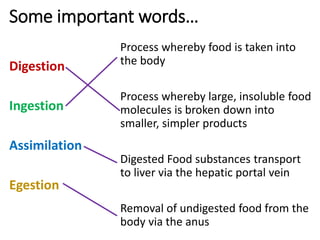
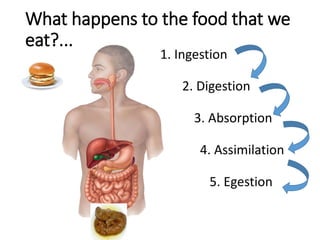
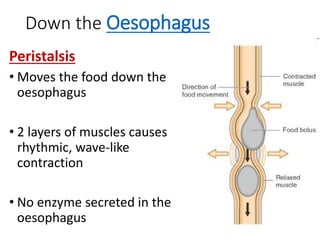
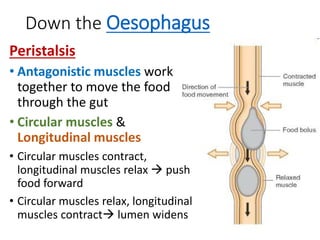
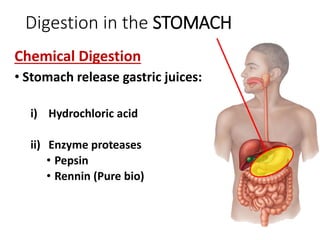
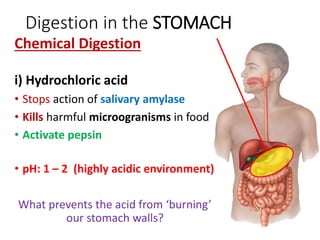
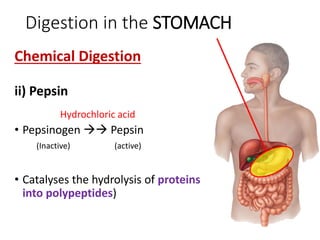
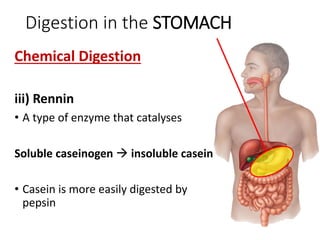
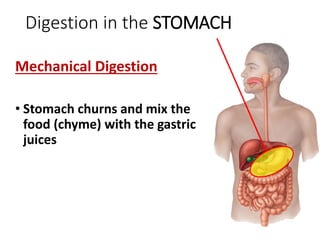
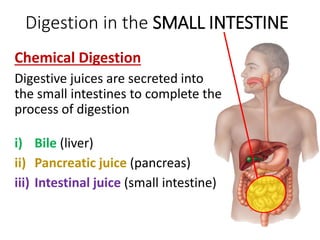
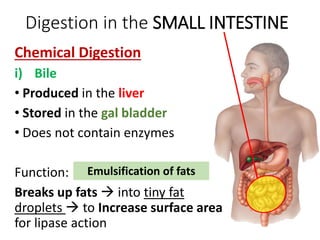
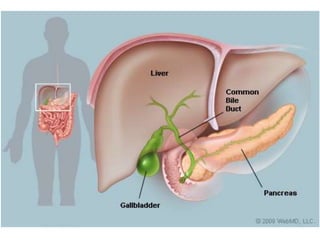
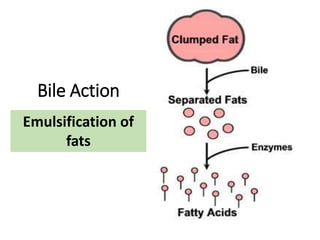
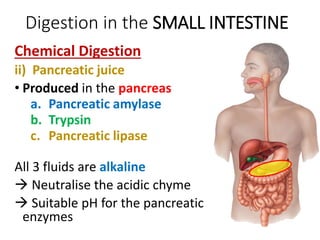
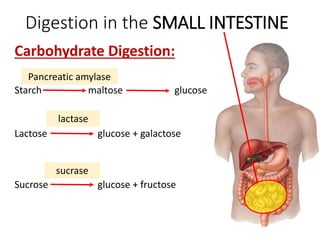
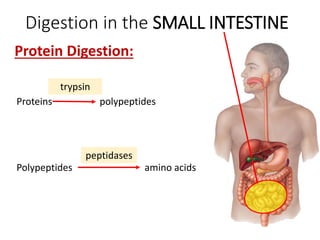
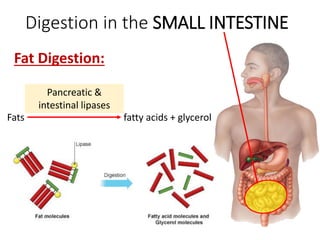
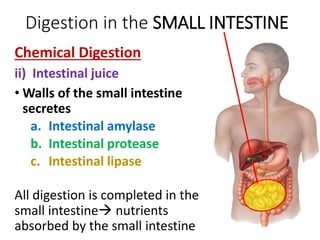
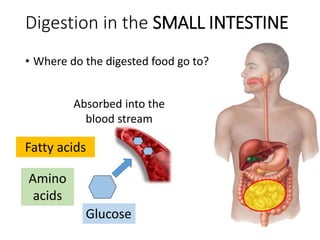
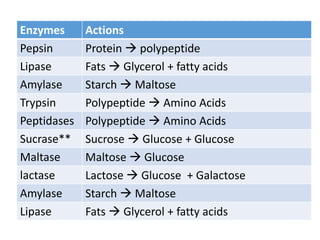
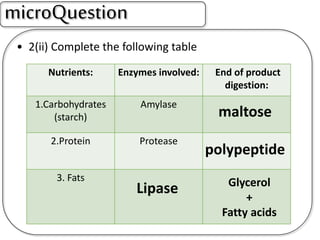
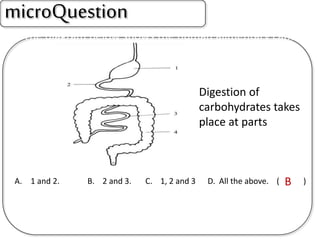
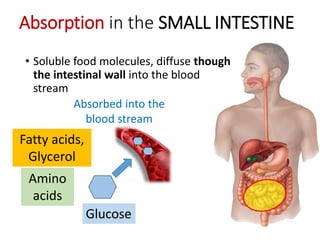
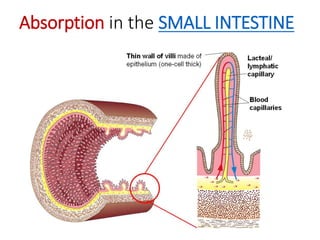
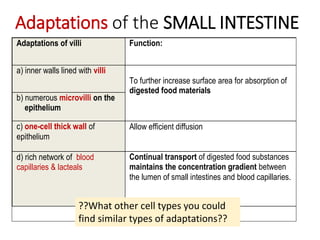
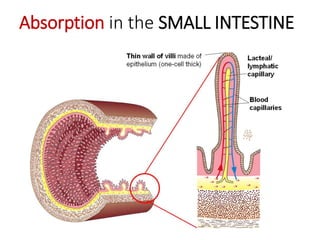
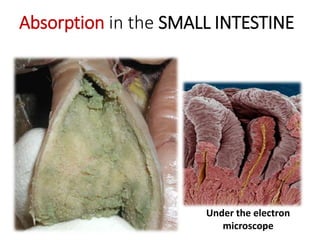
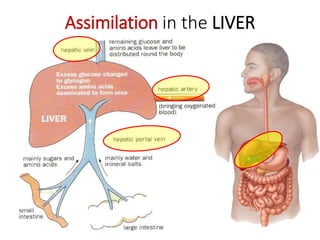
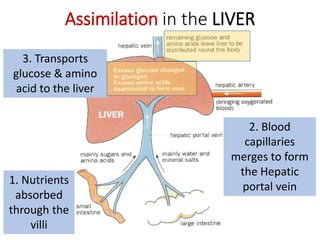
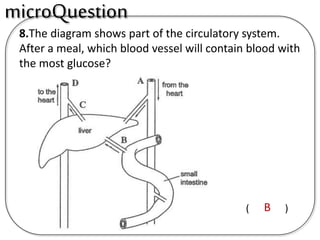
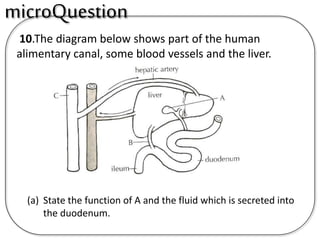
A secretes bile which helps in emulsification of fats.
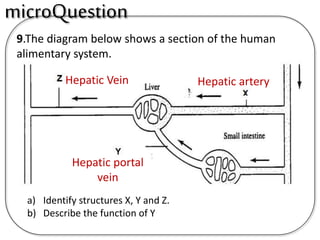
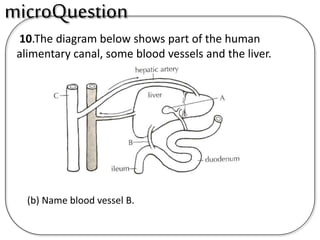
B is the hepatic portal vein.
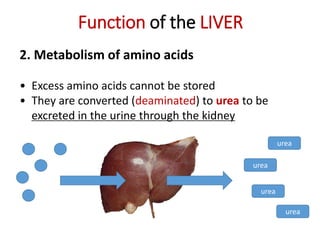
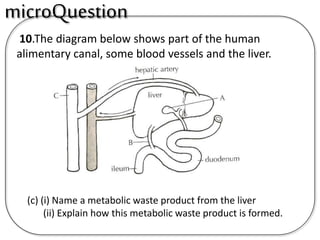
C (i) Urea.
(ii) Urea is formed from the breakdown of excess amino acids in the liver. The amino acids are deaminated and the ammonia produced is converted to urea.
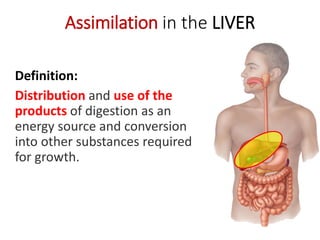
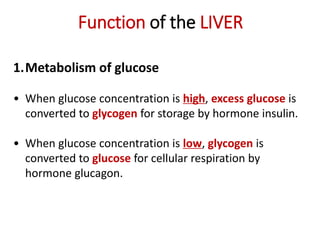
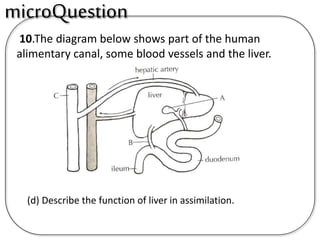
D The liver plays an important role in assimilation. It receives nutrients like glucose and amino acids from the hepatic portal vein after digestion and absorption in the small intestine. It converts excess glucose to glycogen for storage. It also converts excess amino acids into urea which is excreted in urine. This prevents toxic build up of ammonia in the body.