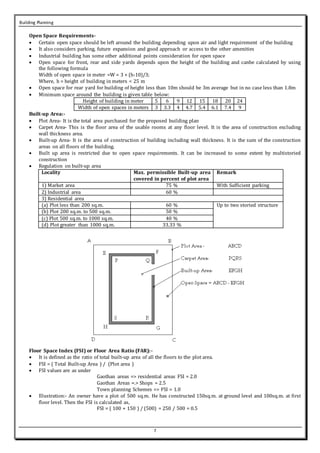
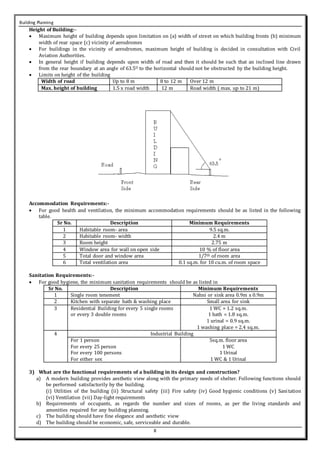
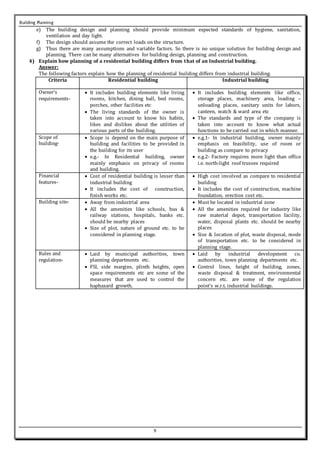
This document summarizes key principles of building planning, including aspect, prospect, privacy, grouping, roominess, furniture requirements, circulation, sanitation, elegance, economy, safety, and noise control. It also discusses building byelaws and their importance in regulating setbacks, building heights, floor space indices (FSI), and open space requirements to facilitate planning and ensure safety. Key factors in planning include positioning rooms for optimal sunlight, ventilation, and views while maintaining privacy. Proper grouping and circulation are also essential for functionality and comfort.

![Building Planning
5
Cleanliness may be achieved by non-absorbent flooring materials with proper slope, provision of rain water
pipes for terrace, adequate slopes and dados in baths, water closets etc.
9) Elegance
a) A functionally well planned structure may not necessarily invite attention of user due to lack of elegance
b) Thus the principle of elegance deals with beautifying the structure outwardly.
c) Elegance may be improved by combination of the following depending on economy
Increasing the plinth height of structure
Use of arches for windows, doors etc
Different coloring patterns for walls
Combination of flat and sloped roofing
Use of decorative (building) materials
Integration of structure with surroundings by proper landscaping
10) Economy
a) Last but not the least, any planning would fail if the cost incurred is not considered
b) However, a structure requiring less investment initially may prove to be costlier in the long run due to
high maintenance cost.
c) Although one construct house during his life time, a costly structure may not be practically feasible. Hence
an optimum policy should be framed wherein the functional utility, comfort as well as cost of the
structure.
d) No general rules can be made to achieve economy
e) But it can be achieved by keeping the minimum dimensions of rooms, doors, windows, simple design etc.
11) Safety [Q: What Safety precautions are necessary in a building? Explain. // Write a short note on ‘General
Safety of Building’.]
a) Every building should be stable and durable. It should also be safe against fire and lightening.
b) Safety against fire: -
Every building should be well equipped with the first aid and fire extinguishers, heat and smoke
detectors, alarm system etc.
In addition to fire fighting equipment, water buckets, sand buckets should also be made available.
The electrical fittings should be checked from time to time to protect the building from fire due to
short-circuiting.
The building should be provided with emergency stair-case to escape from fire.
c) Safety against lightening: -
Generally residential buildings are subjected to the lightening danger.
Only the tall buildings are likely to be affected.
Proper lightening protection system should be provided on all important public buildings.
This system must form a continuous chain of conductors from the roof to the ground so that the stroke
of lightening should be discharged to earth within a short interval of time.
12) Noise control
a) Noise is defined as any undesirable sound of any frequency and any intensity other than the desired
sound.
b) Noise may be either indoor noise or outdoor noise. It may be air borne or structure borne.
Indoor Noise- caused due to radio, TV, conversation, banging of doors or windows, machinery etc.
Outdoor noise- caused due to traffic mainly, hawkers, loud speakers etc.
Air borne noise- carried through air and travel through openings.
Structure borne noise- carried by structure and difficult to control.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-2buildingplanningfinal-180202113112/85/Unit-2-building-planning-final-5-320.jpg)