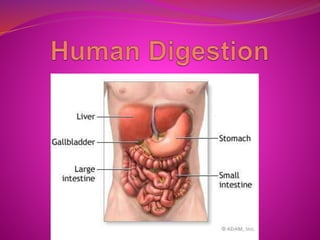
The document discusses the human digestive system and nutrition. It describes the process of ingestion, digestion, and absorption of nutrients. The major parts of the digestive system are described including the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum. The document outlines the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food at each stage as well as the roles of accessory organs like the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. Common digestive disorders are also briefly discussed.