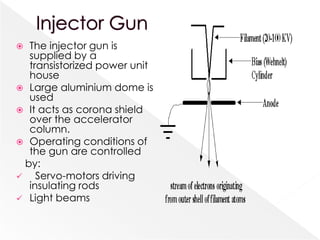
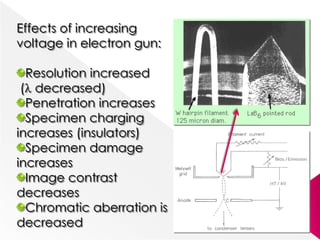
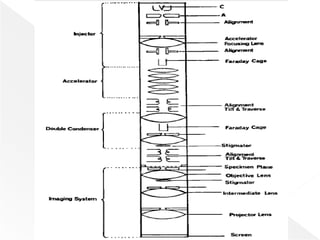
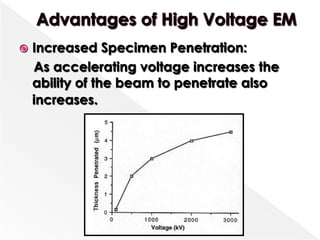
Higher accelerating voltages in transmission electron microscopes (TEMs) allow for shorter electron wavelengths and improved resolution. A 1 MeV TEM can achieve resolutions around 0.5 angstroms. Maintaining a stable high voltage, such as within 0.5 volts for a 1 MeV microscope, is important. Increasing the voltage improves resolution and penetration depth but can also increase specimen charging and damage.