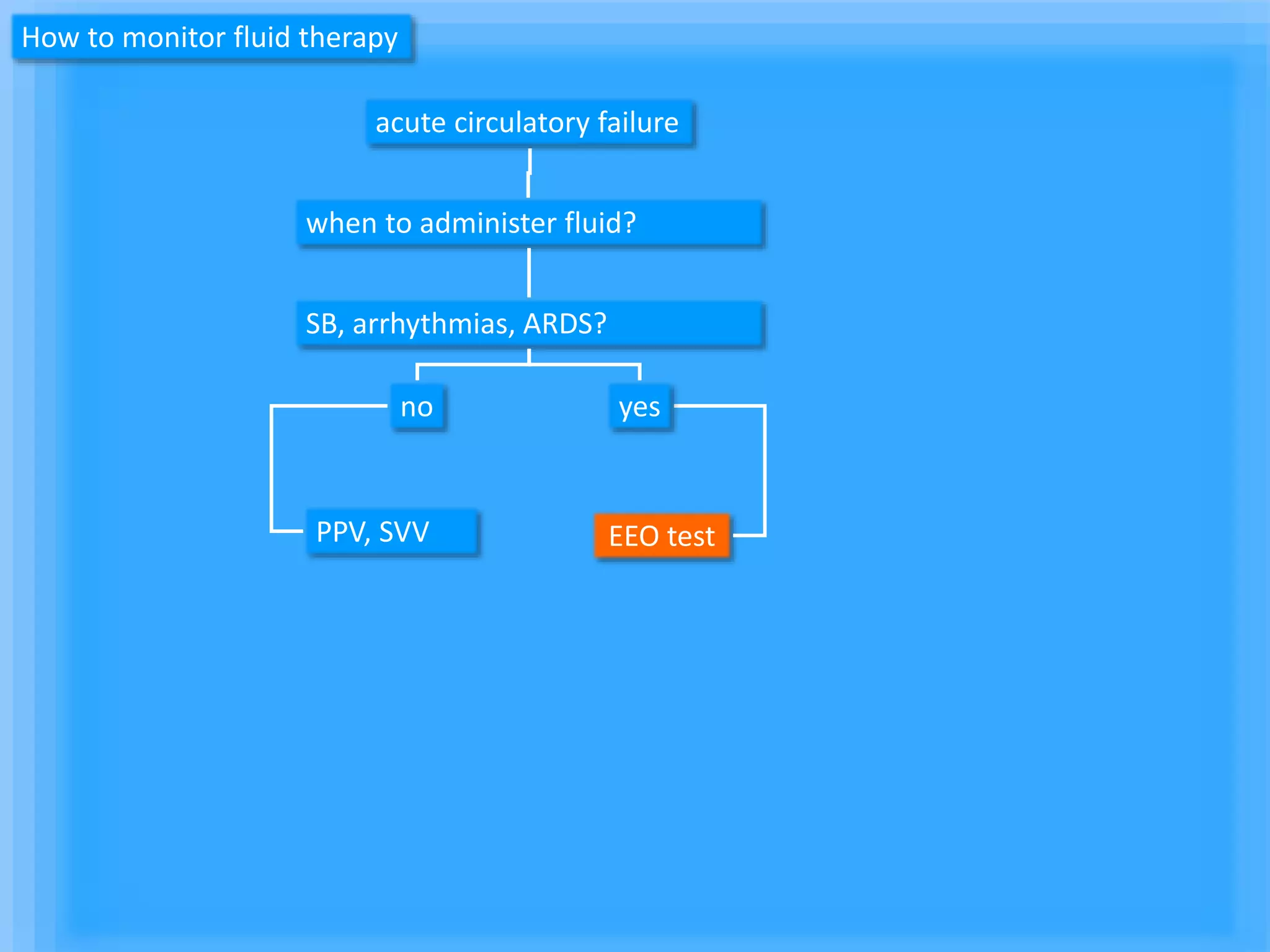
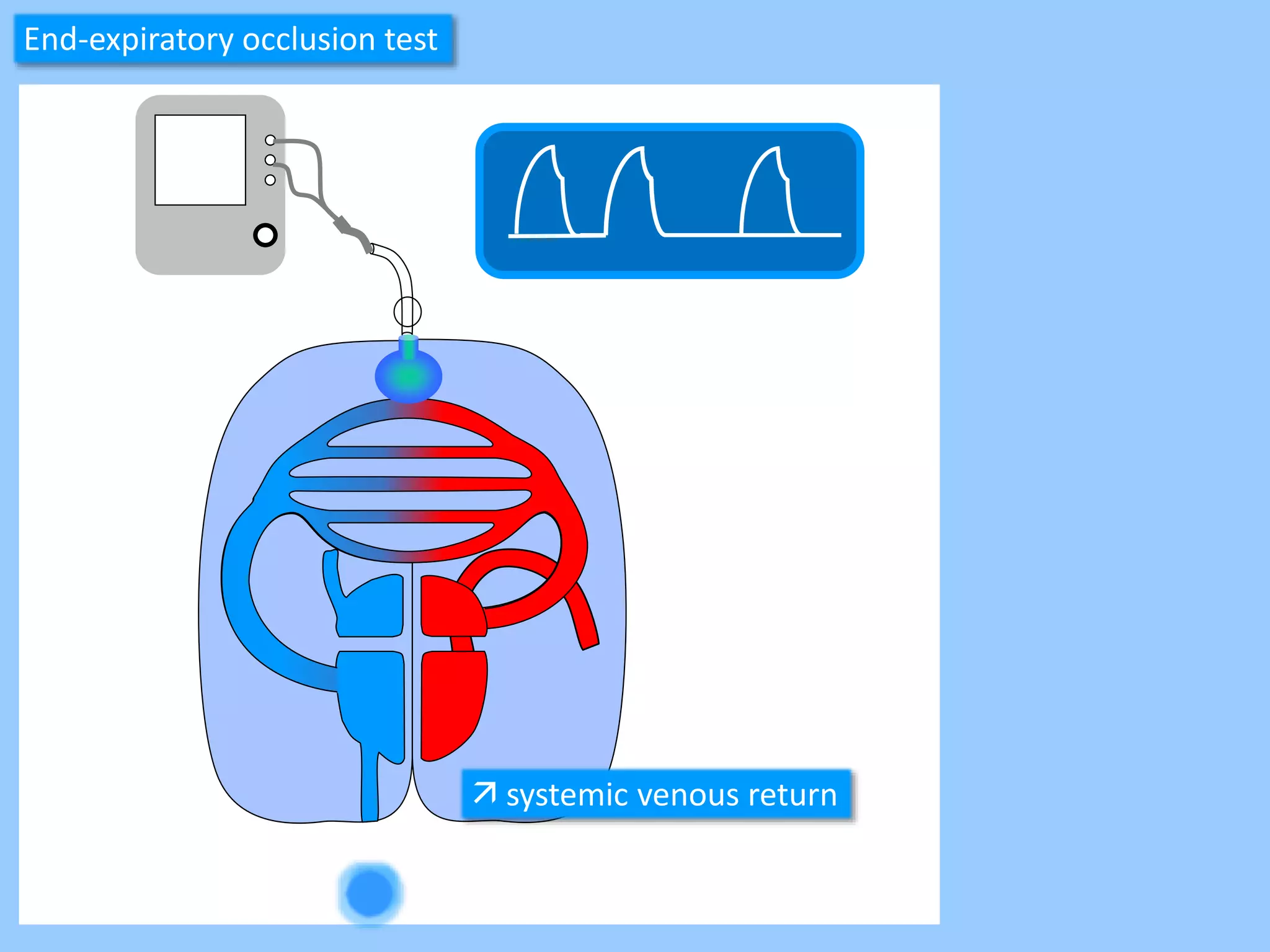
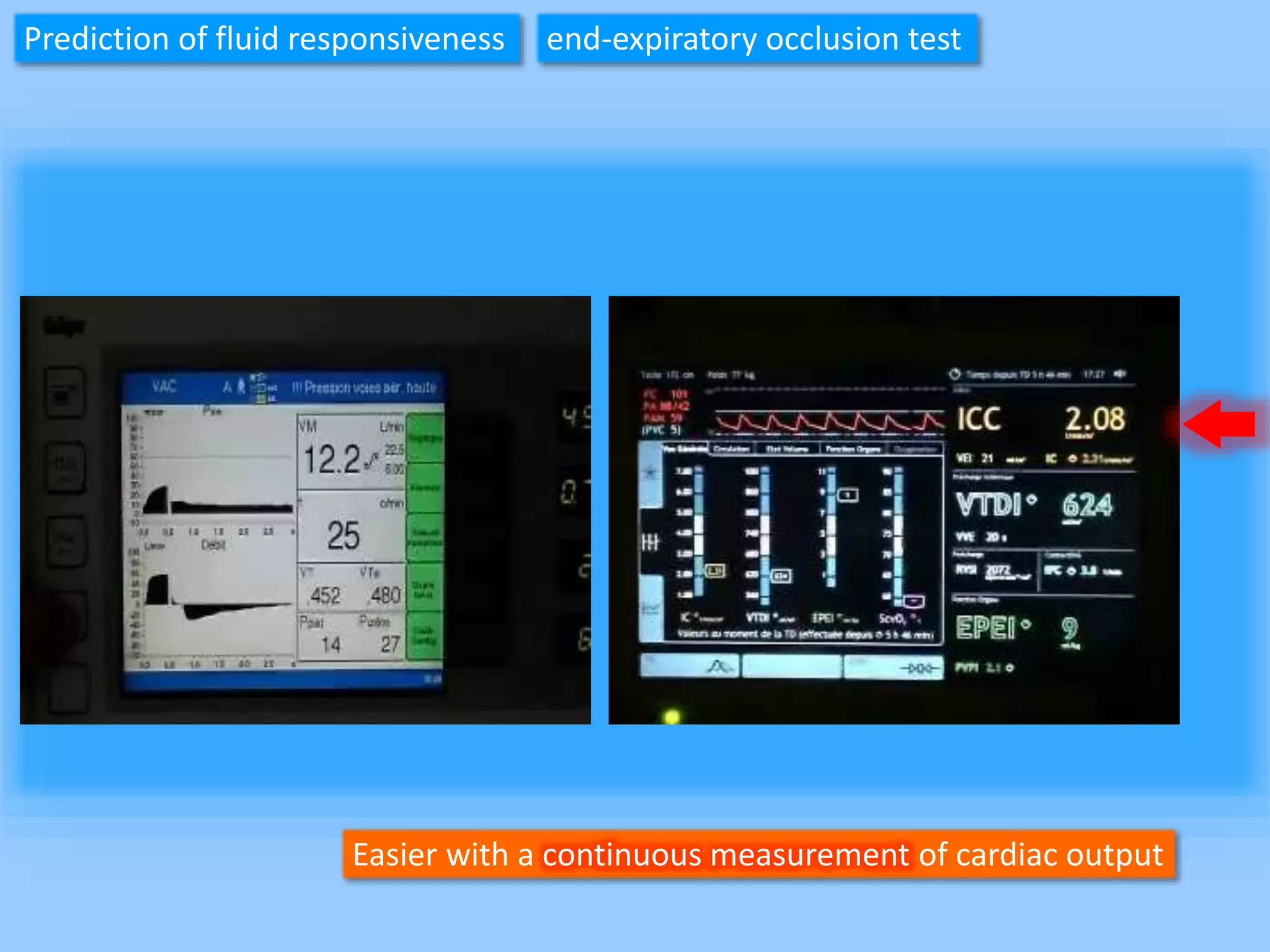
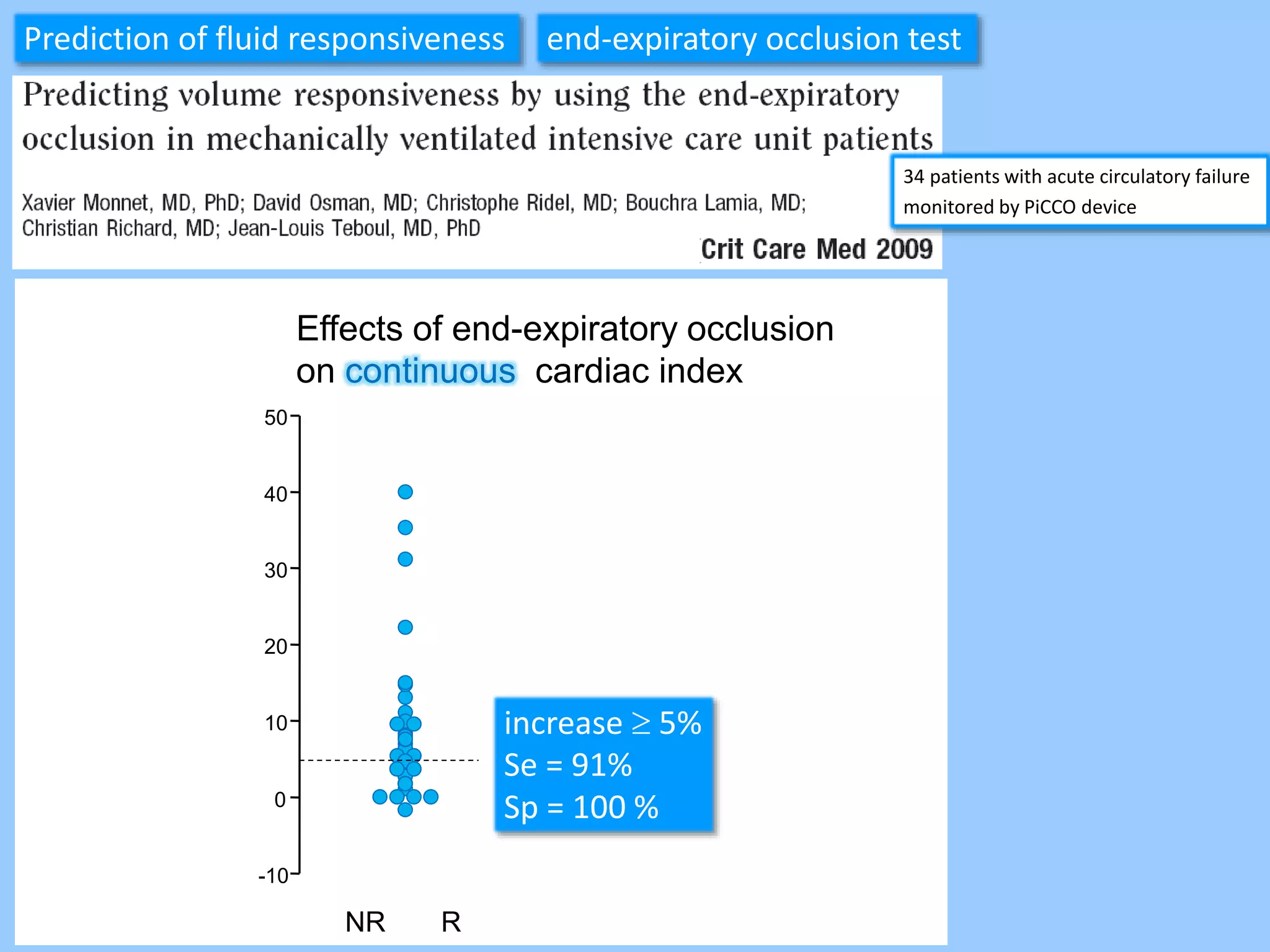
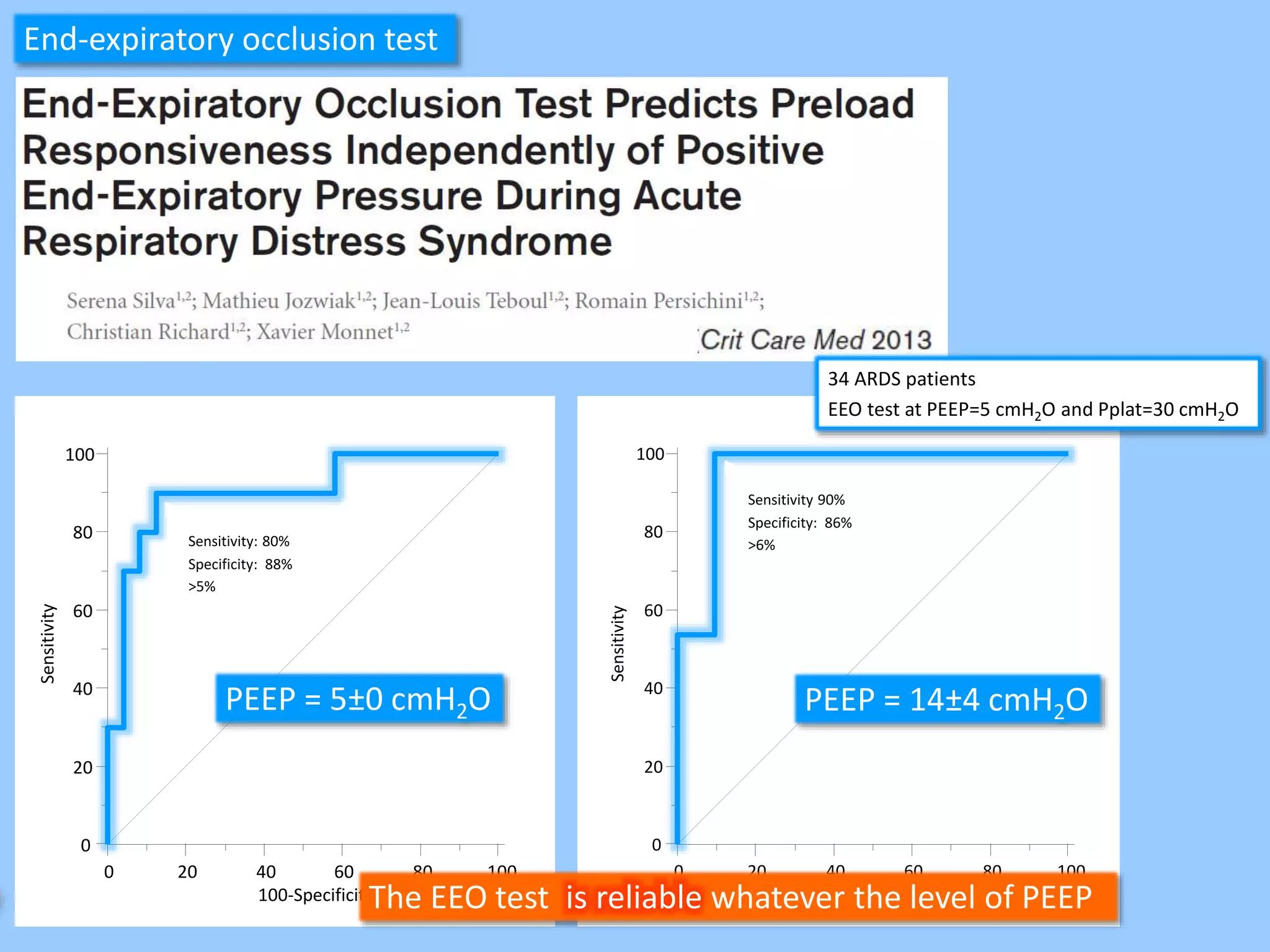
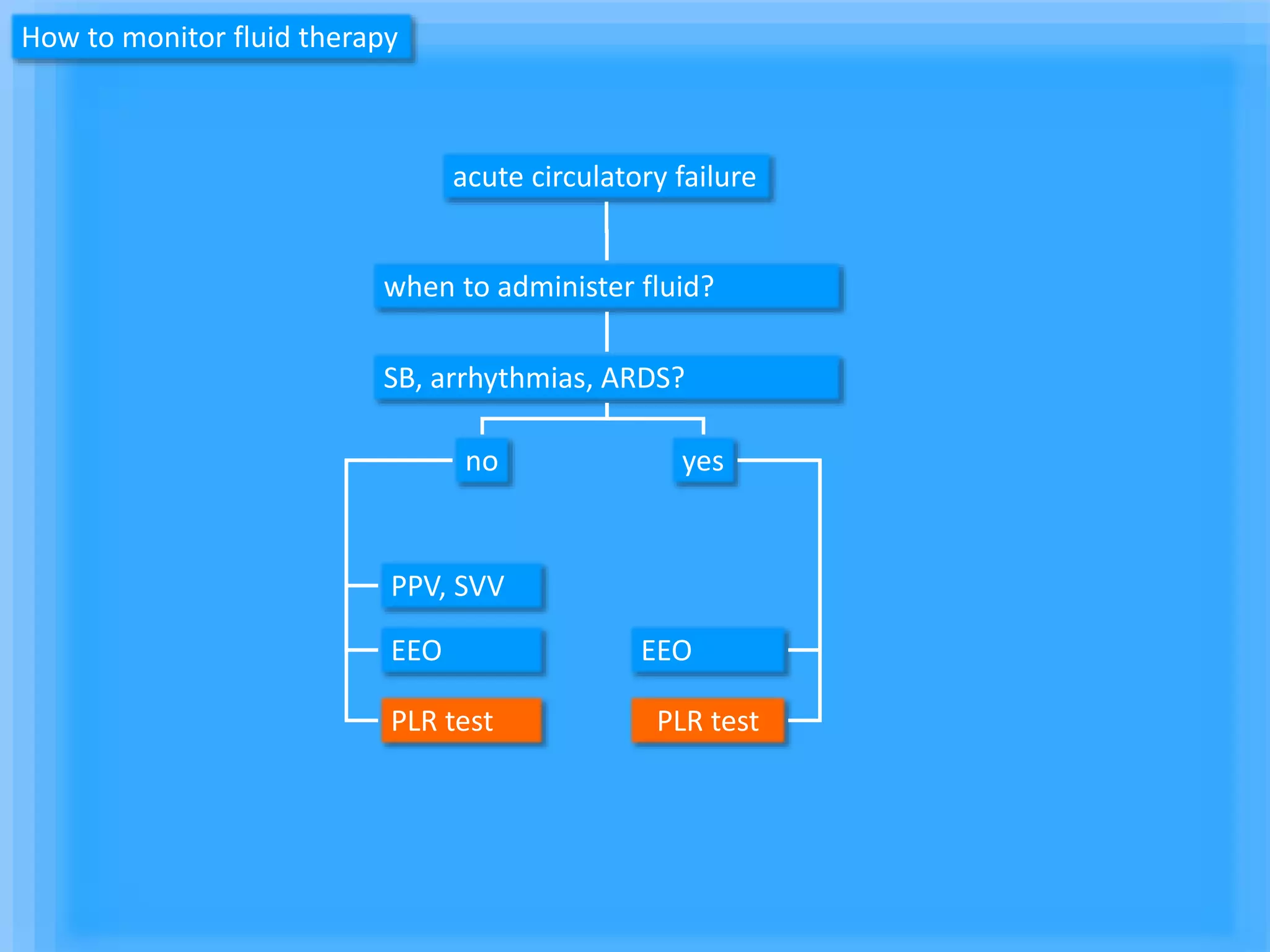
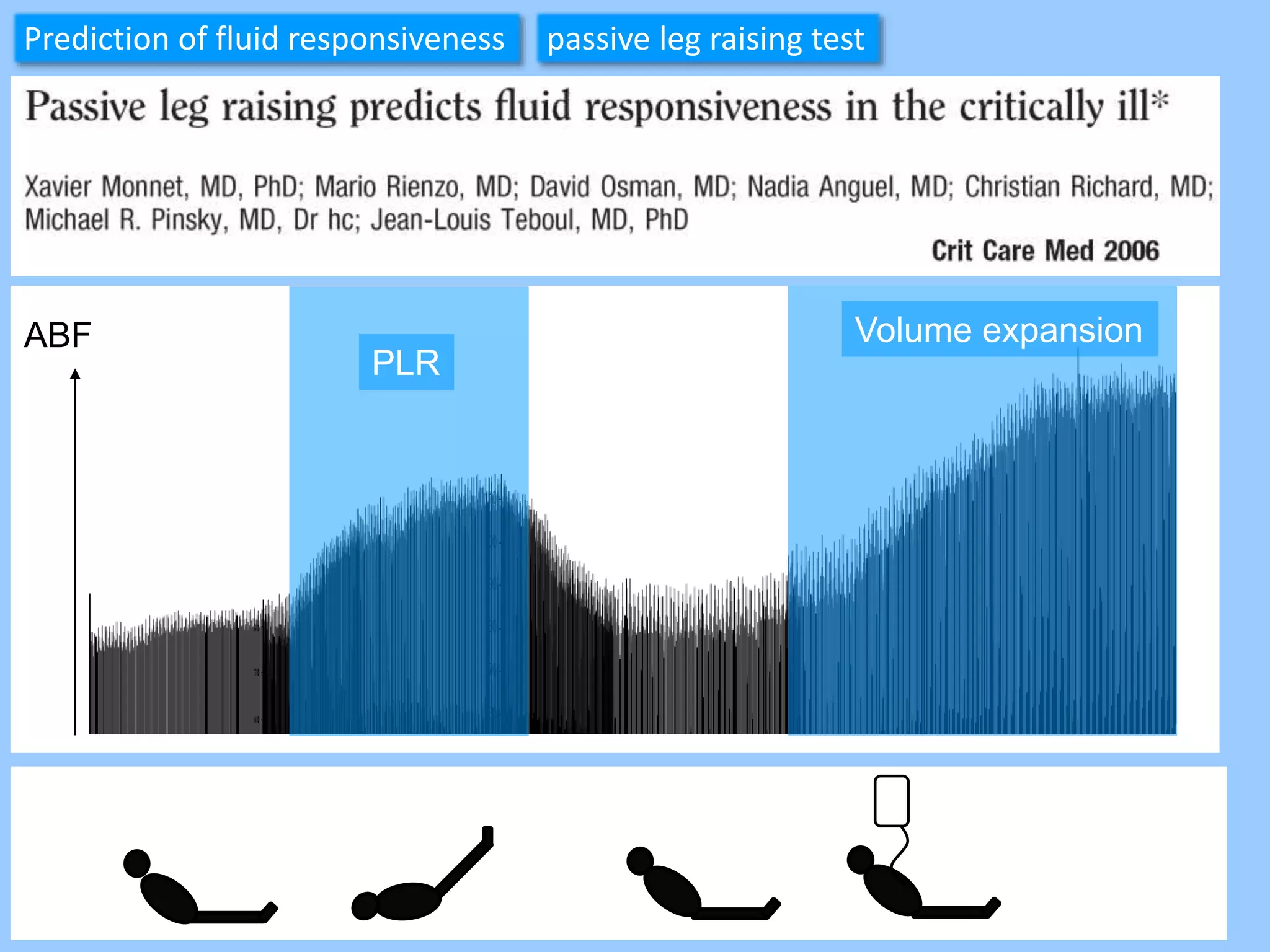
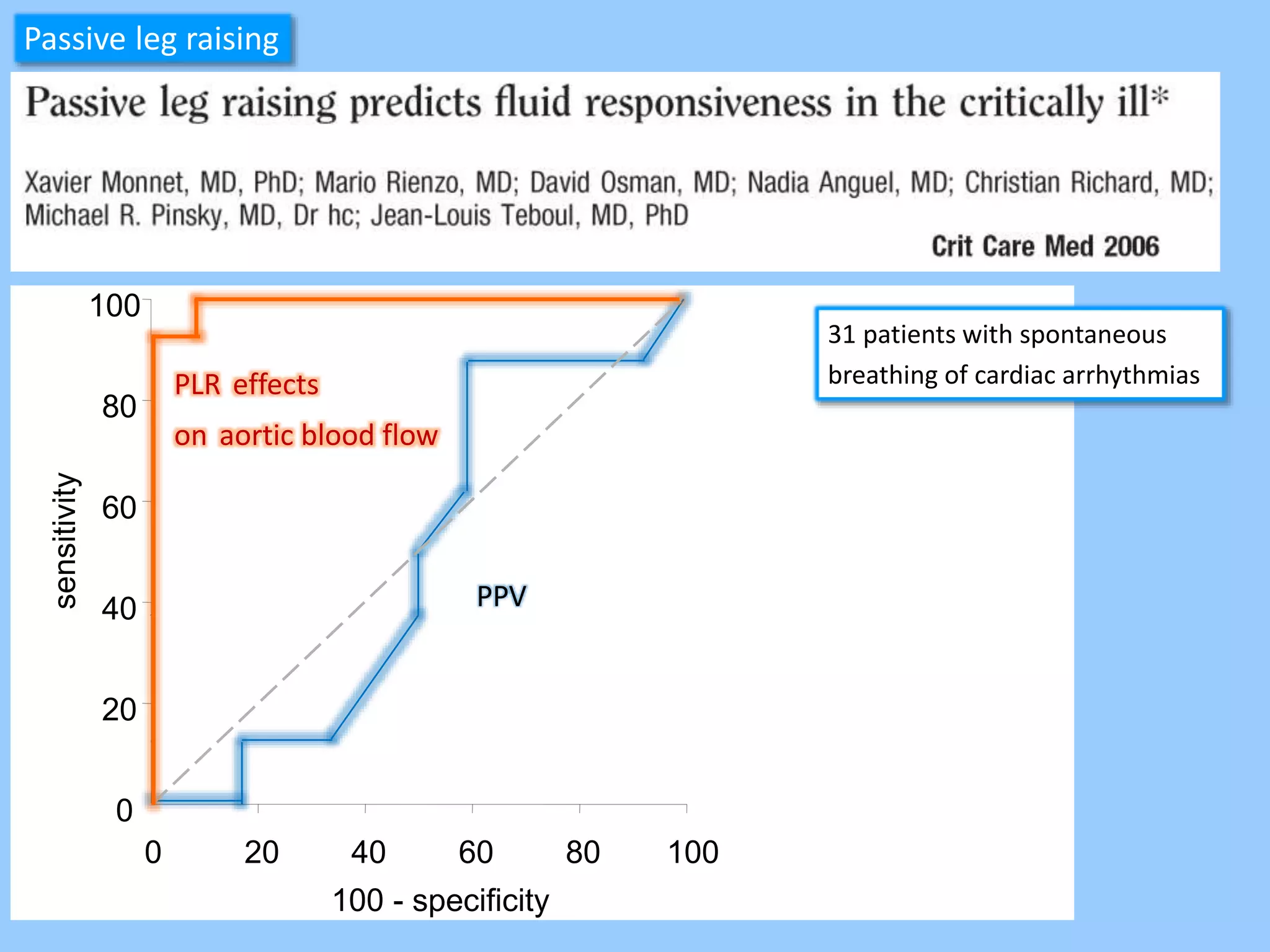
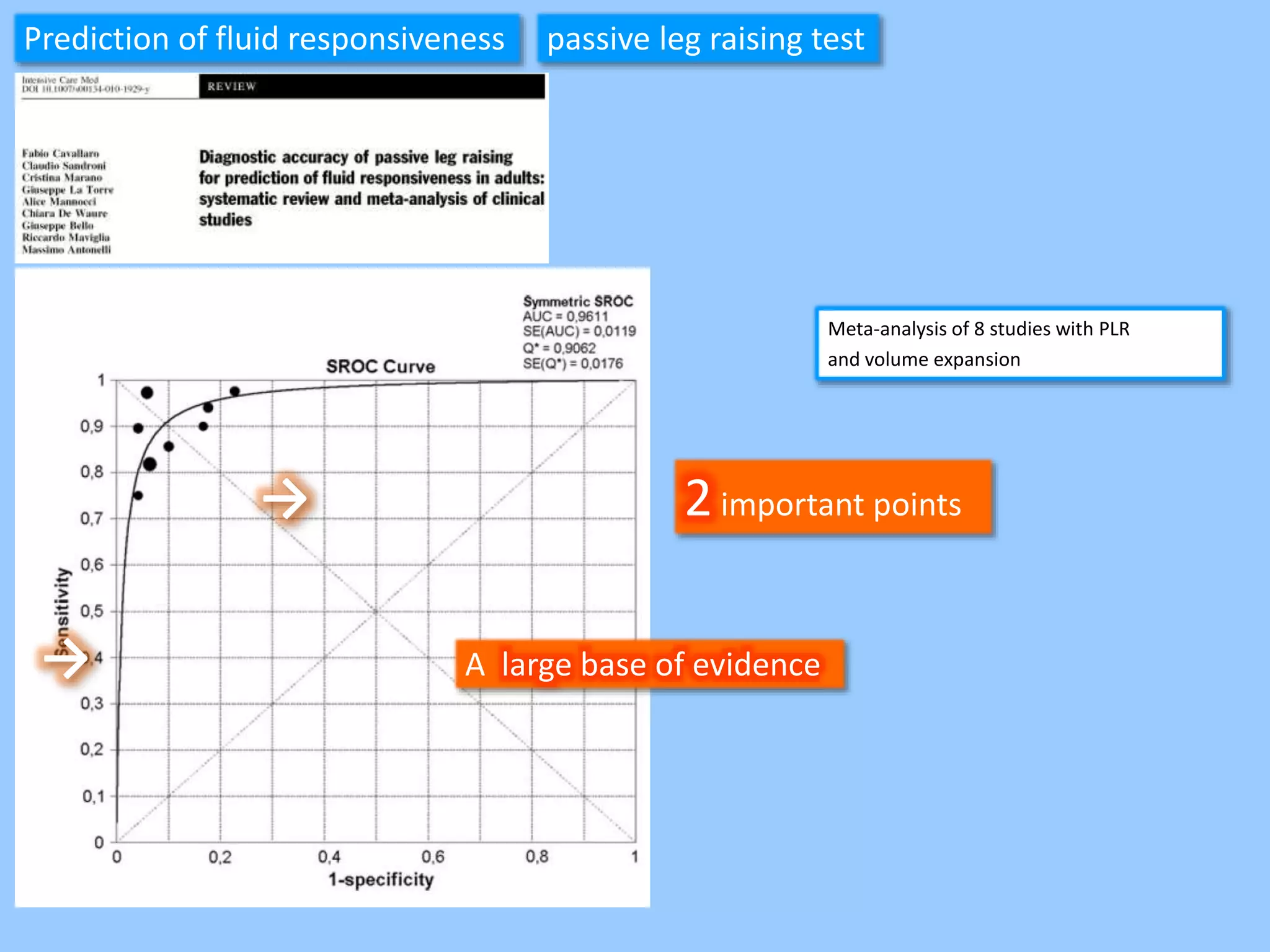
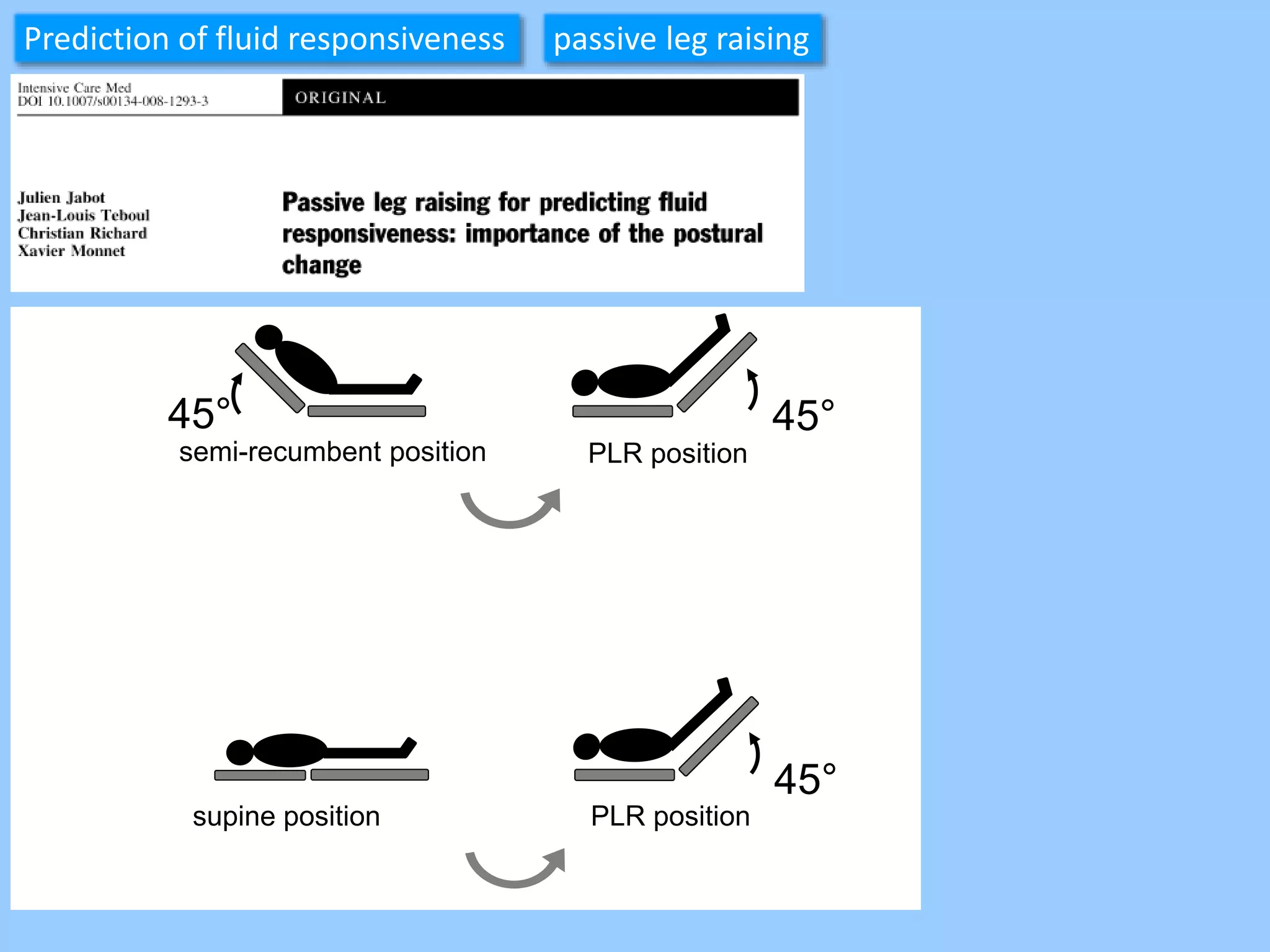
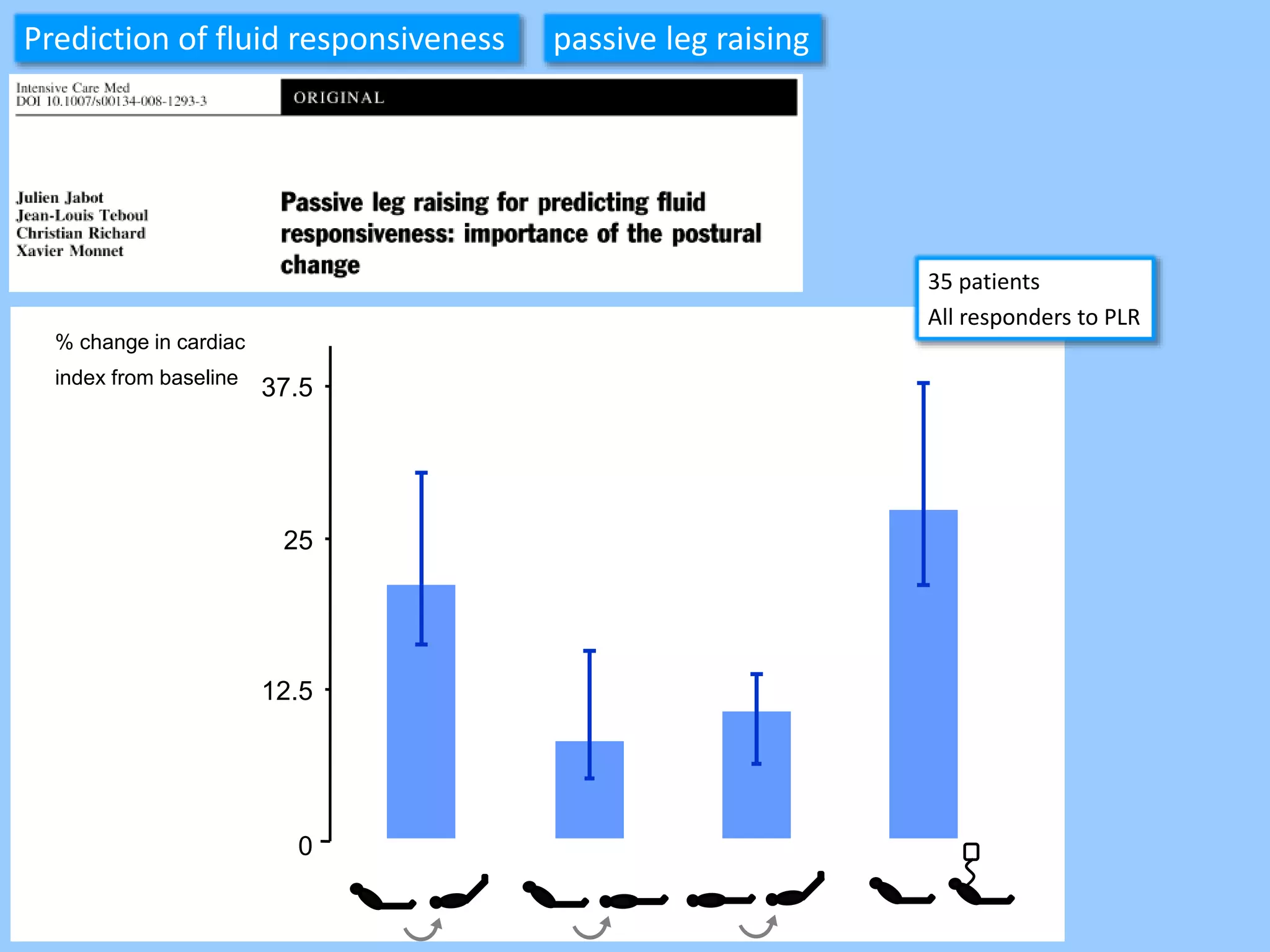
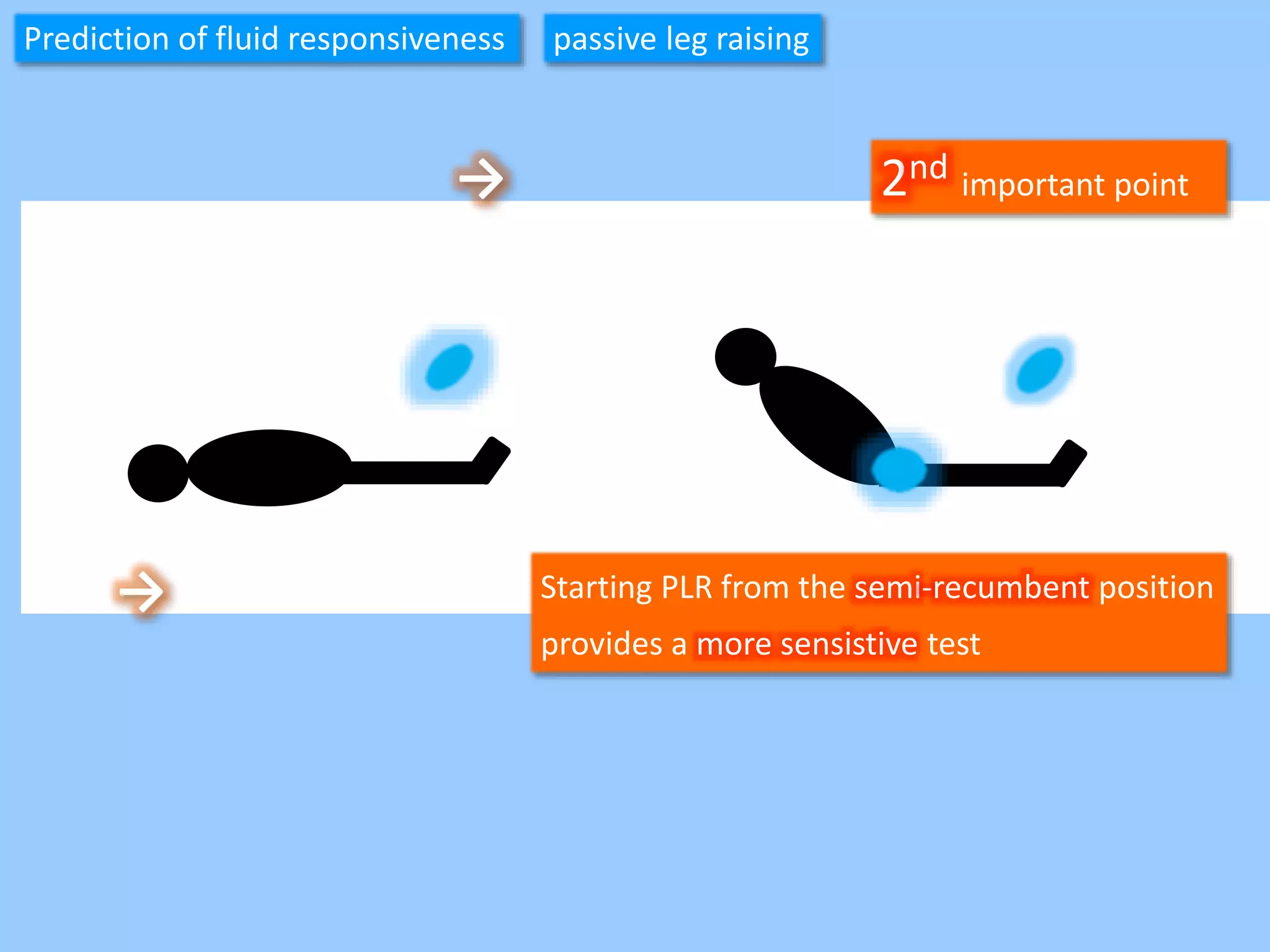
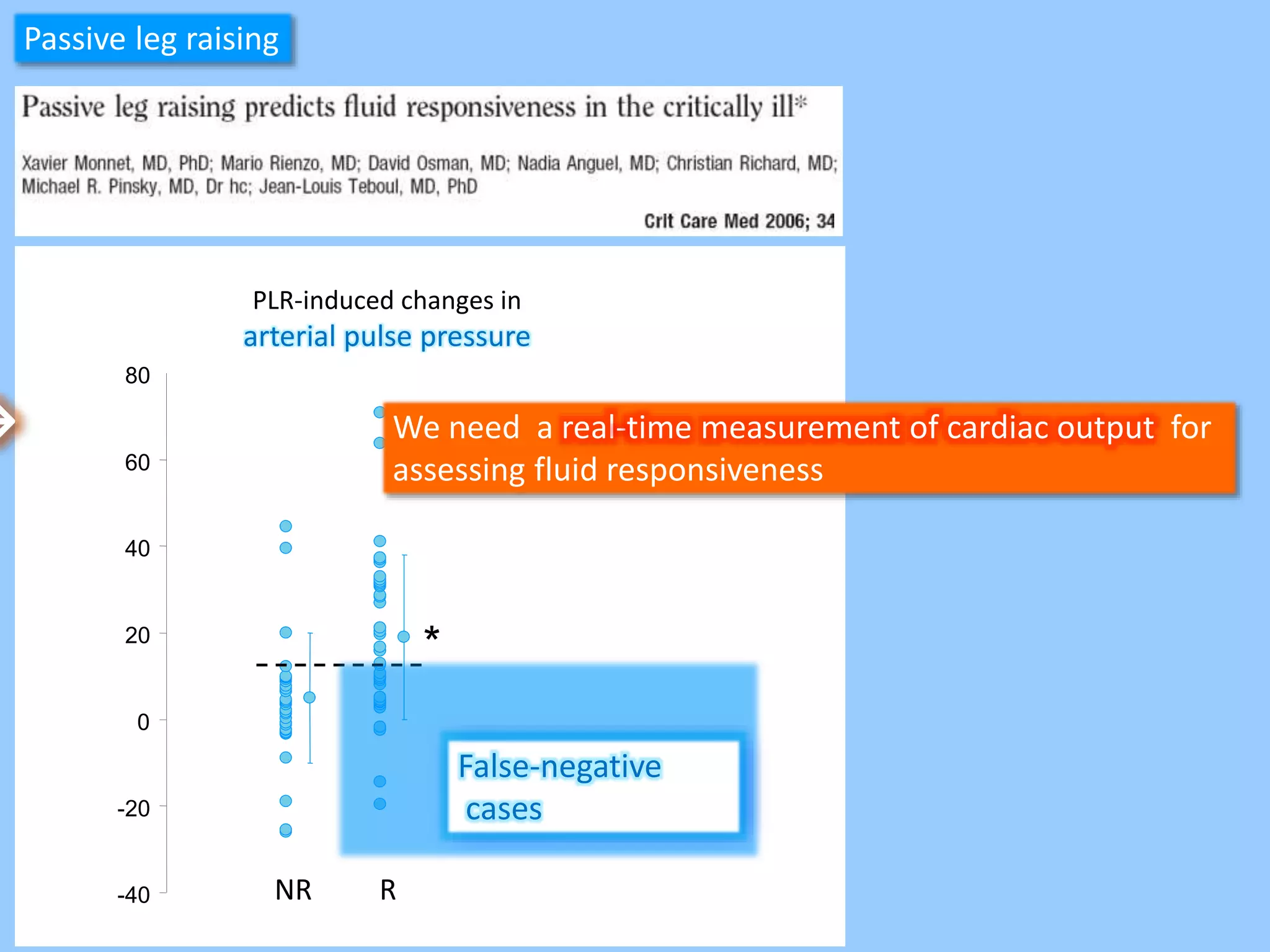
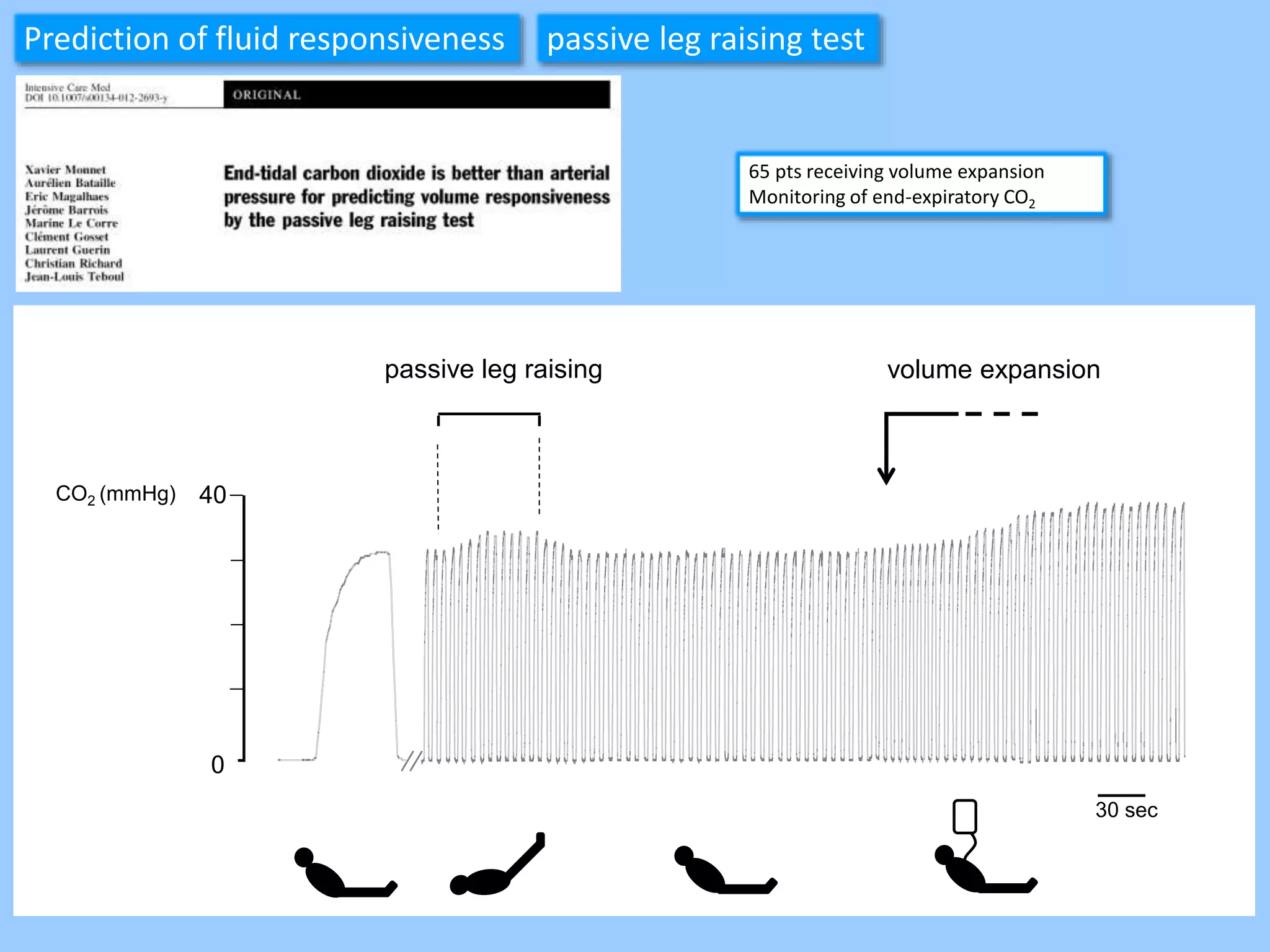
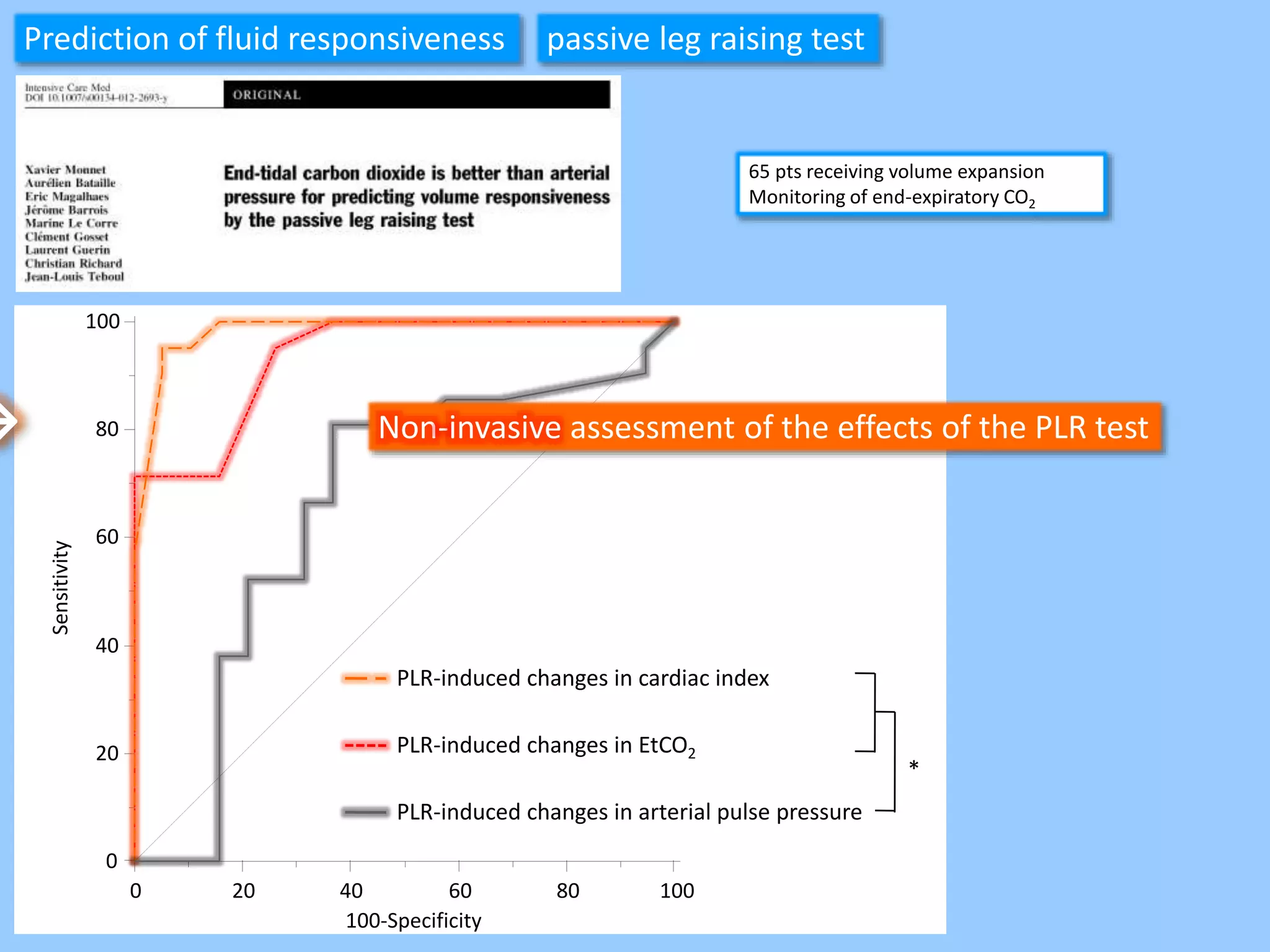
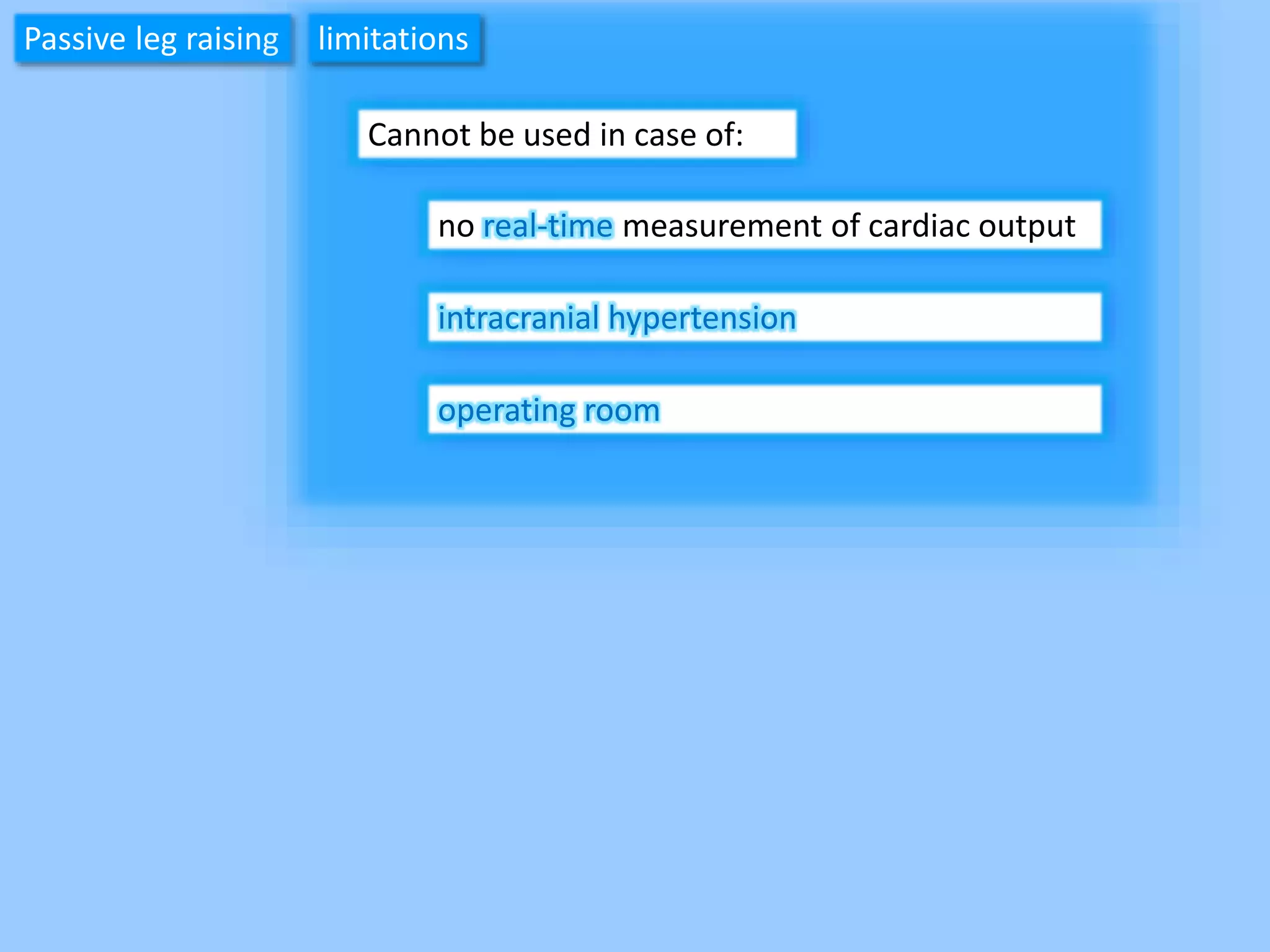
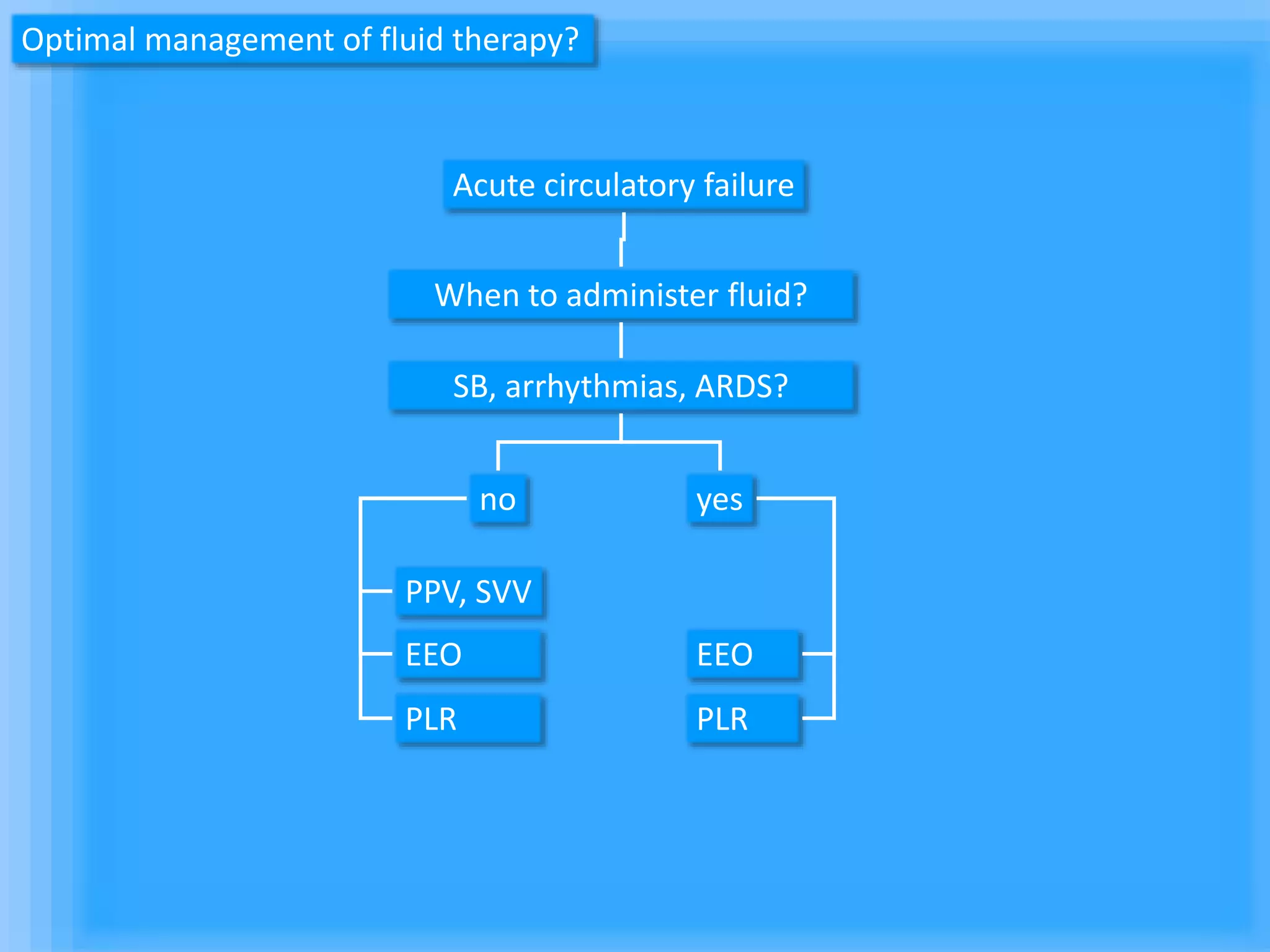
The document discusses methods for assessing fluid responsiveness in patients with acute circulatory failure. It finds that the end-expiratory occlusion (EEO) test can predict fluid responsiveness except in patients with strong spontaneous breathing. The passive leg raising (PLR) test is reliable when pulse pressure variation cannot be used, but requires starting from a semi-recumbent position and monitoring cardiac output. Non-invasive measures like changes in end-tidal carbon dioxide may also assess PLR effects. Both EEO and PLR have limitations and cannot be used in all cases.