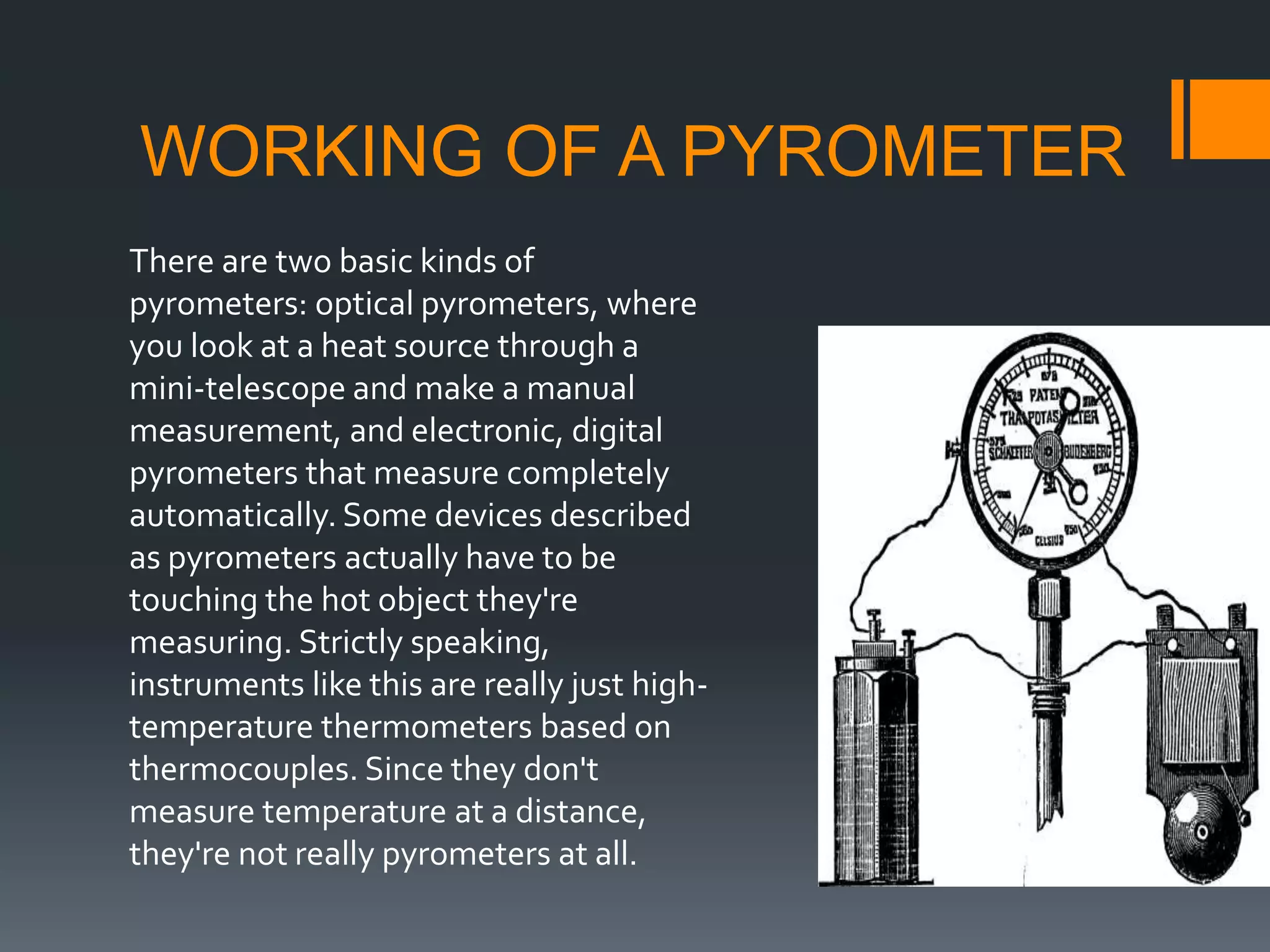
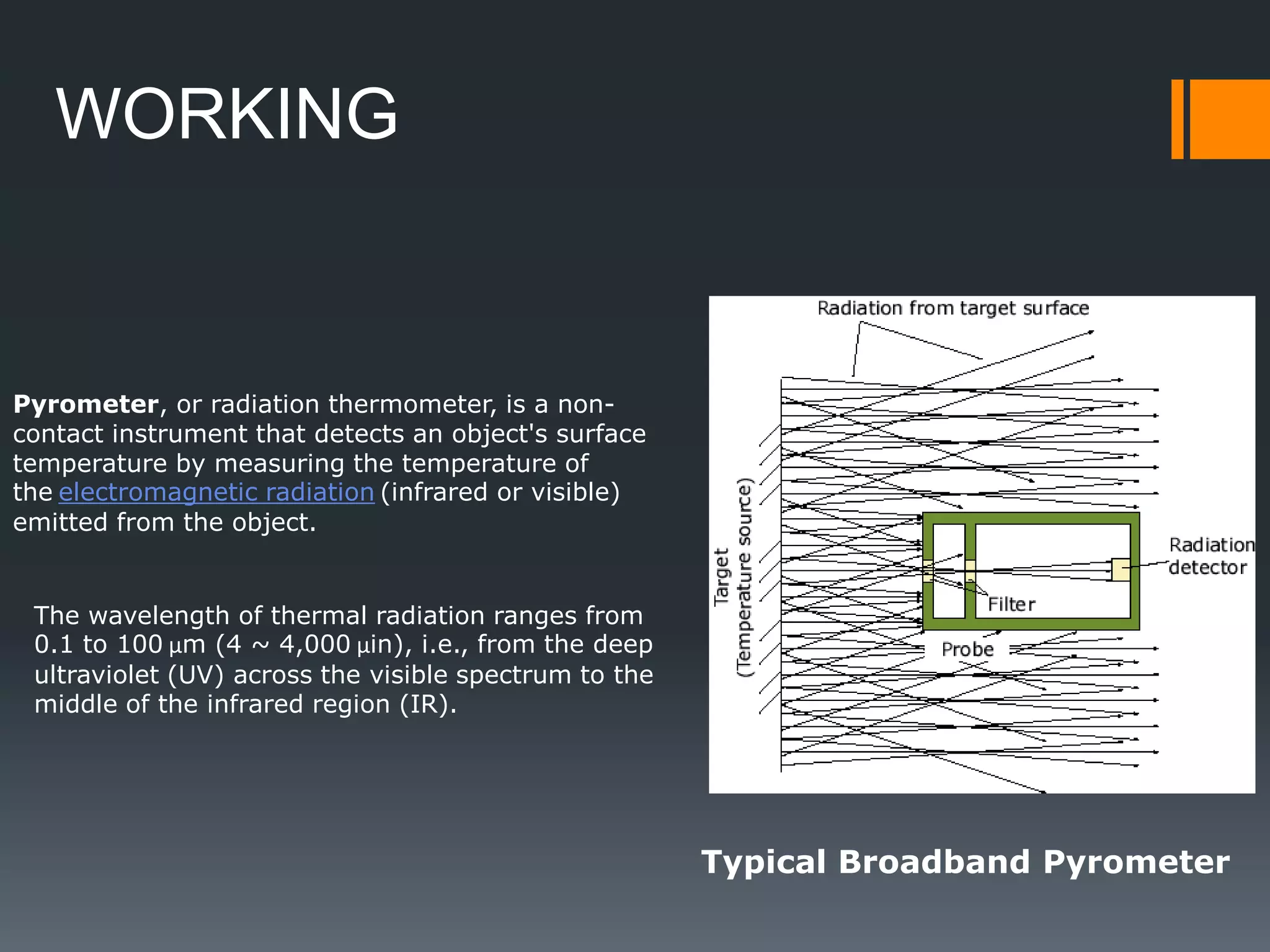
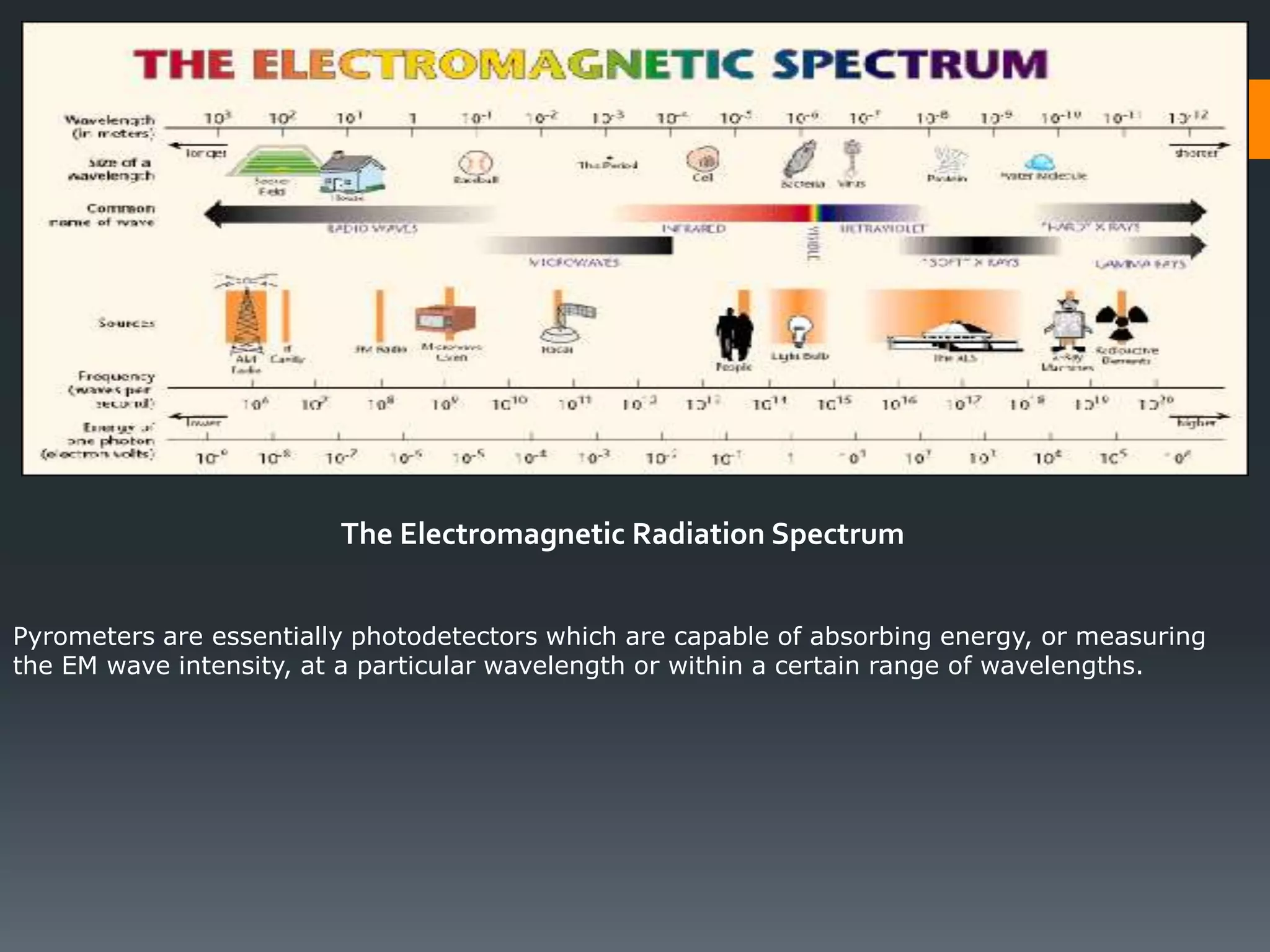
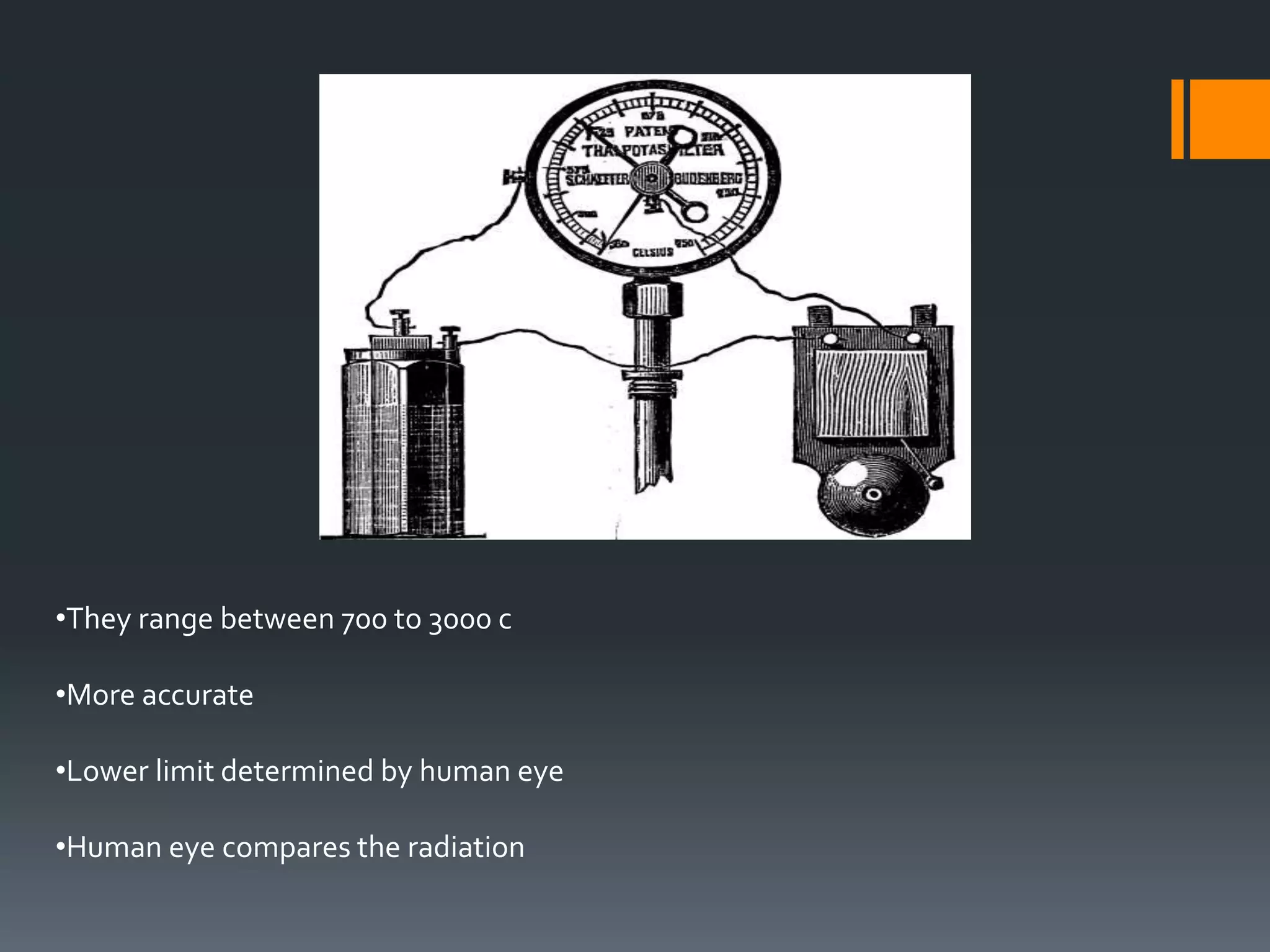
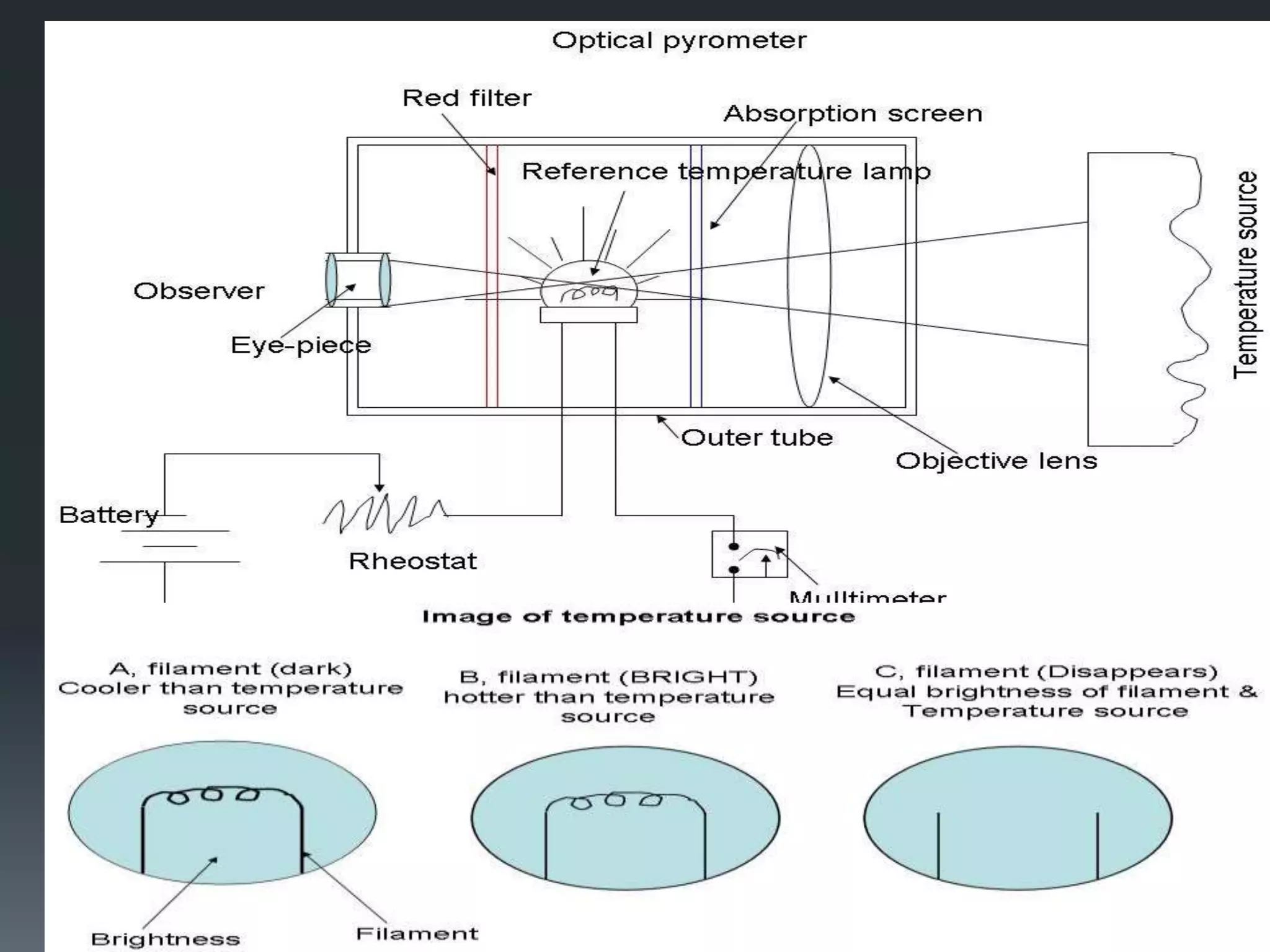
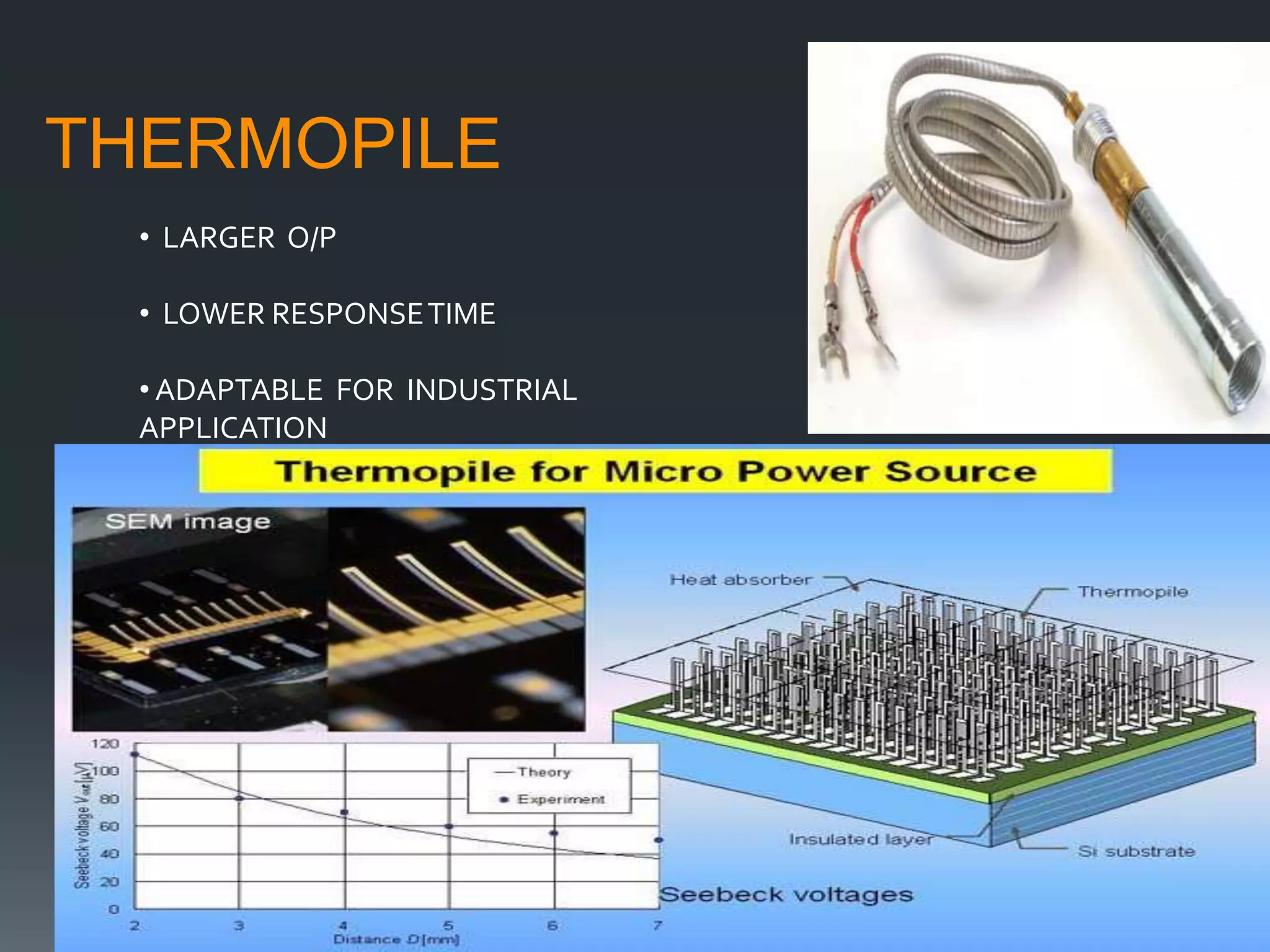
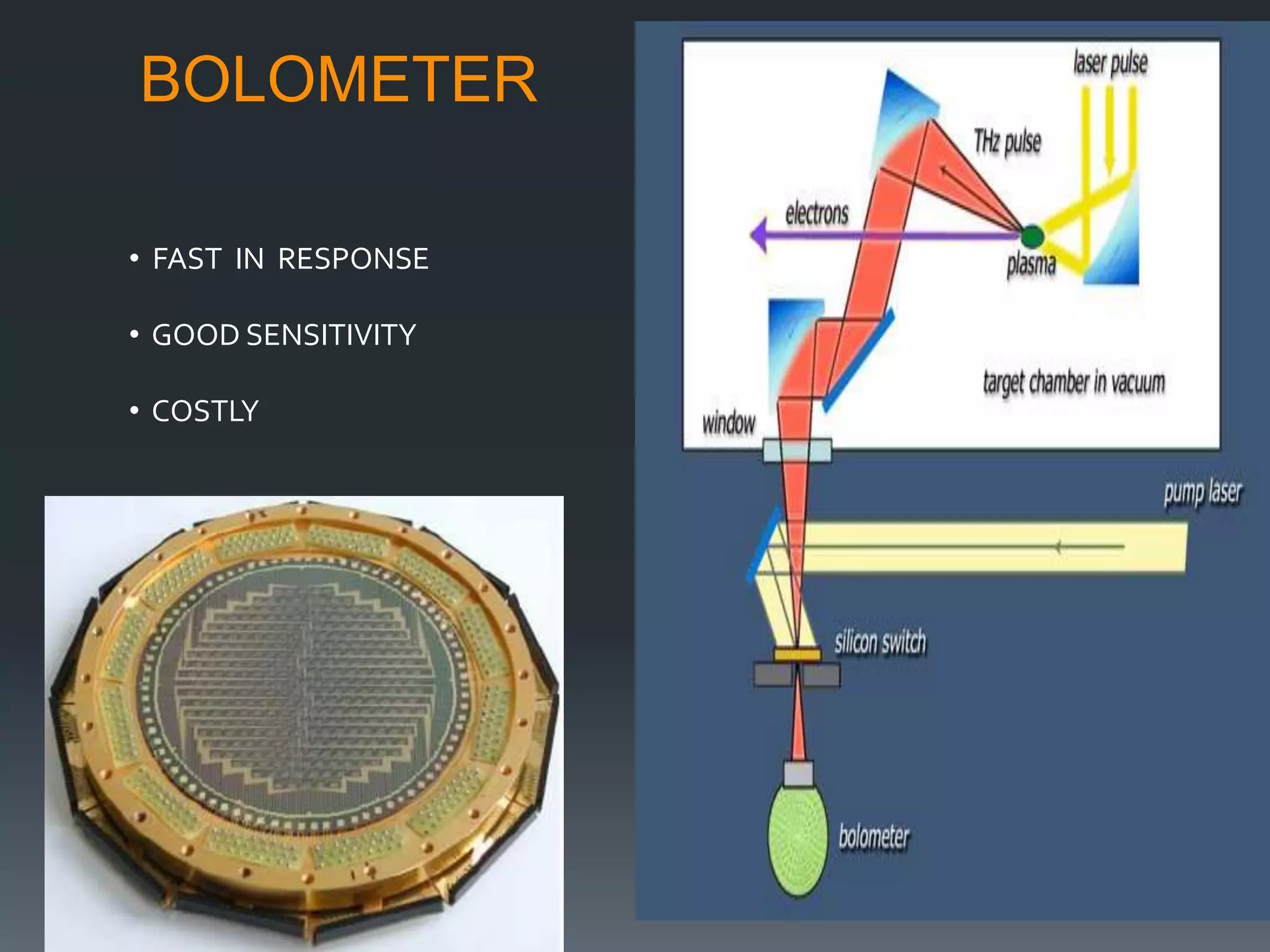
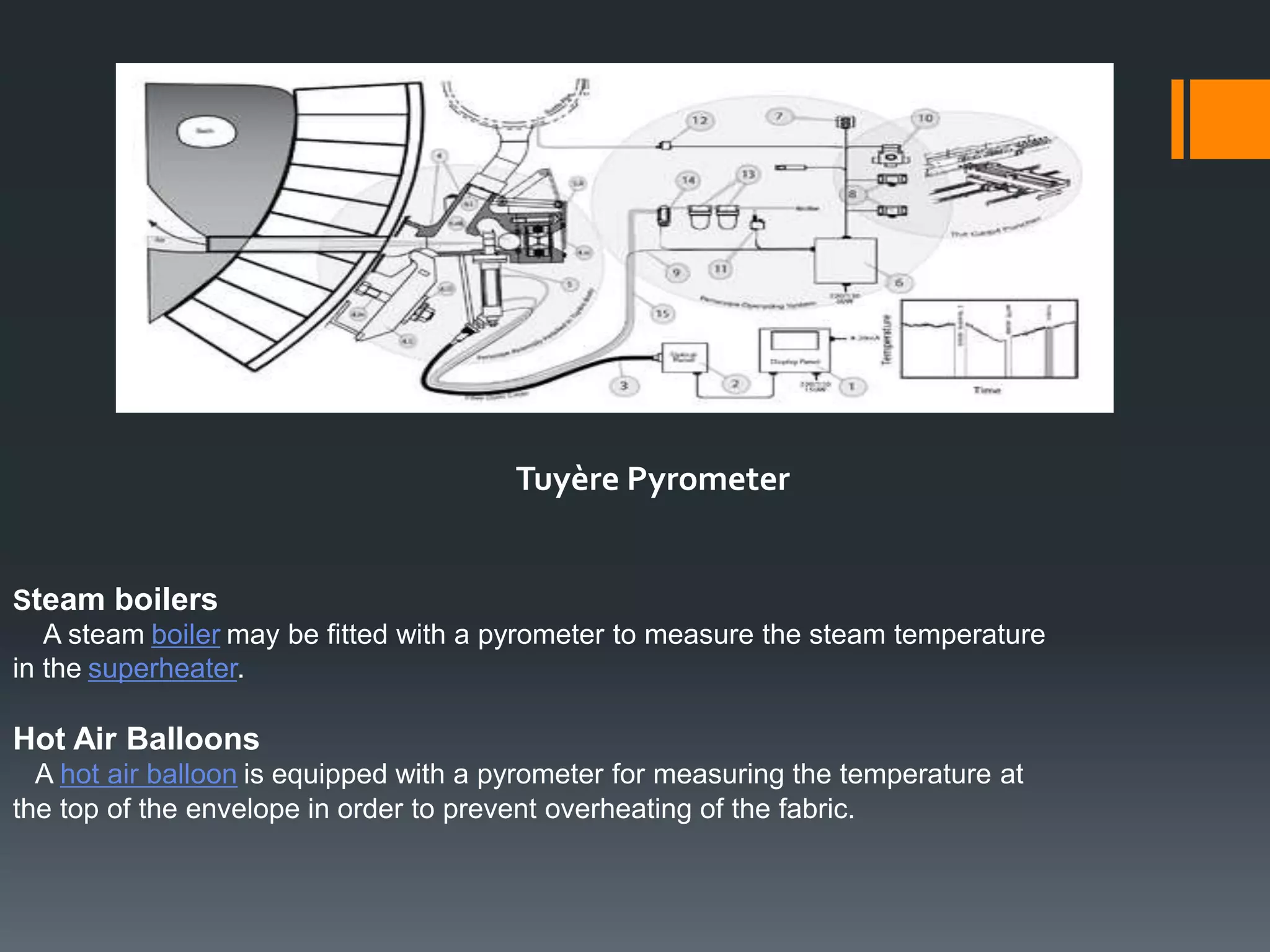
A pyrometer is a non-contact device that measures the surface temperature of an object by detecting the thermal radiation it emits. Modern pyrometers became available in 1901 with the development of the disappearing filament pyrometer. Issues with early pyrometers relying on emissivity led to the development of ratio or two-color pyrometers. There are different types of pyrometers including optical, radiation, digital, and infrared pyrometers that use various detectors like thermopiles, photocells, bolometers, and thermistors. Pyrometers are useful for measuring temperatures of moving or inaccessible objects and are widely used in industries like smelting, heat treatment, and steam boilers.