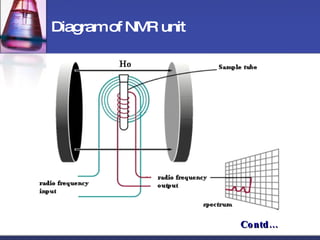
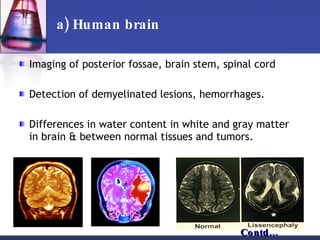
NMR spectroscopy is a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to determine structural information about molecules. It has various applications in biology, such as determining molecular structures, studying drug metabolism and protein folding, analyzing phosphate metabolism in living cells, and studying nucleic acids and lipid bilayers. NMR spectroscopy is also used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to produce detailed images of organs and tissues in the body without using ionizing radiation.