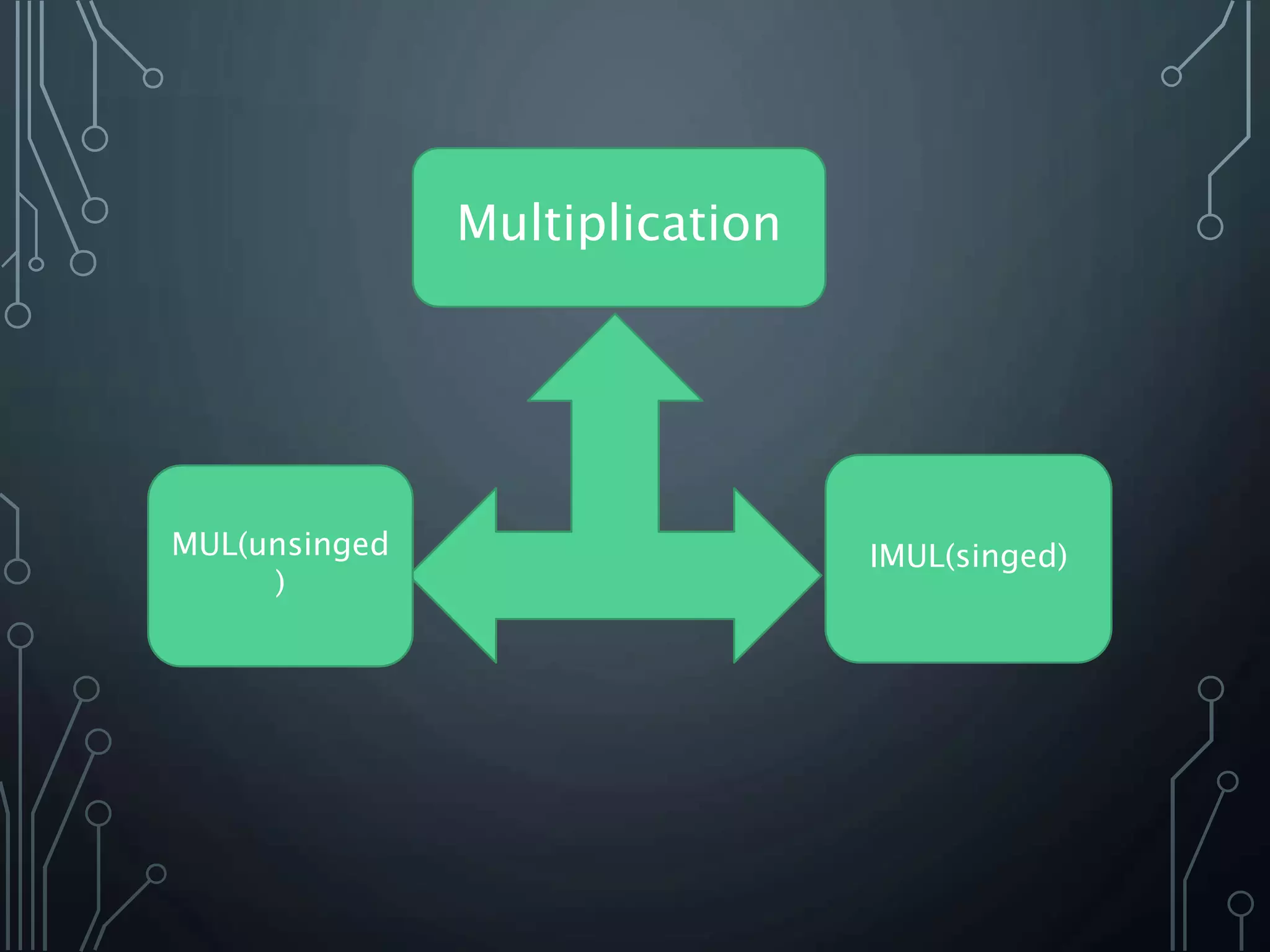
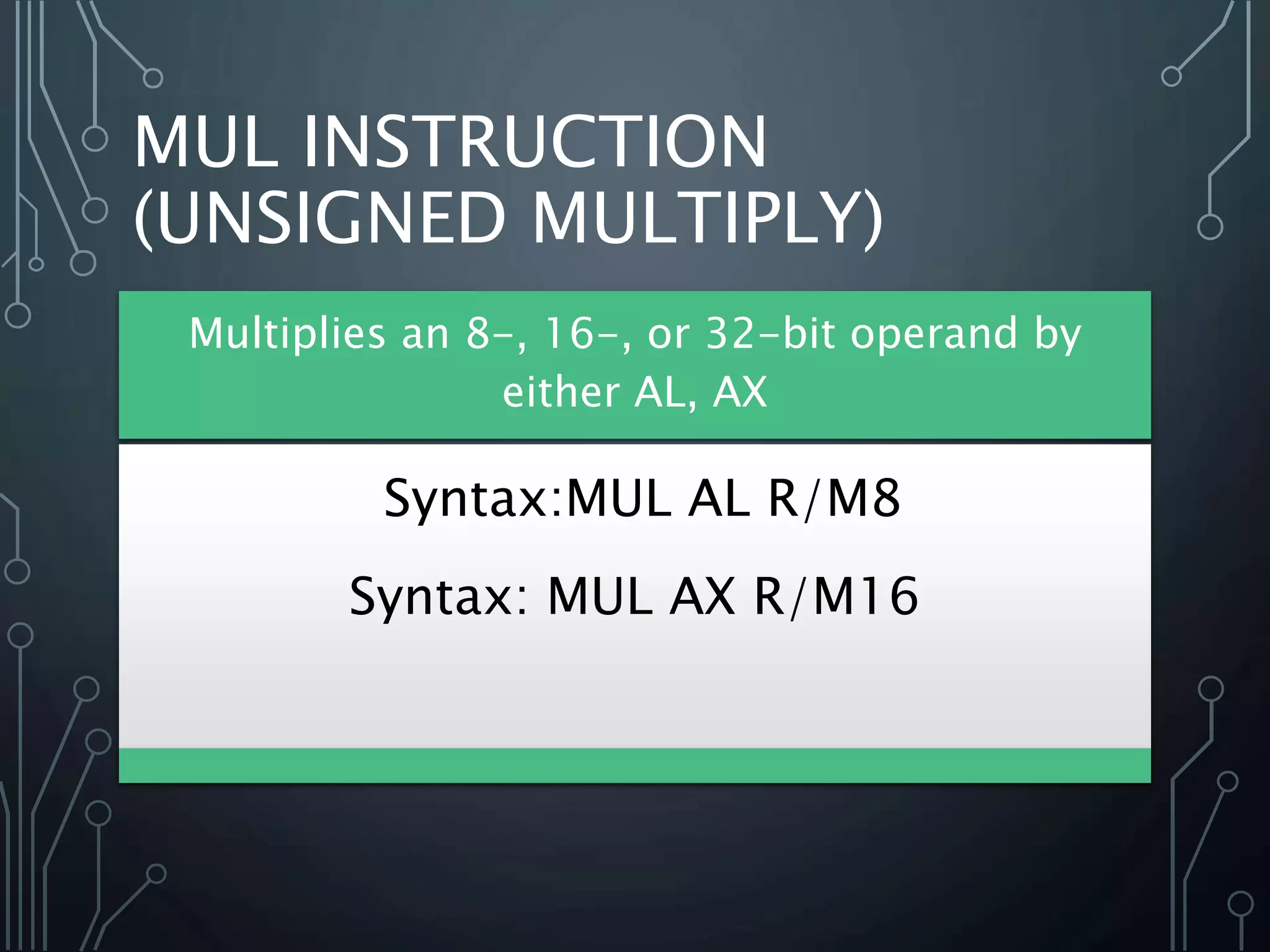
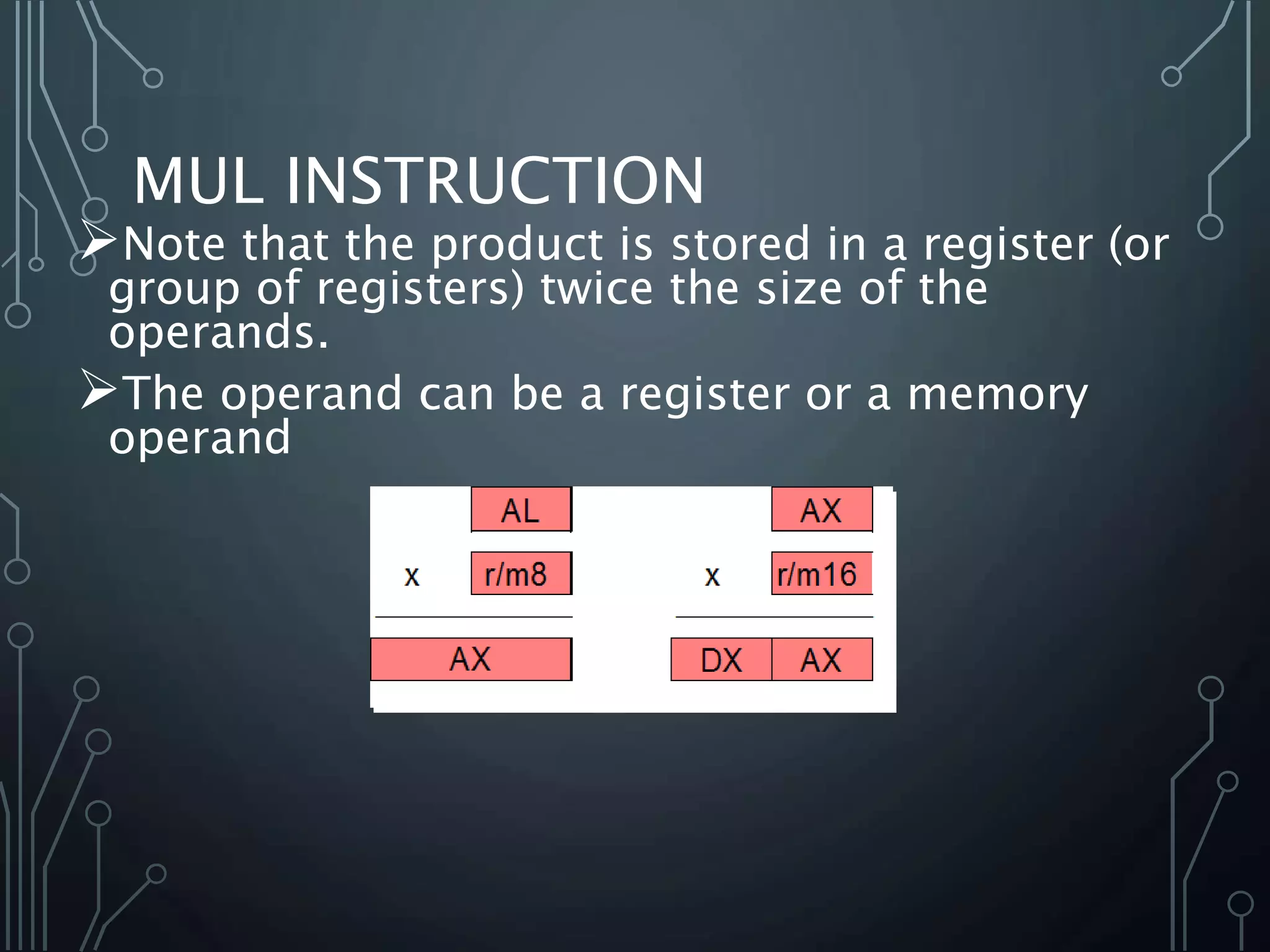
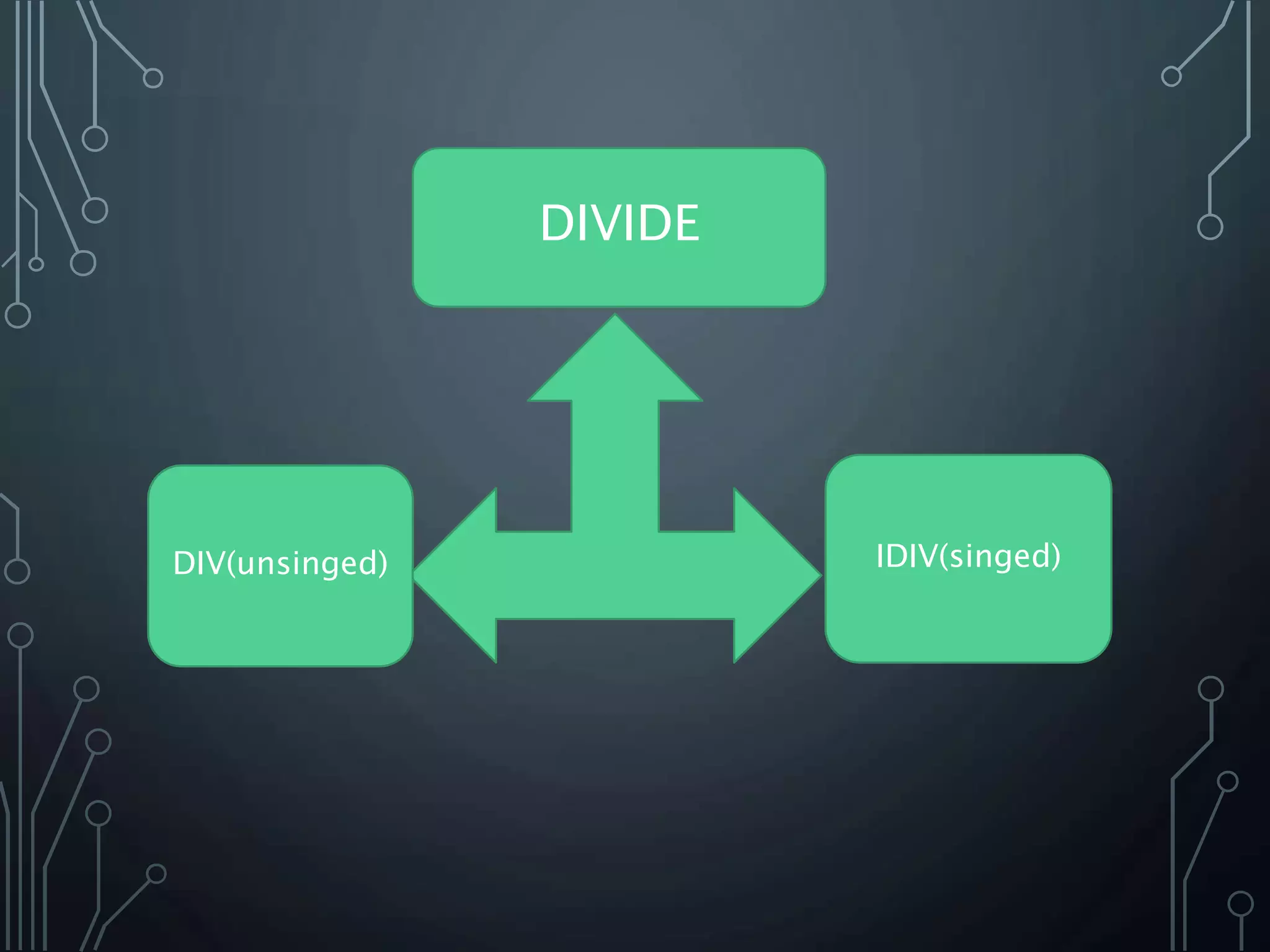
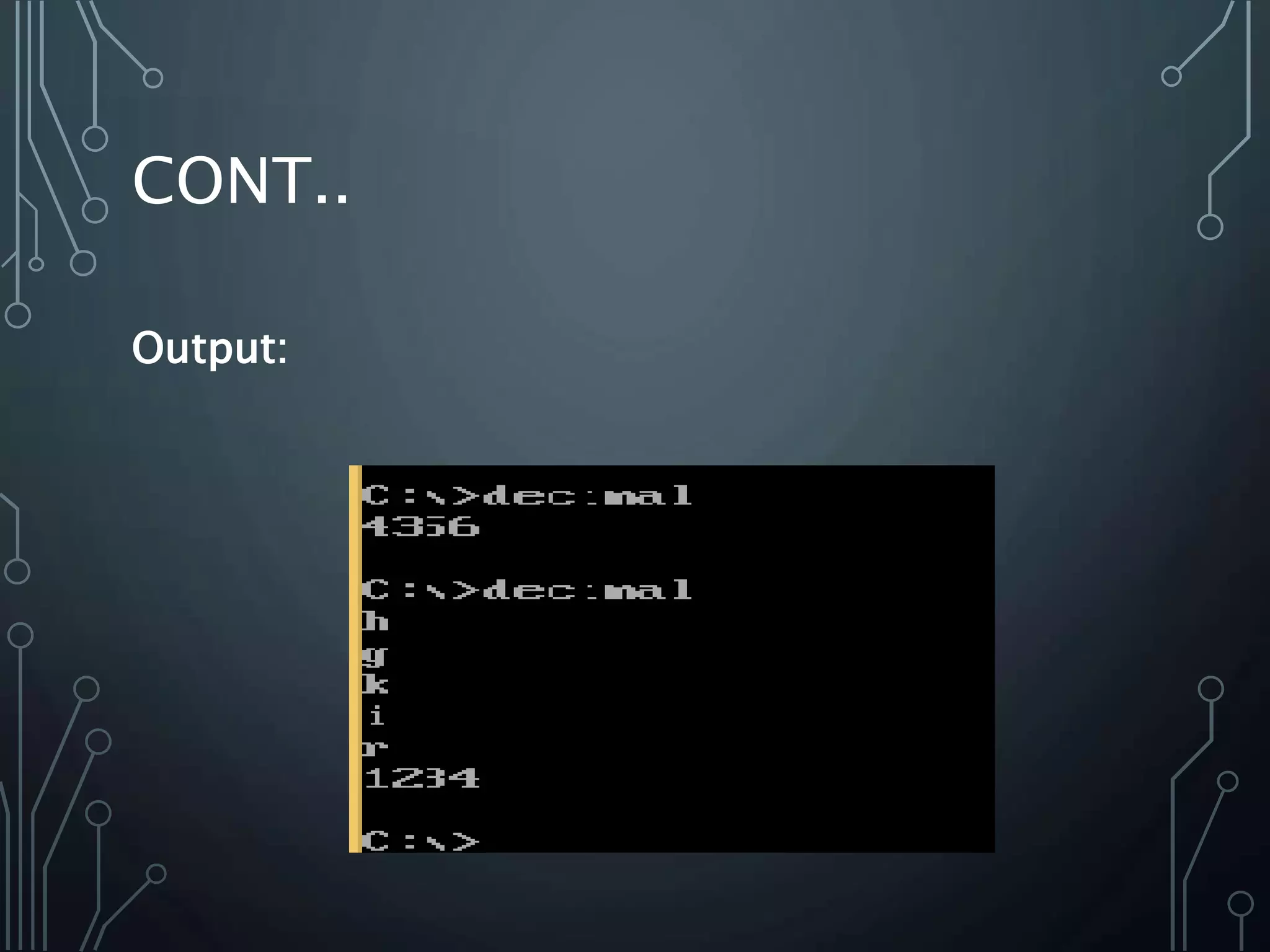
The document provides a detailed overview of multiplication and division instructions (mul, imul, div, idiv) in assembly language, including their syntax, examples, and impact on flags. It also covers the conversion of user input in decimal format to binary representation, along with algorithms for reading and outputting decimal numbers. Furthermore, the document presents source code for handling decimal input and output with considerations for overflow and character conversion.