Embed presentation
Downloaded 882 times
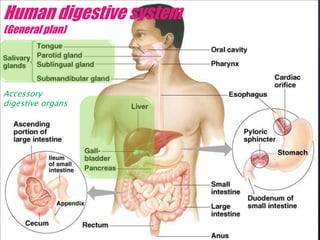
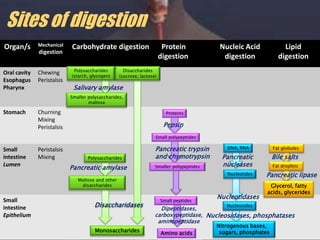
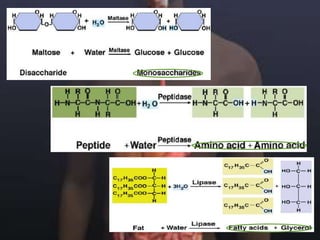
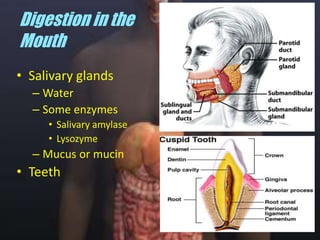
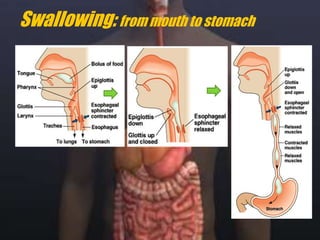
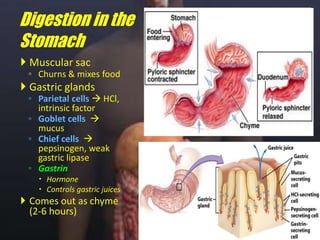
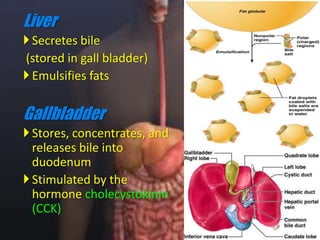
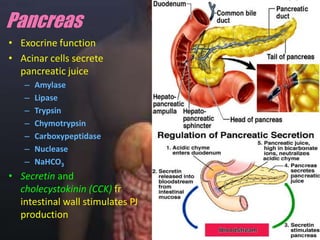
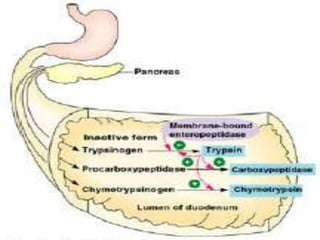
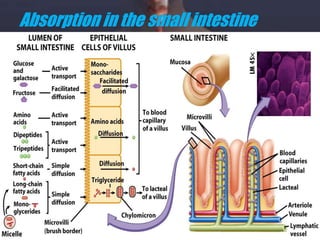
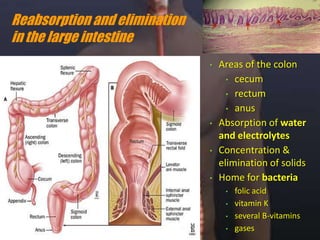
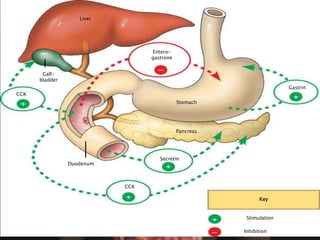


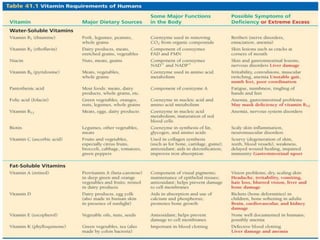
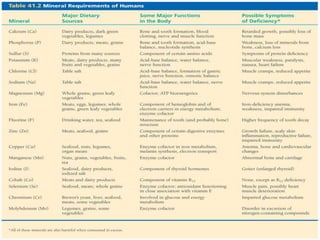
The human digestive system breaks down food through a multi-step process. In the mouth, saliva containing the enzyme amylase begins to break down starches. The stomach further breaks down food using gastric juices containing hydrochloric acid and the enzyme pepsin. The partially digested material then moves to the small intestine where pancreatic juices containing enzymes like trypsin and lipase and bile from the liver finish the breakdown into absorbable molecules. These molecules are then absorbed through the intestinal walls and transported throughout the body. Undigested material moves to the large intestine where water is absorbed before elimination of waste.
















