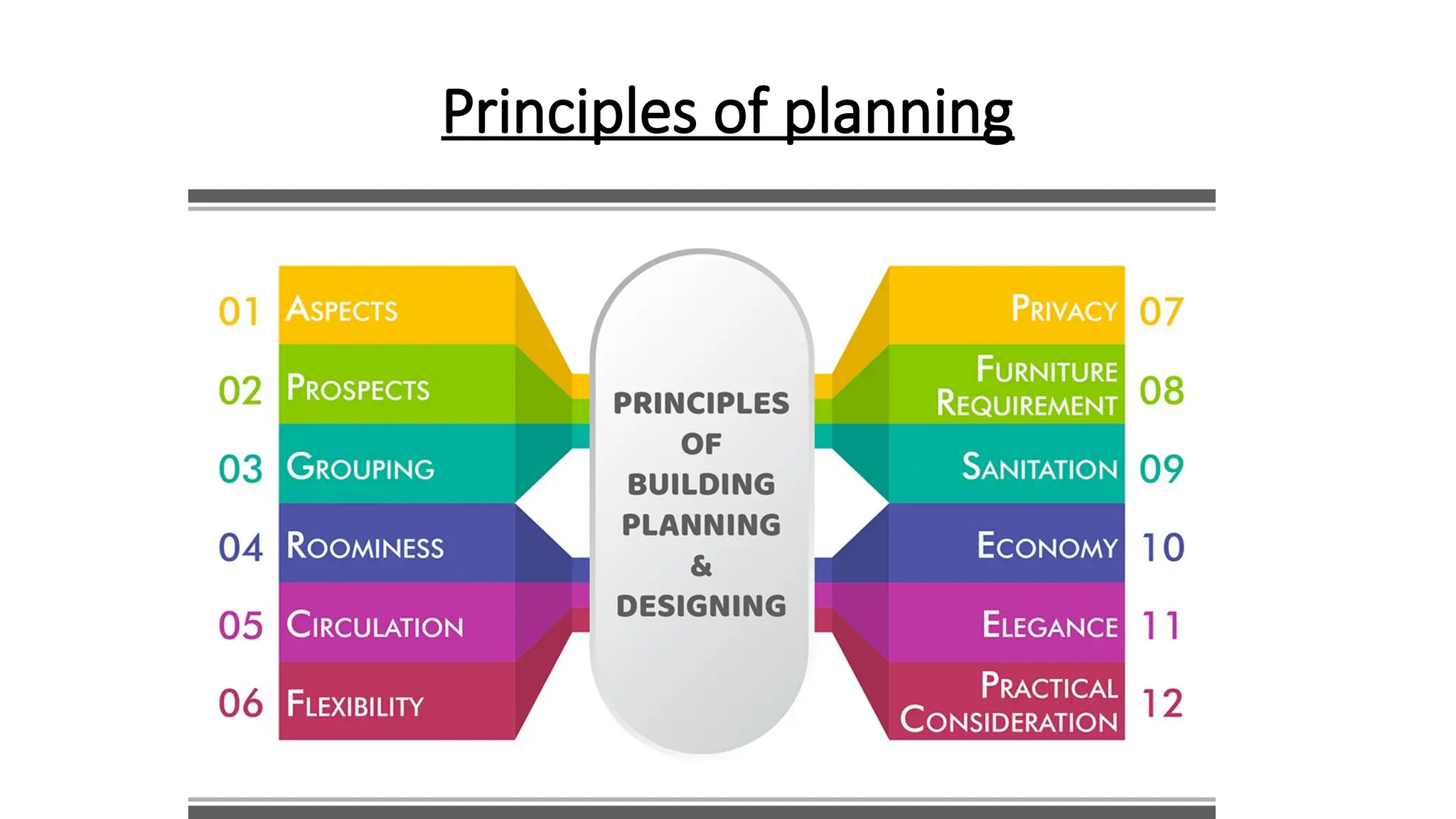
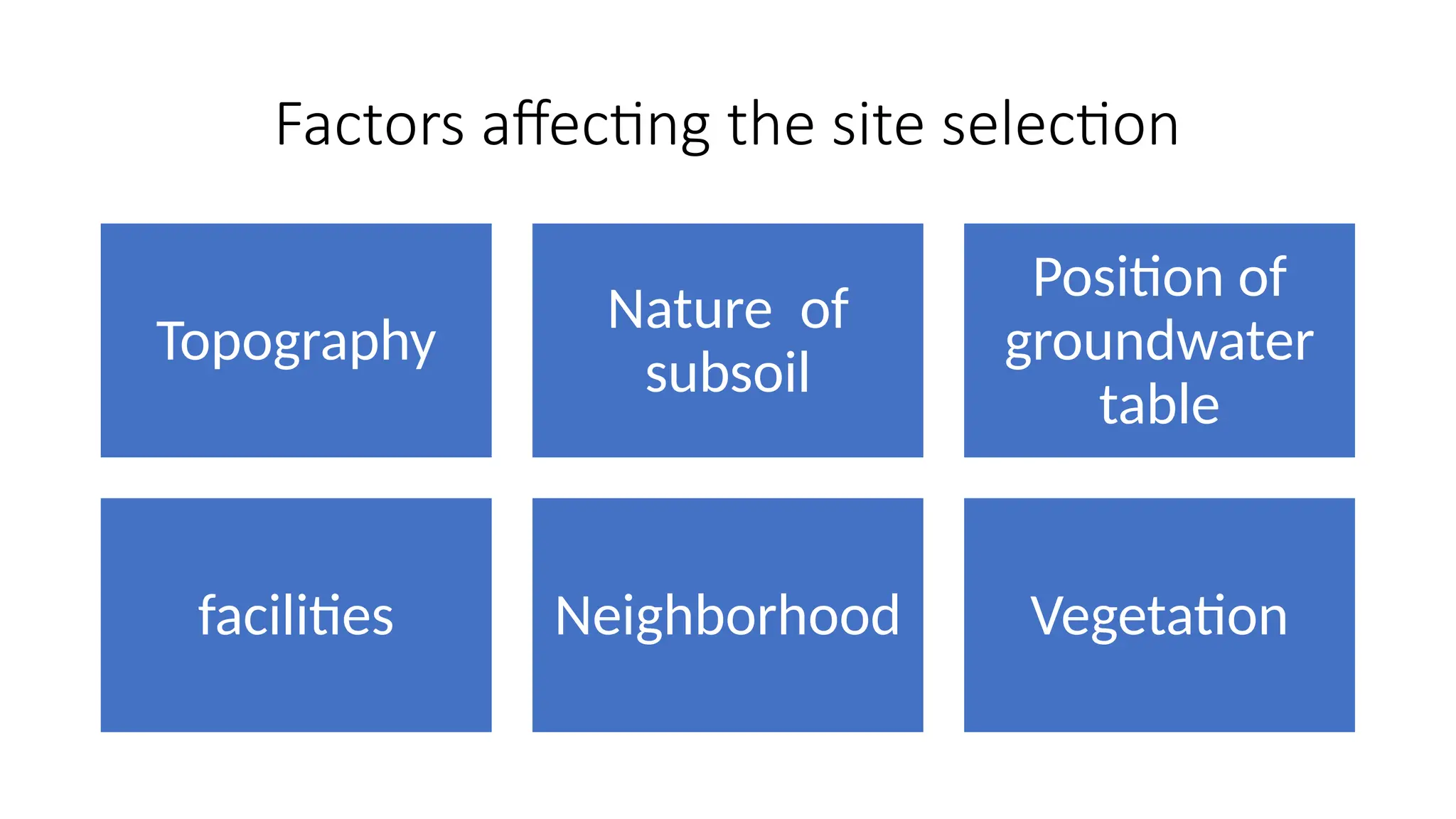
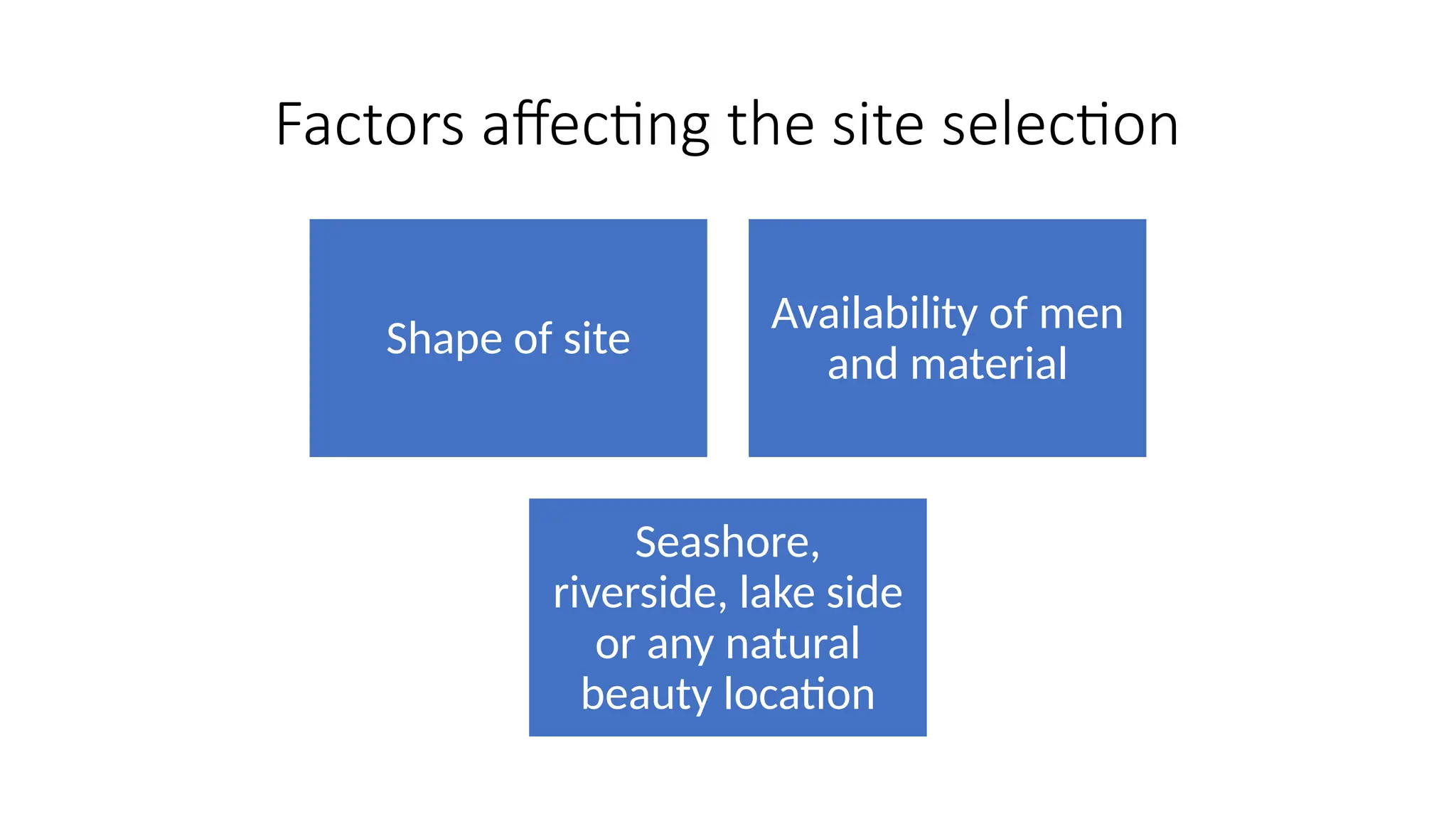
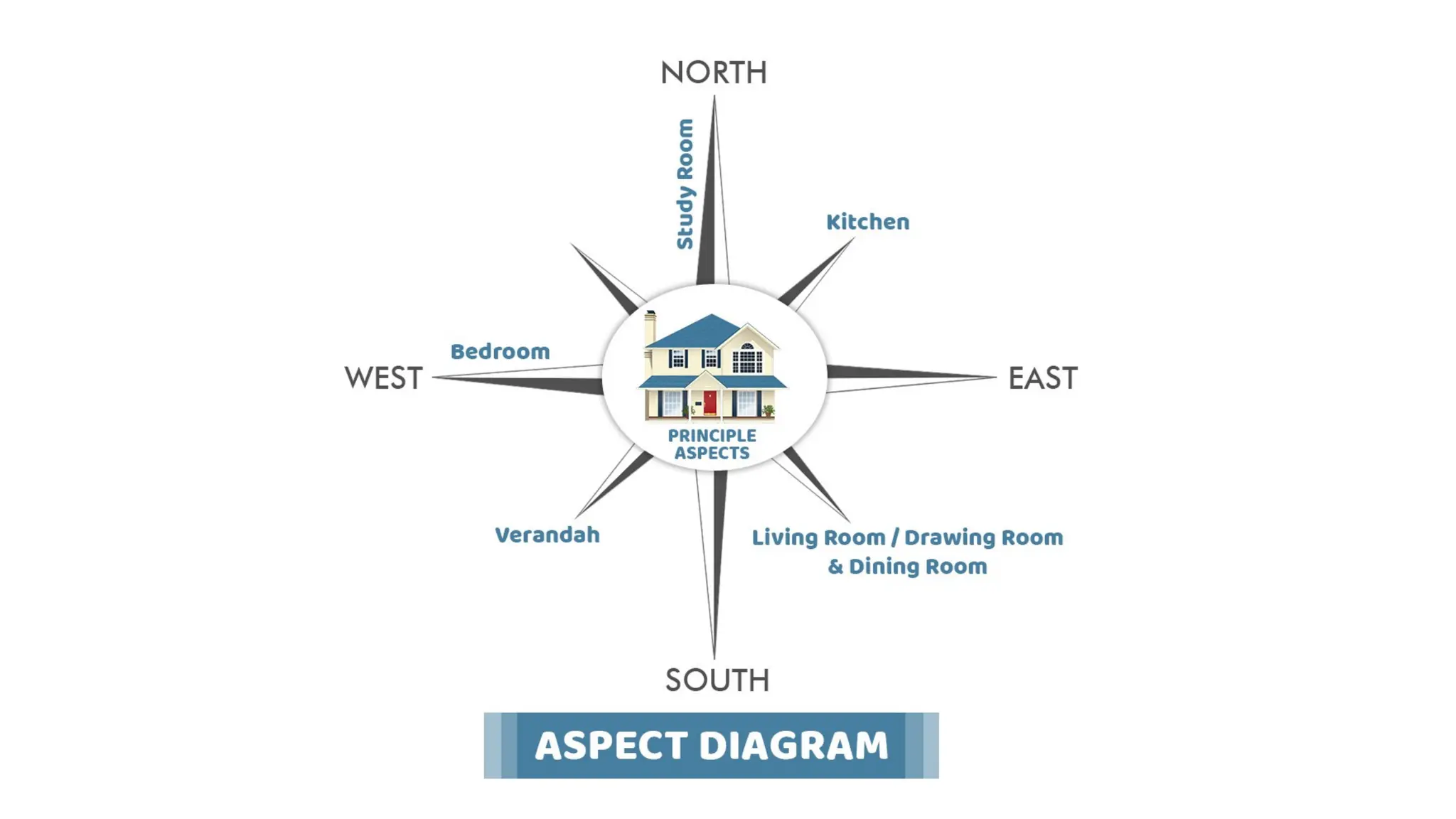
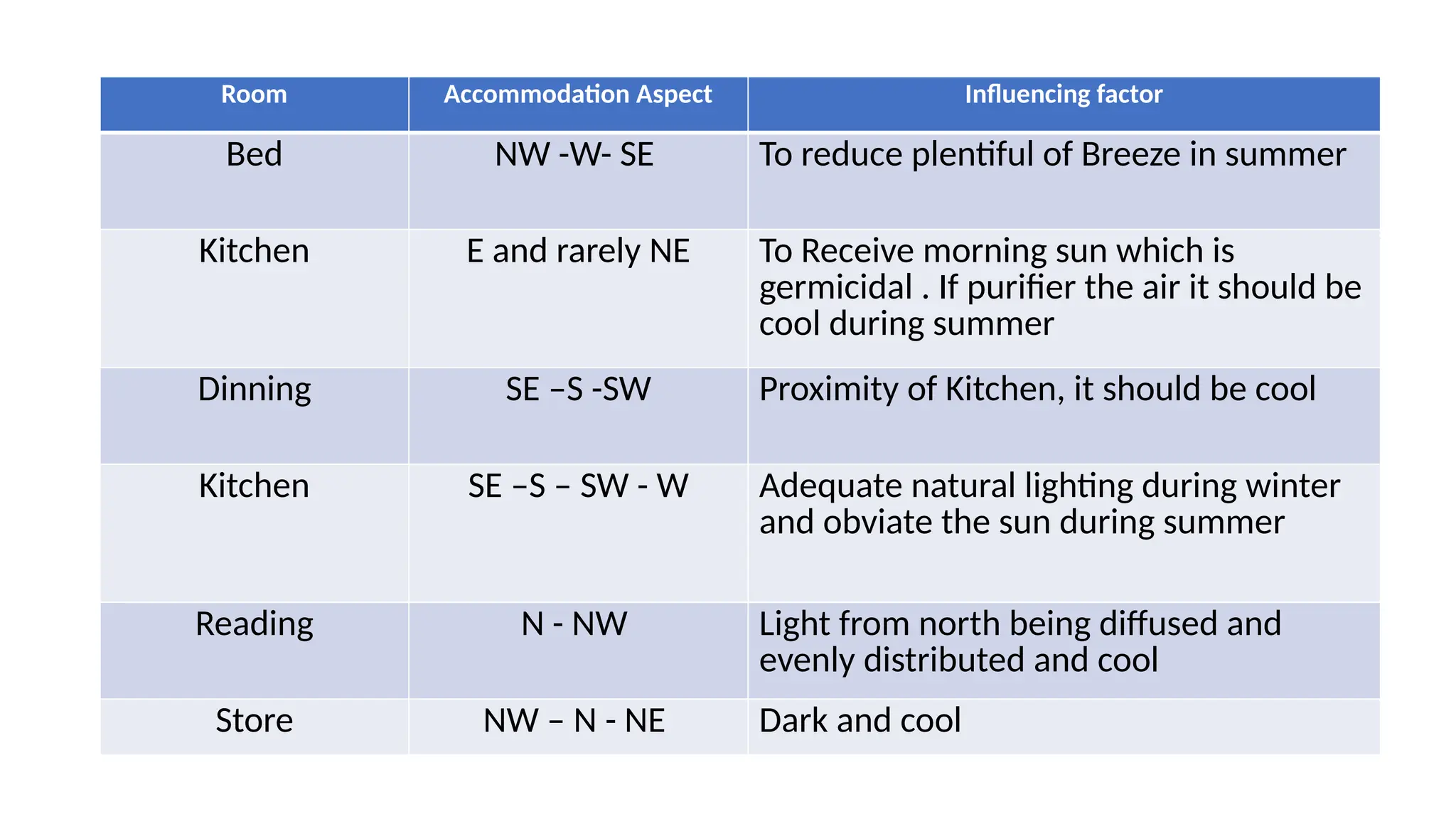
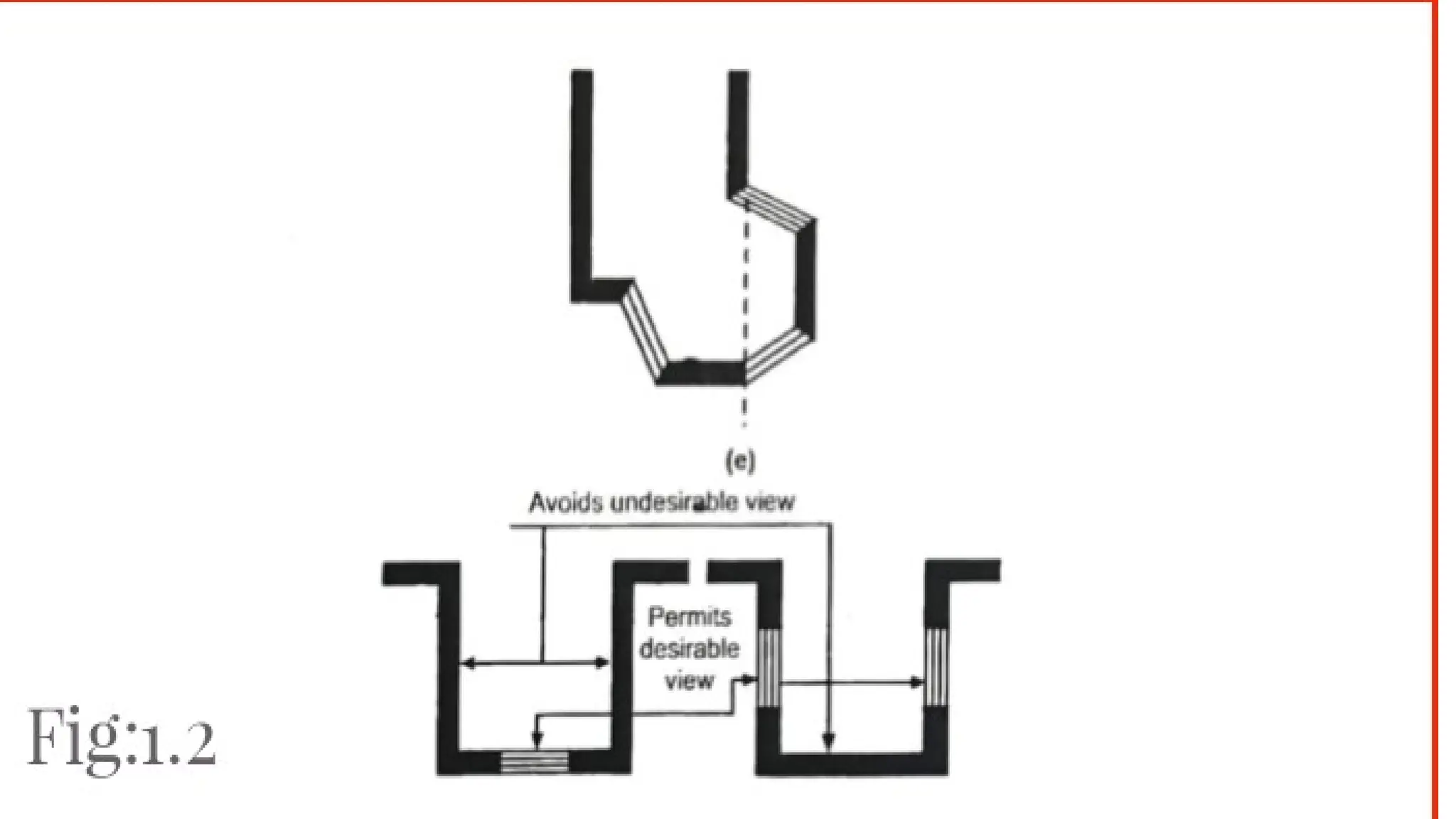
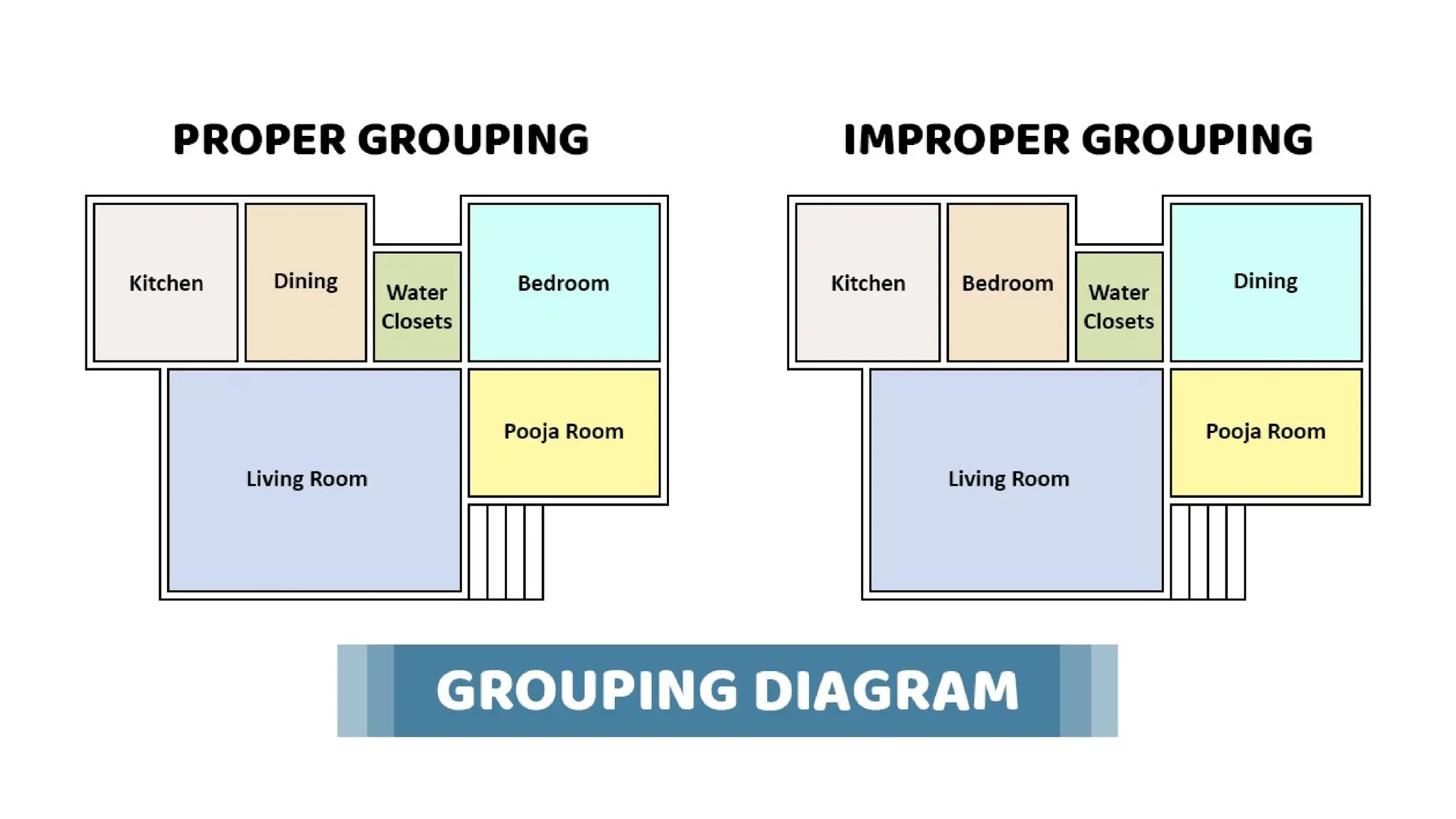
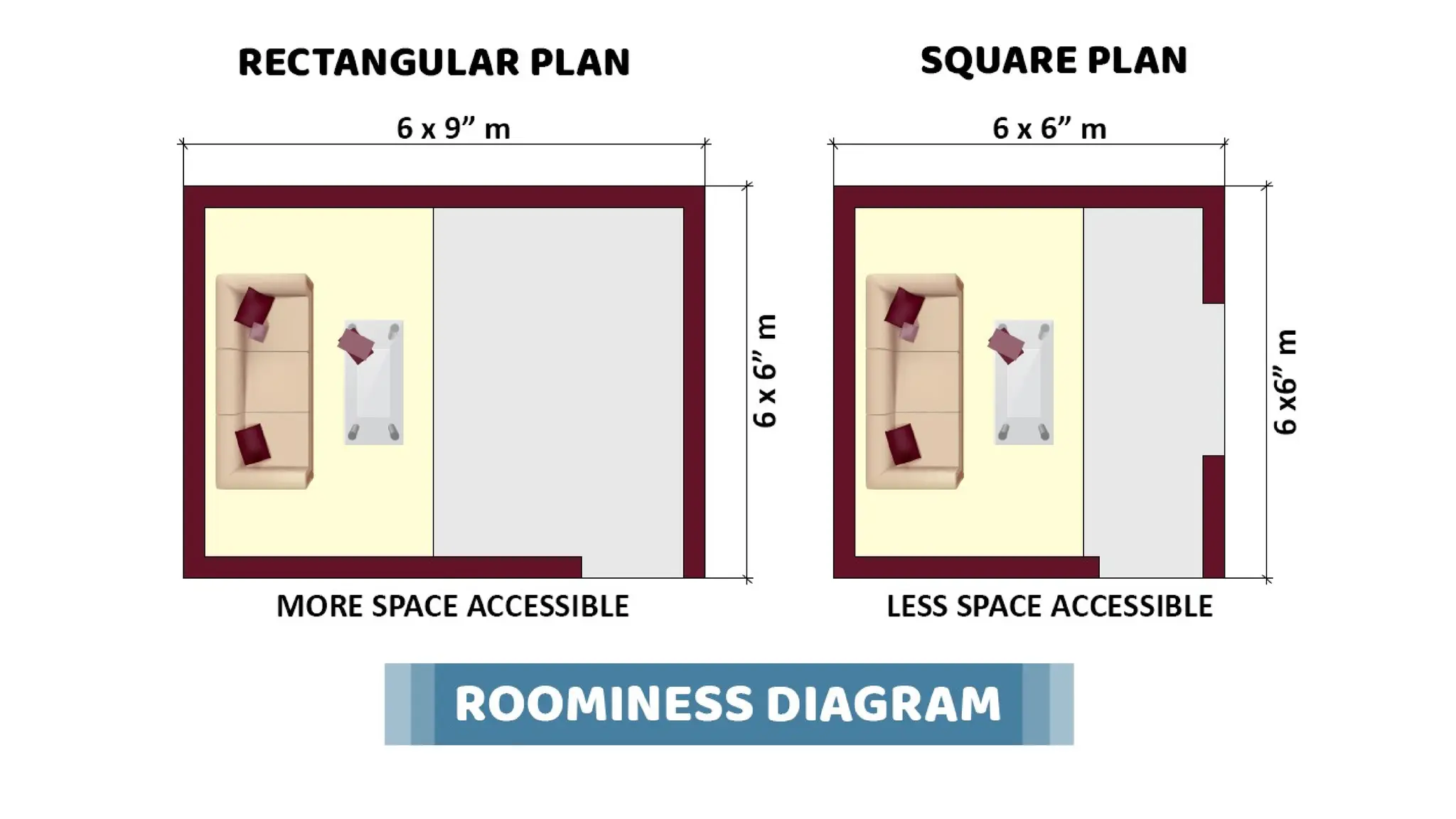
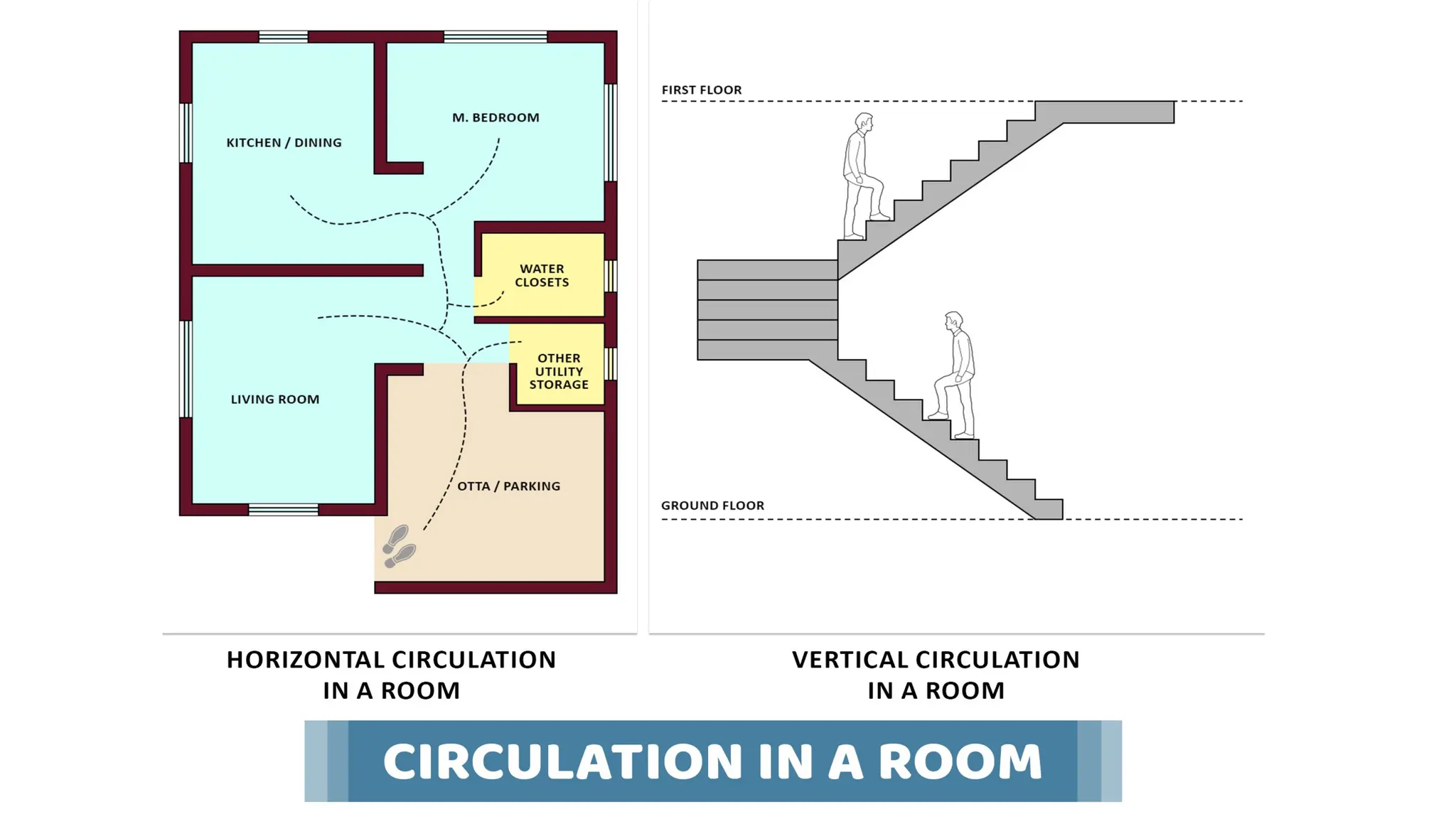
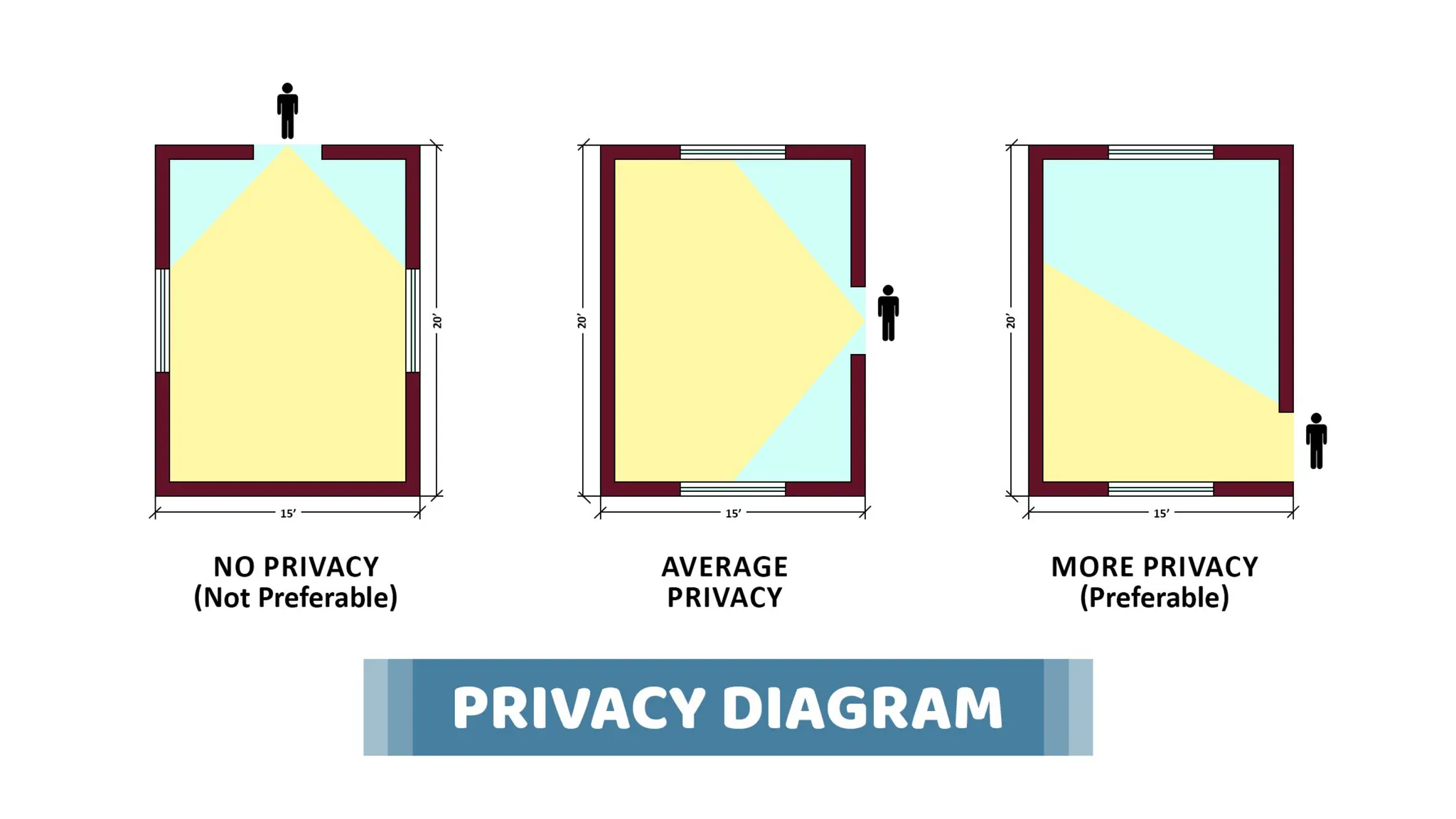
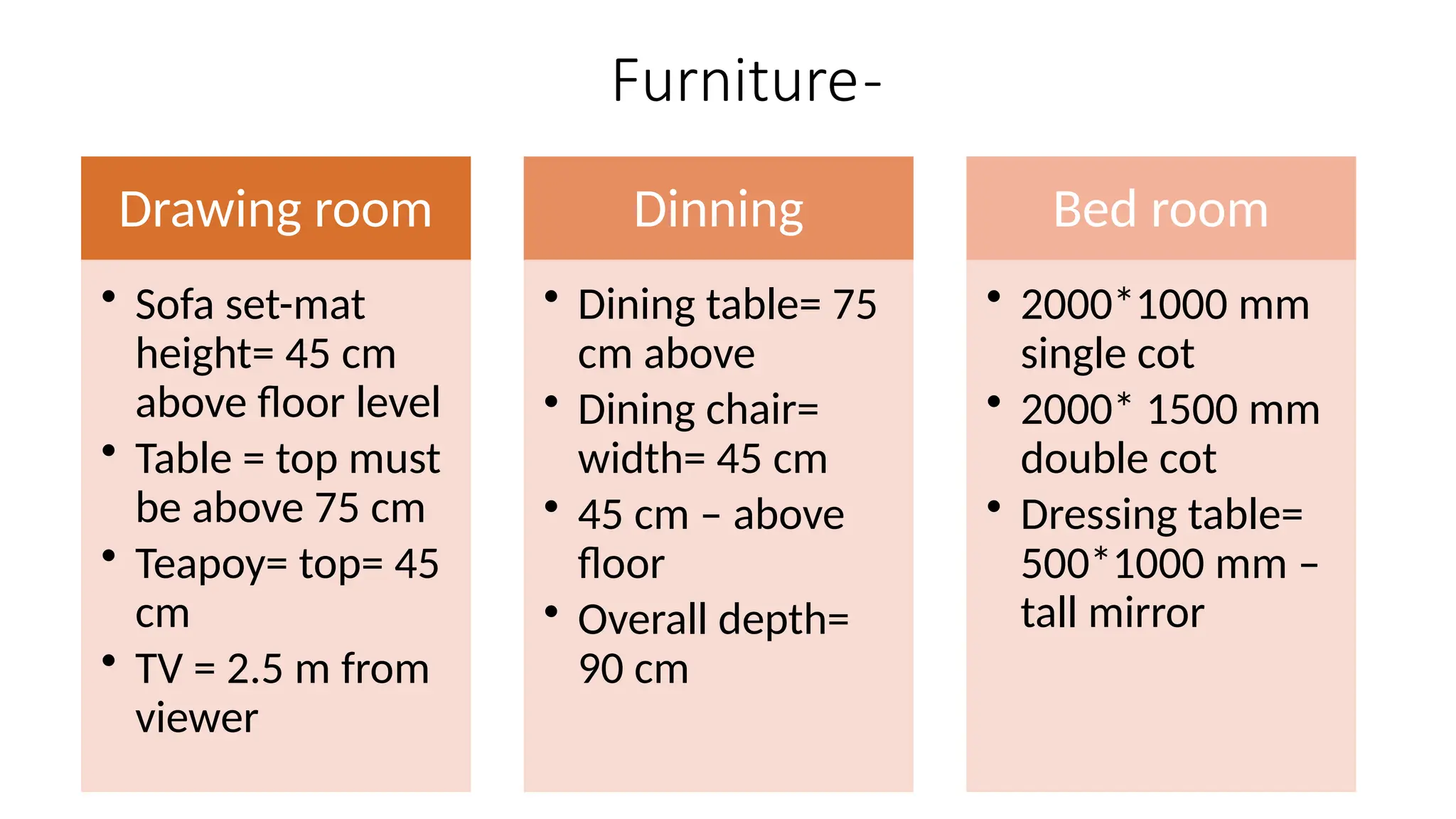
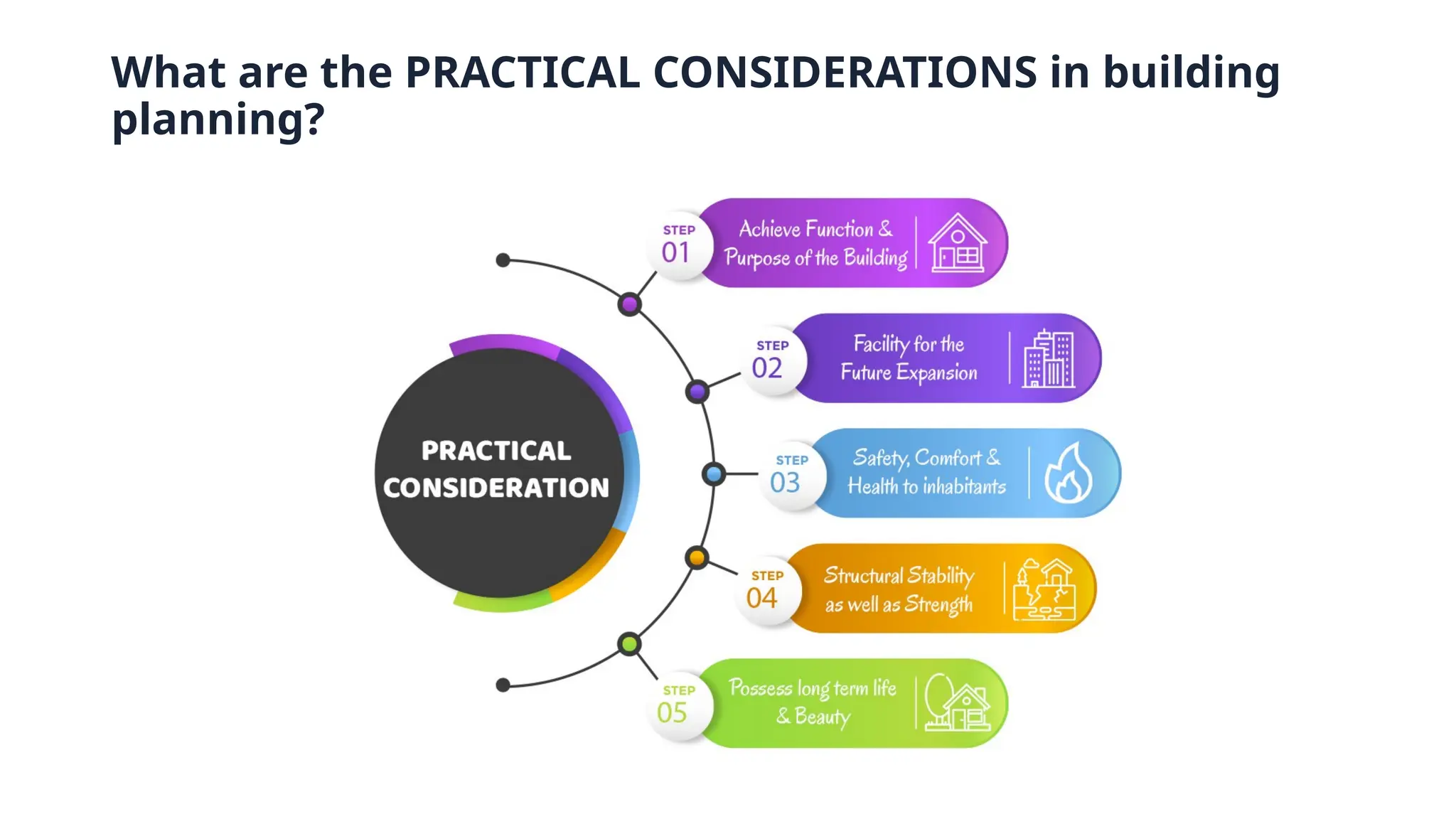
The document discusses the principles of building planning, emphasizing site selection criteria, climate considerations, and the arrangement of rooms for optimal light and ventilation. It covers factors such as aspect, prospect, roominess, circulation, privacy, and the impact of furniture on design, alongside economic and sanitary factors in construction. Finally, it highlights the importance of adhering to local bye-laws for building regulations and planning to ensure safety and compliance.