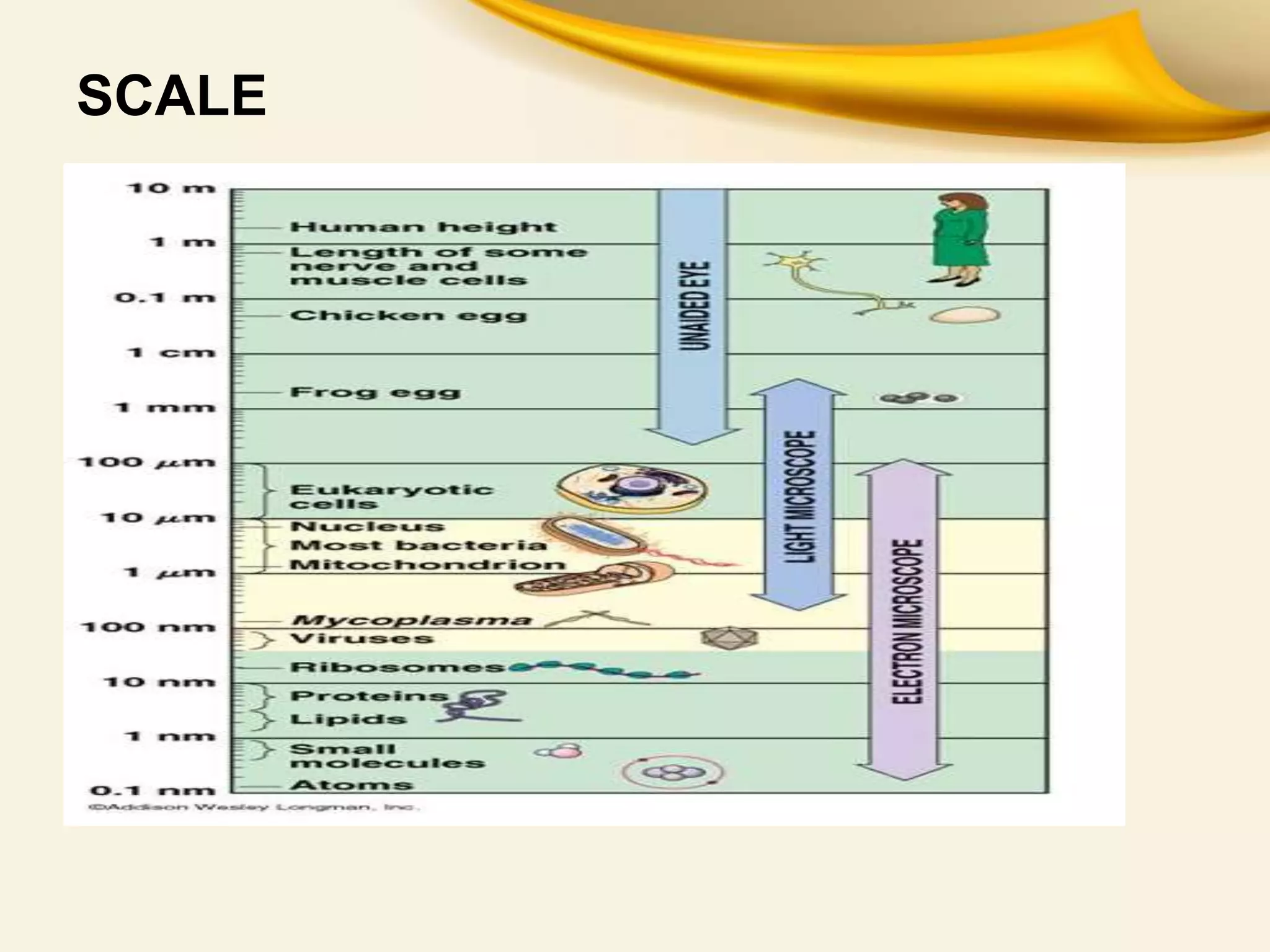
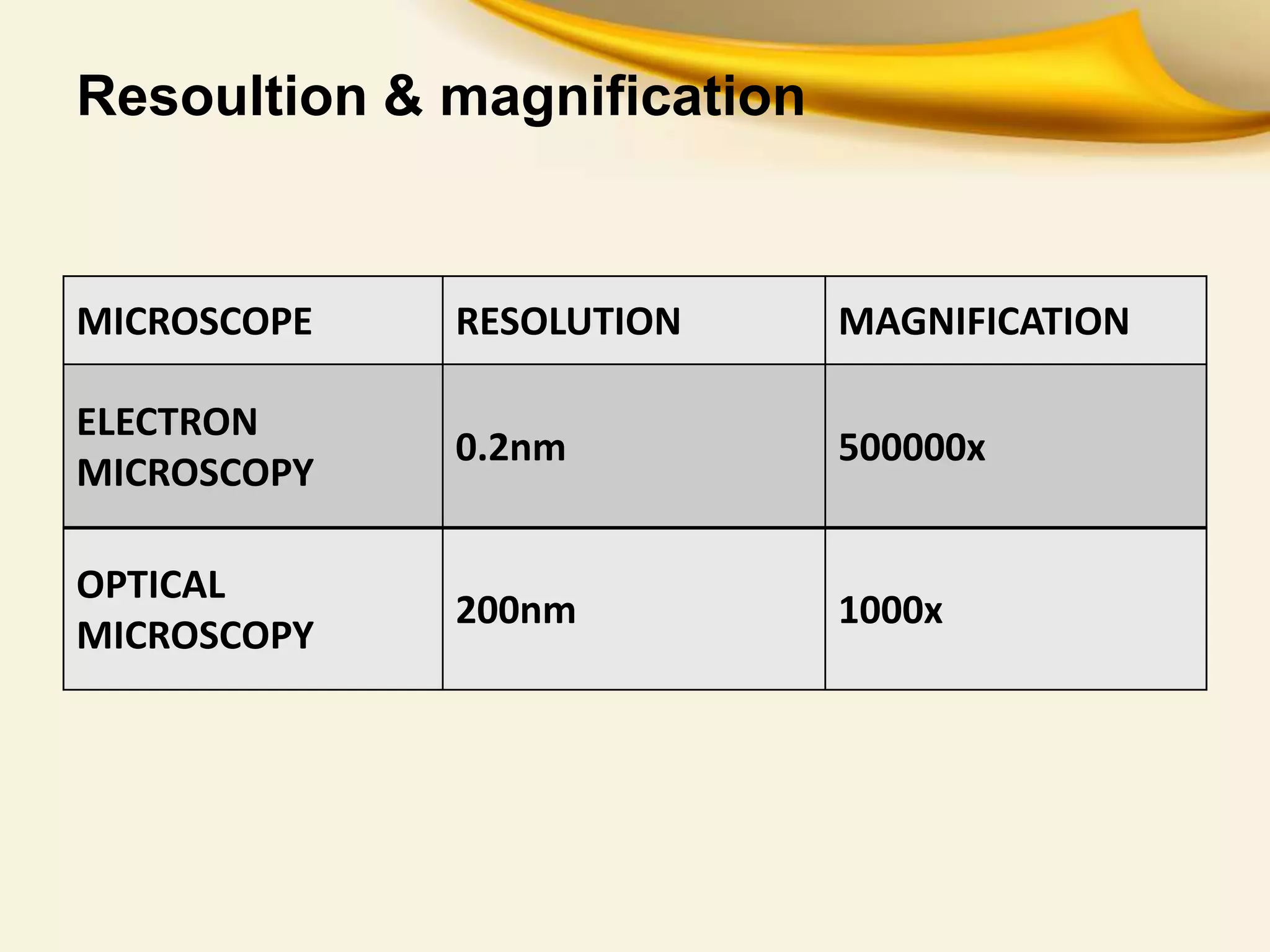
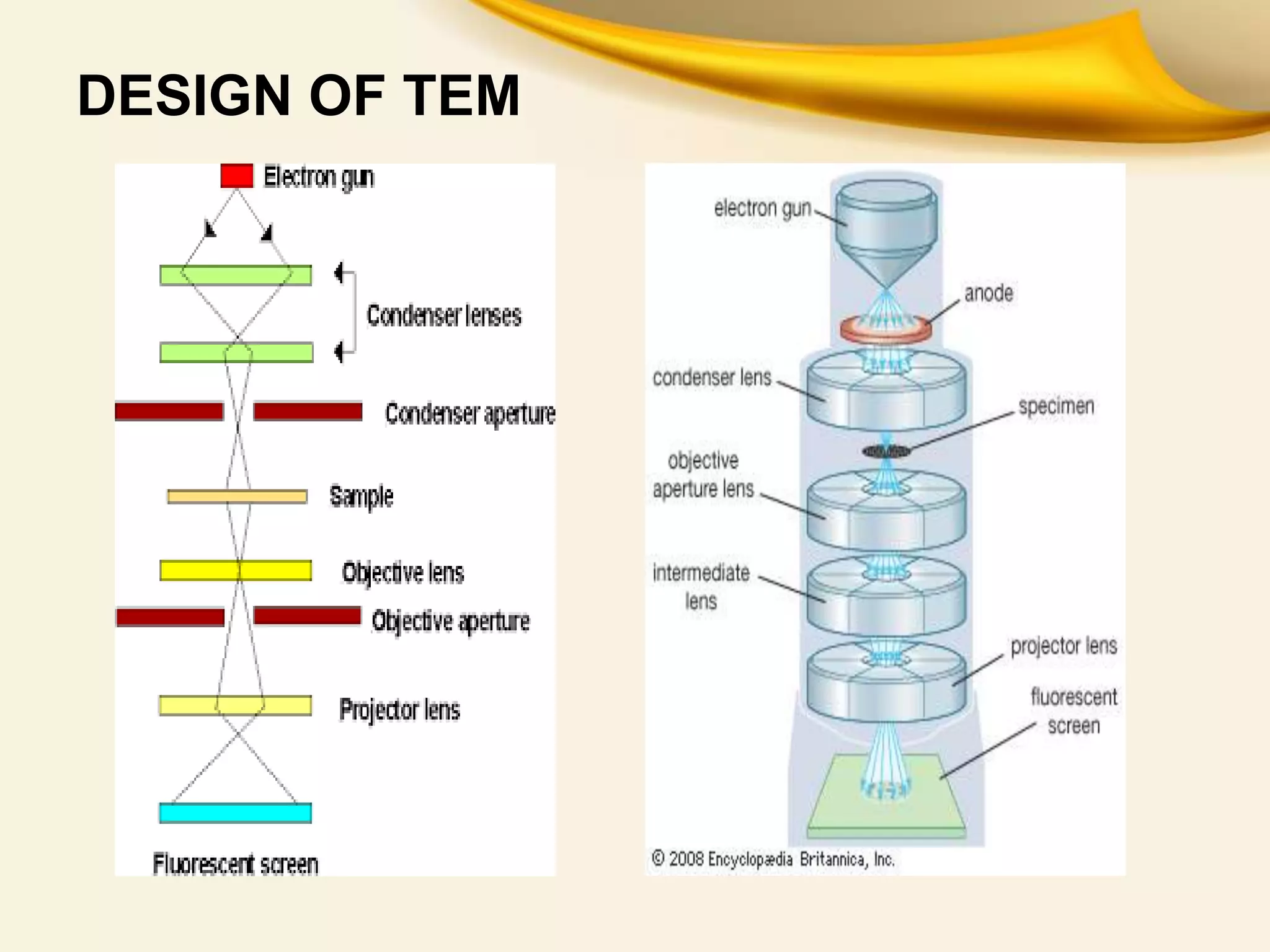
This document provides an overview of Transmitted Electron Microscopy (TEM). It discusses that TEM was first designed in 1931 and uses a beam of electrons to examine objects on a very fine scale, with magnification over 10,000x. The key components of a TEM are an electron gun, condenser lenses, a specimen, objective lenses, projector lenses, and detectors. TEM works by firing electrons through a thin specimen and using magnetic lenses to focus the electrons. Applications include viewing cell structures and nanoparticles. TEM provides high-quality images but also has limitations such as high cost and complex sample preparation.