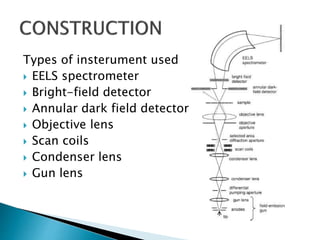
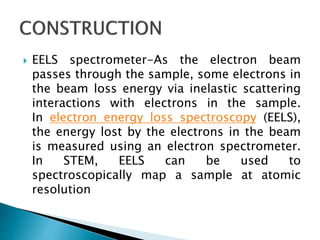
The scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM) uses a finely focused electron beam that scans across the sample in a raster pattern. The STEM provides atomic resolution imaging and analysis through detectors like the EELS spectrometer, bright-field detector, and annular dark-field detector. Scan coils are used to scan the beam across the sample, while the condenser lens demagnifies the electron crossover point for high magnification imaging. The STEM has various applications in materials science and biology for characterizing nano- and atomic-scale structures.