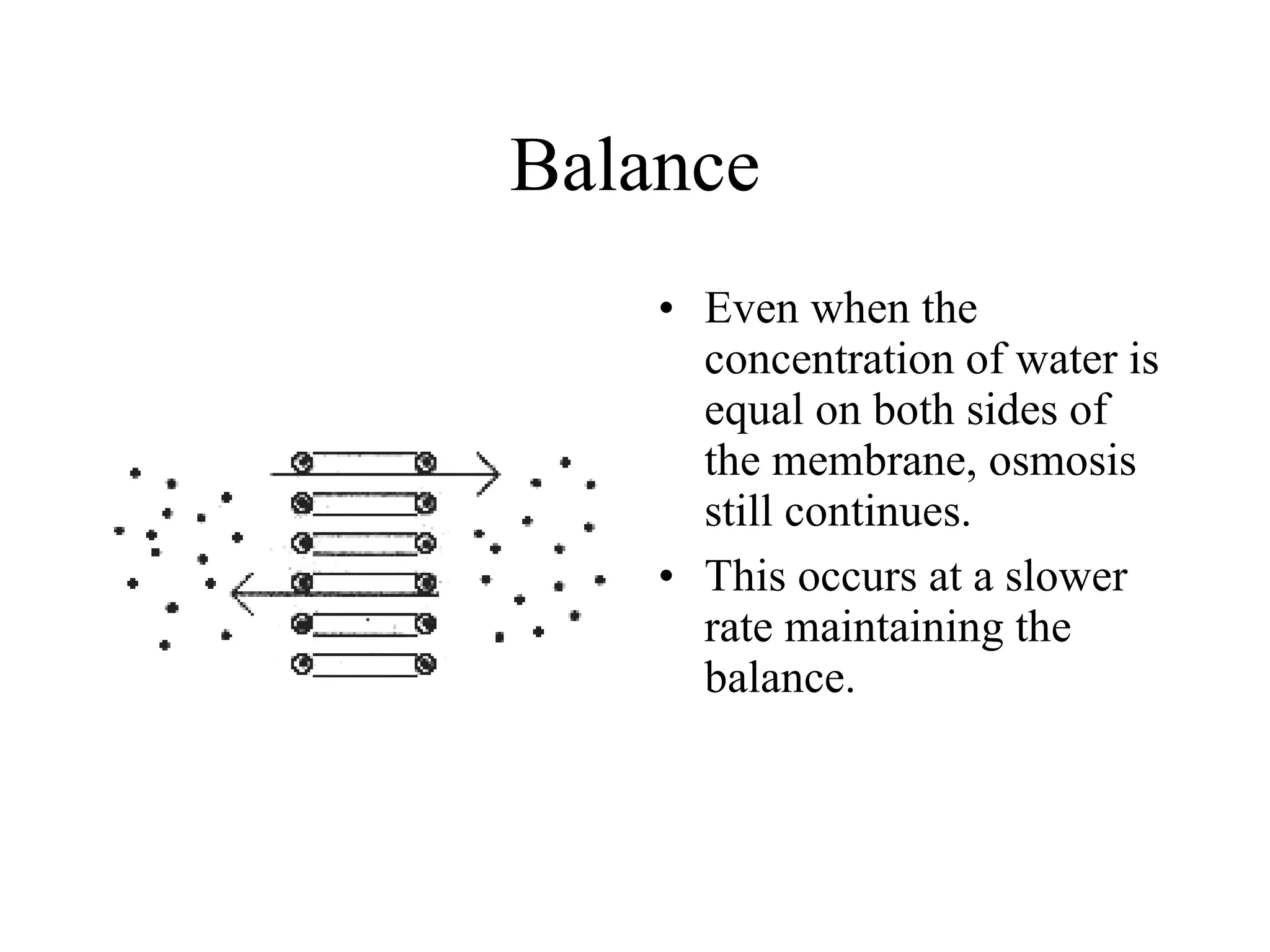
The document discusses cell membrane transport and osmosis. It explains that cell membranes are semi-permeable and allow water and some gases to pass through via diffusion down their concentration gradients. Osmosis is defined as the diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to lower concentration. The document provides examples of how osmosis causes cells to swell or shrink depending if the solutions outside the cell are hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic.