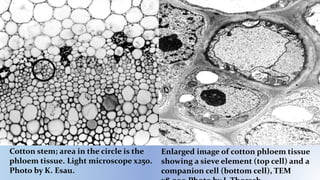
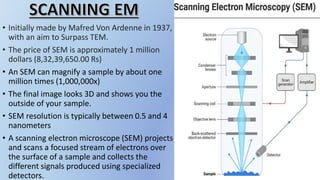
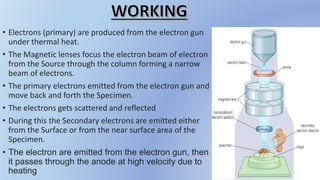
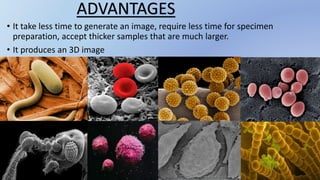
This document provides information about the transmission electron microscope (TEM). It begins by explaining that a TEM uses electron beams to produce highly magnified images of incredibly thin samples, up to 10-50 million times magnification and less than 150nm thick. It describes the basic components and functioning of a TEM, including the electron gun, magnetic lenses, sample stage, imaging system, and detector. Key points are that TEMs allow viewing structures at the molecular level and have a resolution limit of 0.2 micrometers. The document also discusses applications in fields like virology and nanotechnology, and advantages like high magnification and quality images.