Embed presentation
Downloaded 48 times




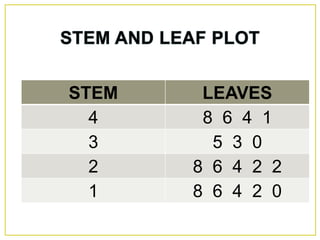
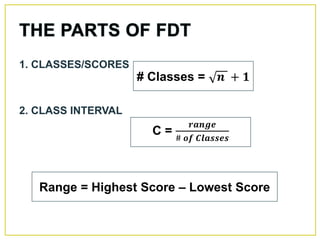

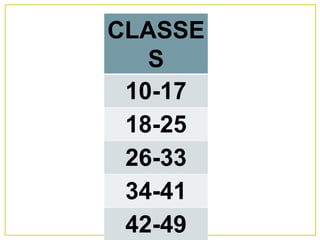
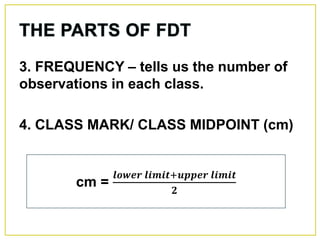
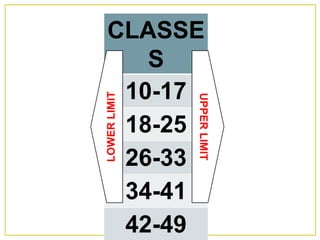
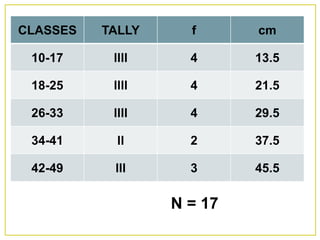

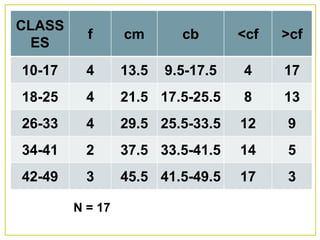

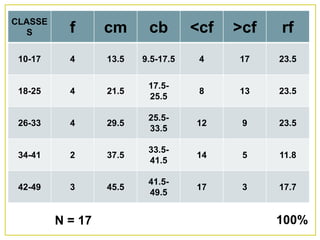

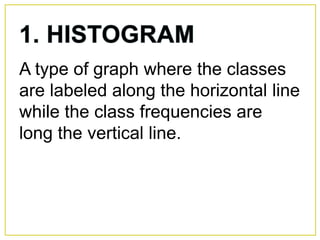




1. The document discusses different methods for presenting numerical data, including tables, graphs, and numerical techniques. 2. It provides examples of tabular data arranged in classes with frequencies, class marks, cumulative frequencies, and relative frequencies. 3. The document also describes histograms and bar graphs as ways to graphically display class data, with histograms using rectangle heights and bar graphs using points at the class midpoint and frequency coordinates.




















