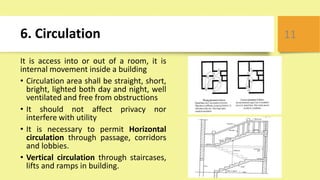
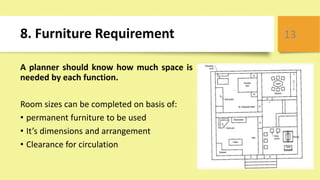
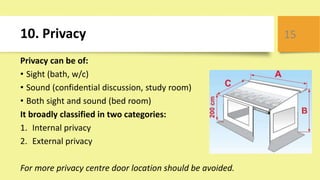
This document outlines key principles of civil engineering planning for building design, including proper orientation, privacy, security, fire safety, and compliance with building codes. It discusses factors like aspect, prospect, grouping, economy, roominess, circulation, flexibility, furniture requirements, elegance, privacy, and sanitation that influence building planning. Specific guidelines are provided for window placement based on climate, recommended room aspects, grouping rooms by function, achieving economy in design, ensuring adequate space and circulation, flexibility of room usage, and maintaining privacy, lighting, ventilation, and cleanliness for sanitation.