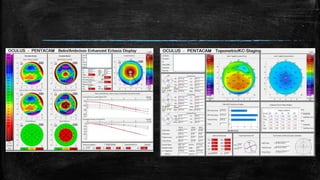
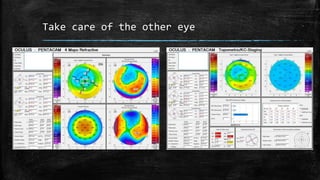
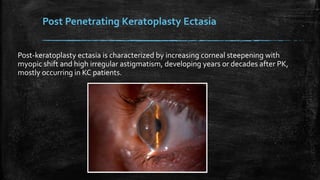
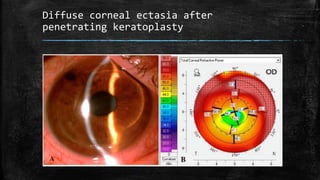
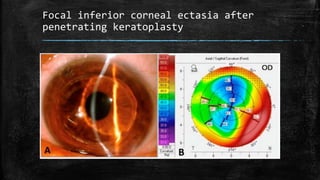
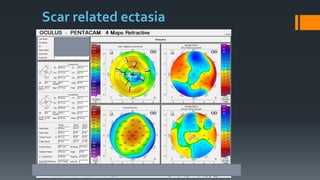
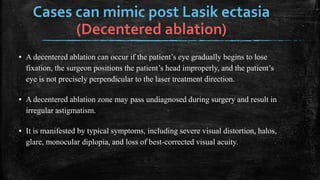
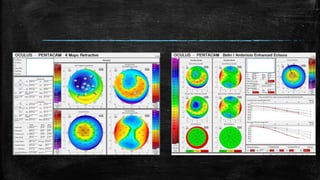
1) Secondary ectasia refers to corneal shape changes caused by external factors like previous refractive surgery or corneal transplantation.
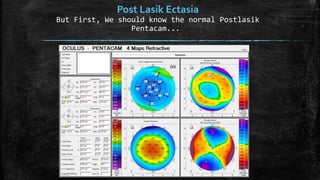
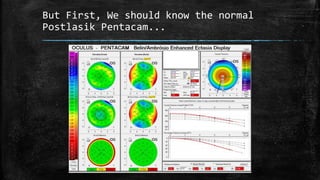
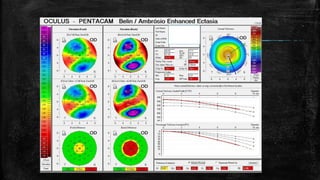
2) Post-LASIK ectasia is a rare complication characterized by progressive myopia and astigmatism due to thinning and protrusion of the cornea. Risk factors include young age and pre-existing thin corneas.
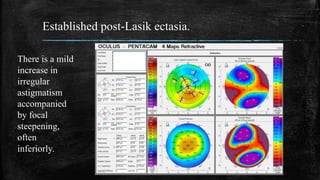
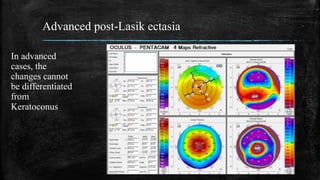
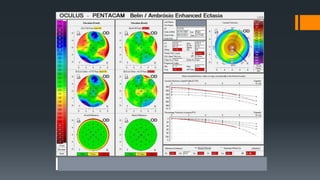
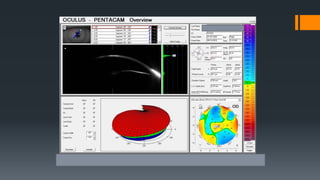
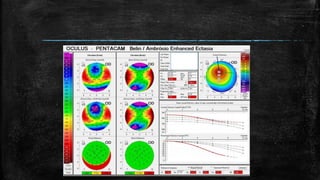
3) On Pentacam, early post-LASIK ectasia shows mild corneal thinning and elevation changes mostly in the inferior cornea, while advanced cases resemble keratoconus with significant steepening and irregularity.