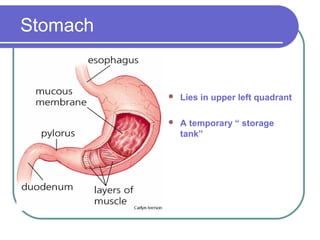
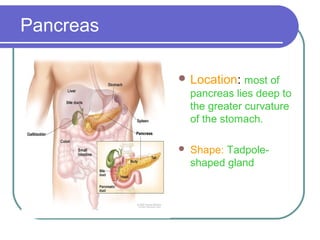
The document summarizes the key components and functions of the digestive system. It describes the digestive tract as a long twisting tube starting at the mouth and ending at the anus. It then discusses four main organs - the liver, stomach, gallbladder, and pancreas. The liver produces bile and filters toxins from the blood. The stomach stores, breaks down, and mixes food before slowly emptying it into the small intestine. The gallbladder stores and releases bile to aid digestion. The pancreas produces hormones like insulin that regulate blood sugar and enzymes that help break down food.