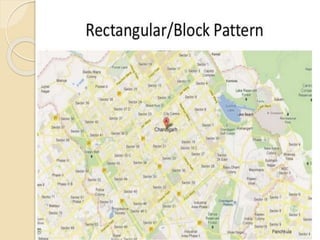
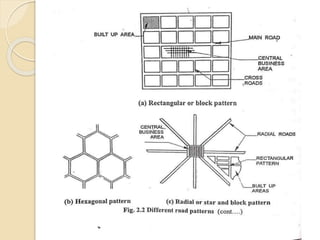
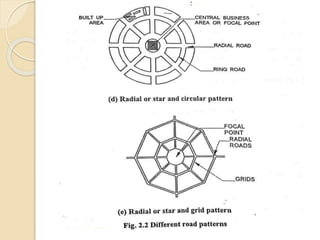
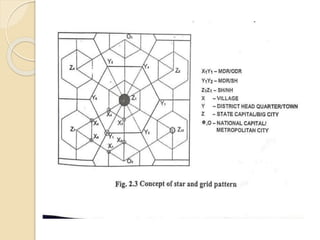
The document discusses different methods of classifying roads based on various factors such as weather conditions, surface material, location, function, and traffic. Roads are generally classified as all-weather or fair-weather depending on seasonal access. They can also be paved or unpaved based on surface material. Location and function is considered the most acceptable classification method, dividing roads into national highways, state highways, major district roads, other district roads, and village roads. Urban roads are additionally classified as arterial, sub-arterial, collector, and local streets. Road patterns are discussed including rectangular, radial, hexagonal, and combinations of radial and grid designs.