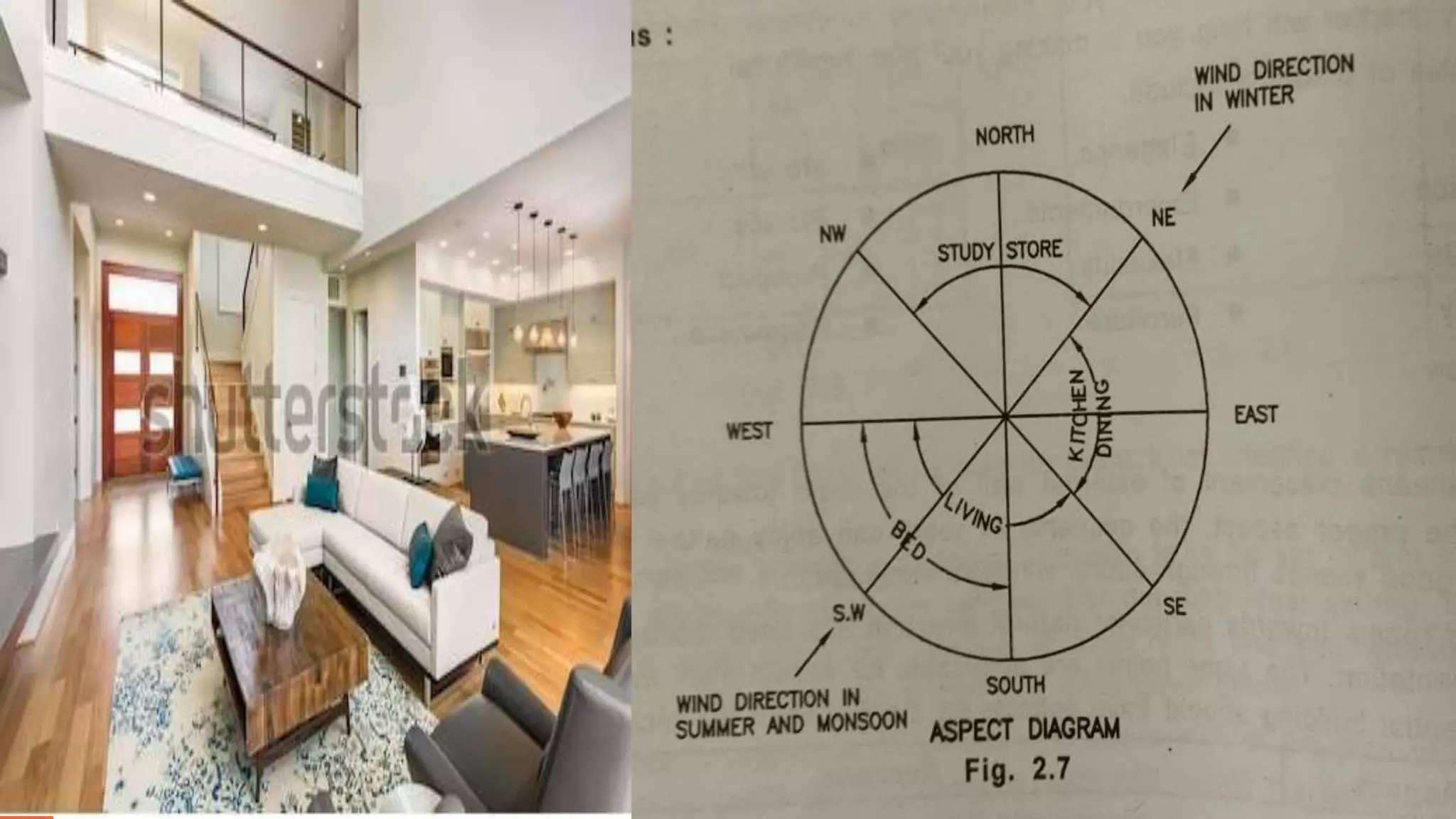
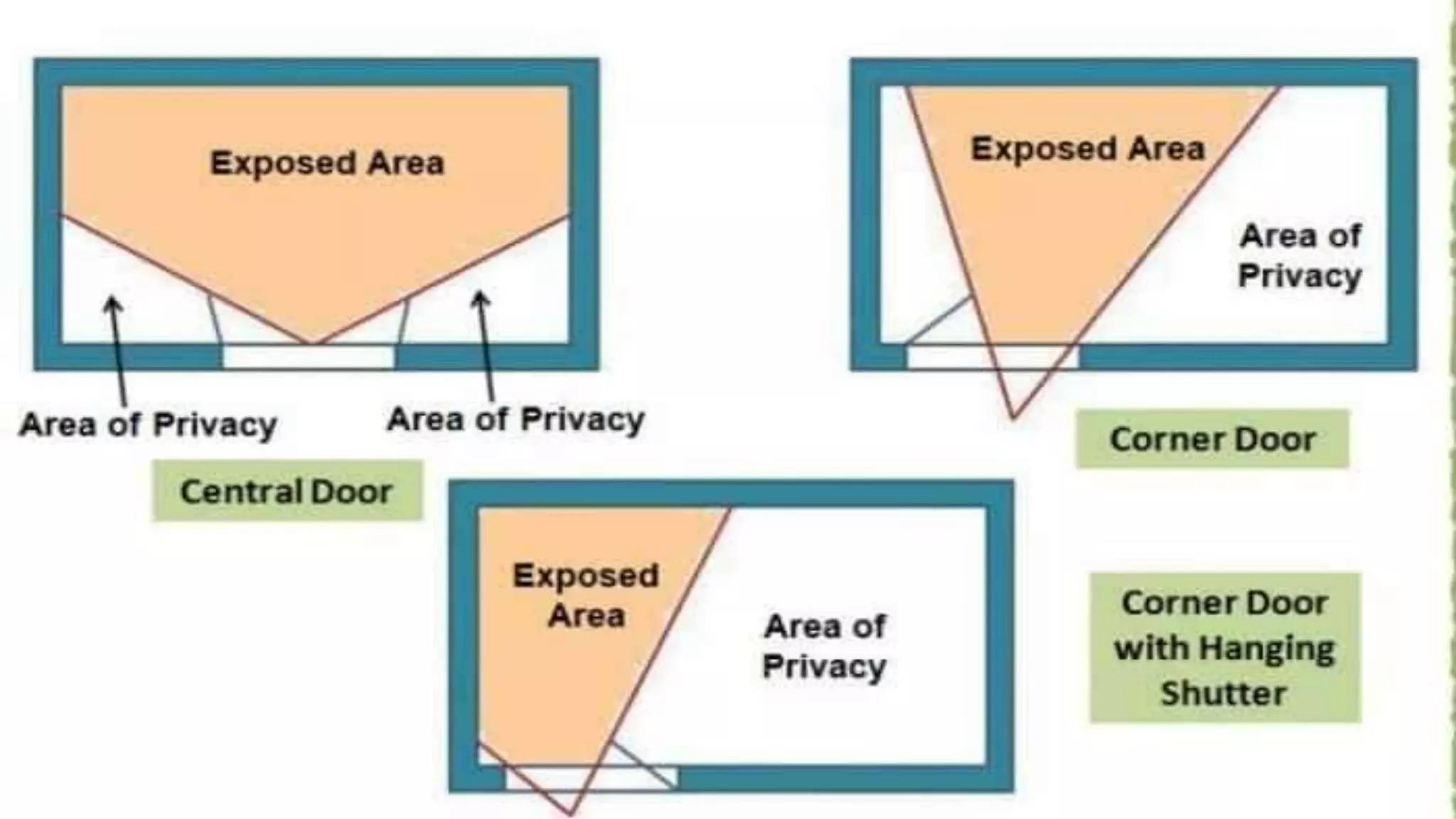
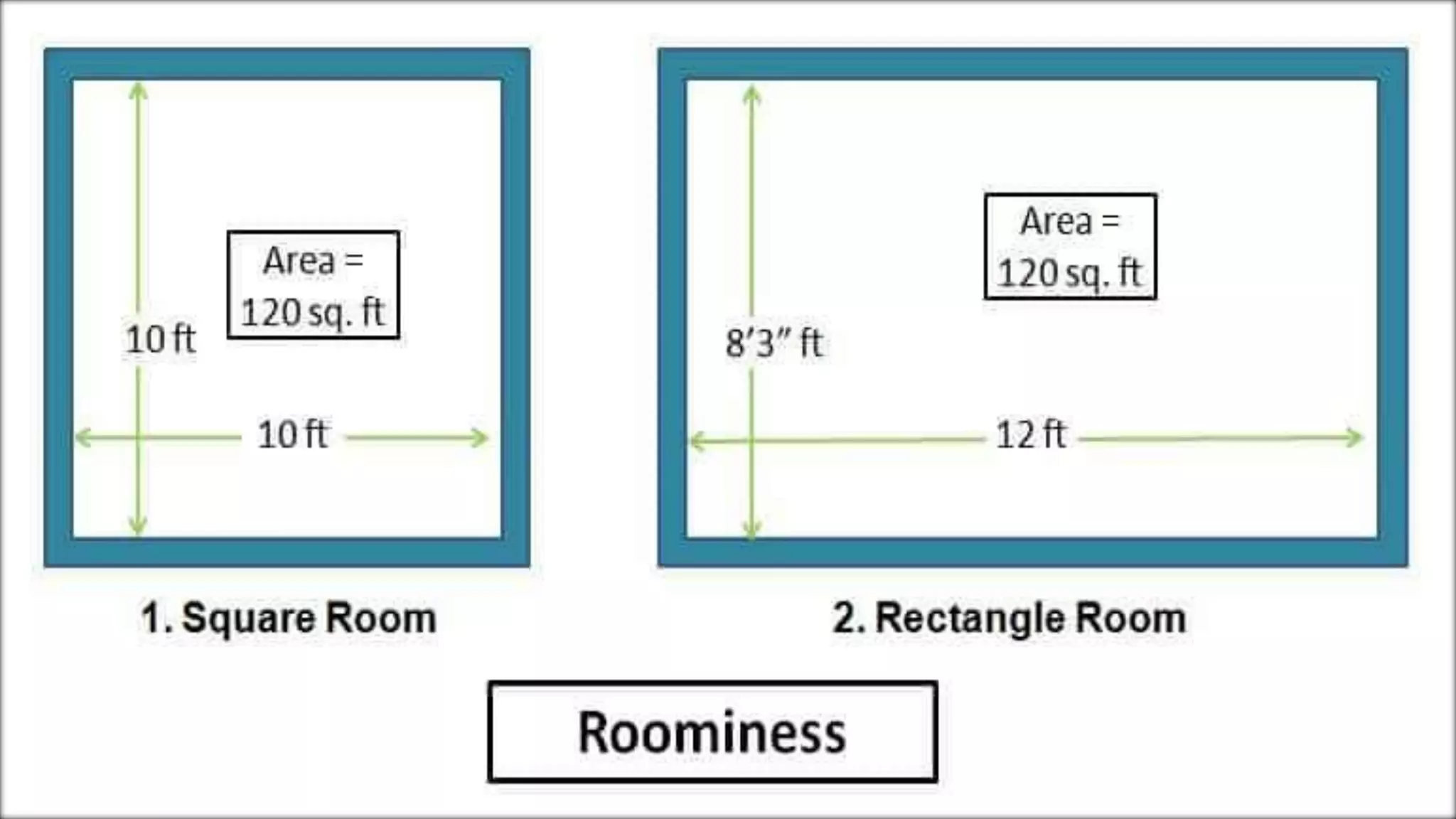
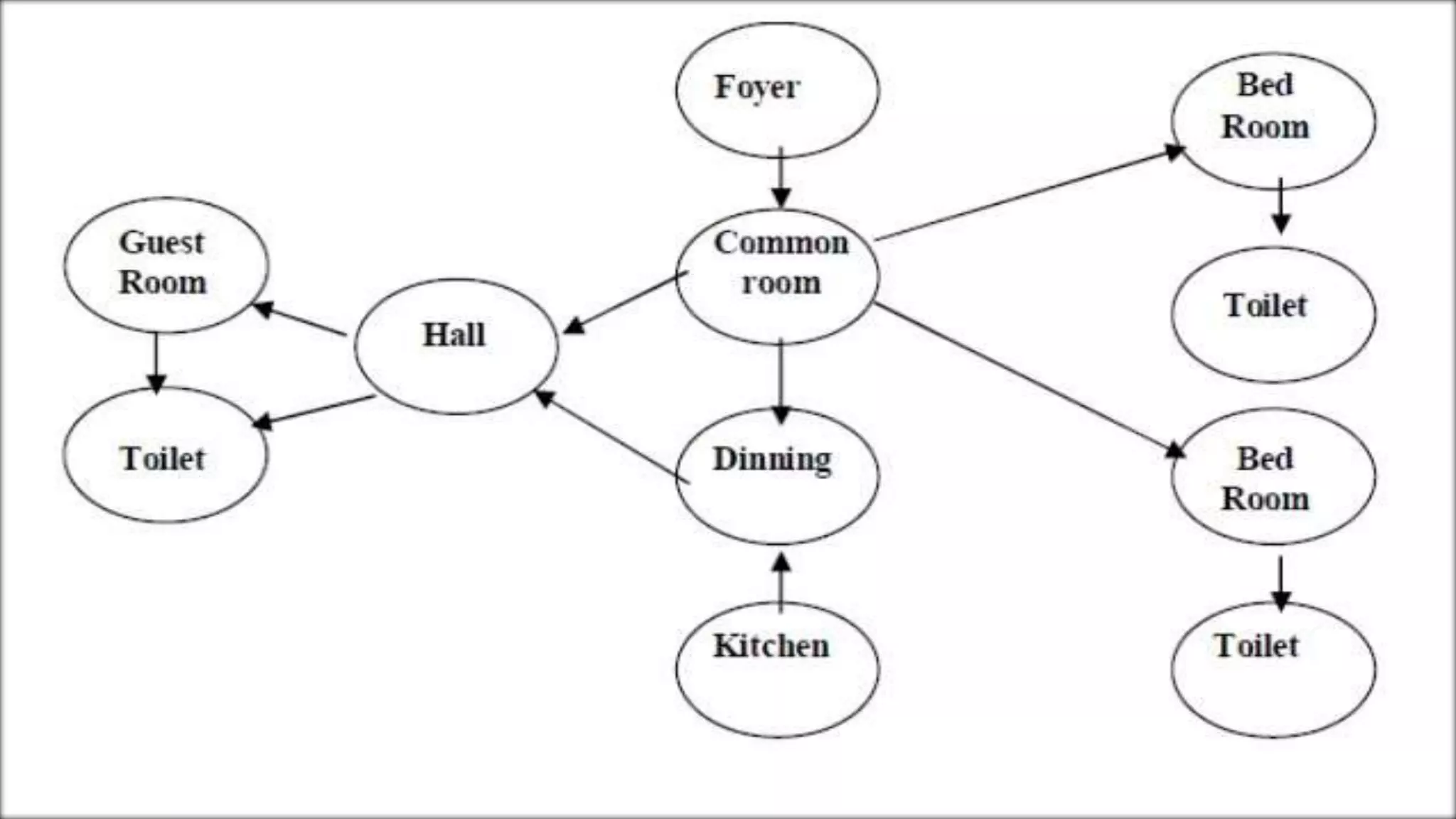
This document outlines various principles of planning that should be considered when designing a building, including aspect, prospect, privacy, circulation, roominess, grouping, elegance, sanitation, flexibility, economy, and practical considerations. Aspect refers to positioning rooms to maximize natural light and ventilation. Privacy and circulation relate to internal access and separation of spaces. Other principles ensure adequate space, logical grouping of rooms, attractive design, hygiene, adaptability, cost-effectiveness, and durability. The guidelines are meant to create well-planned, functional, and comfortable buildings.