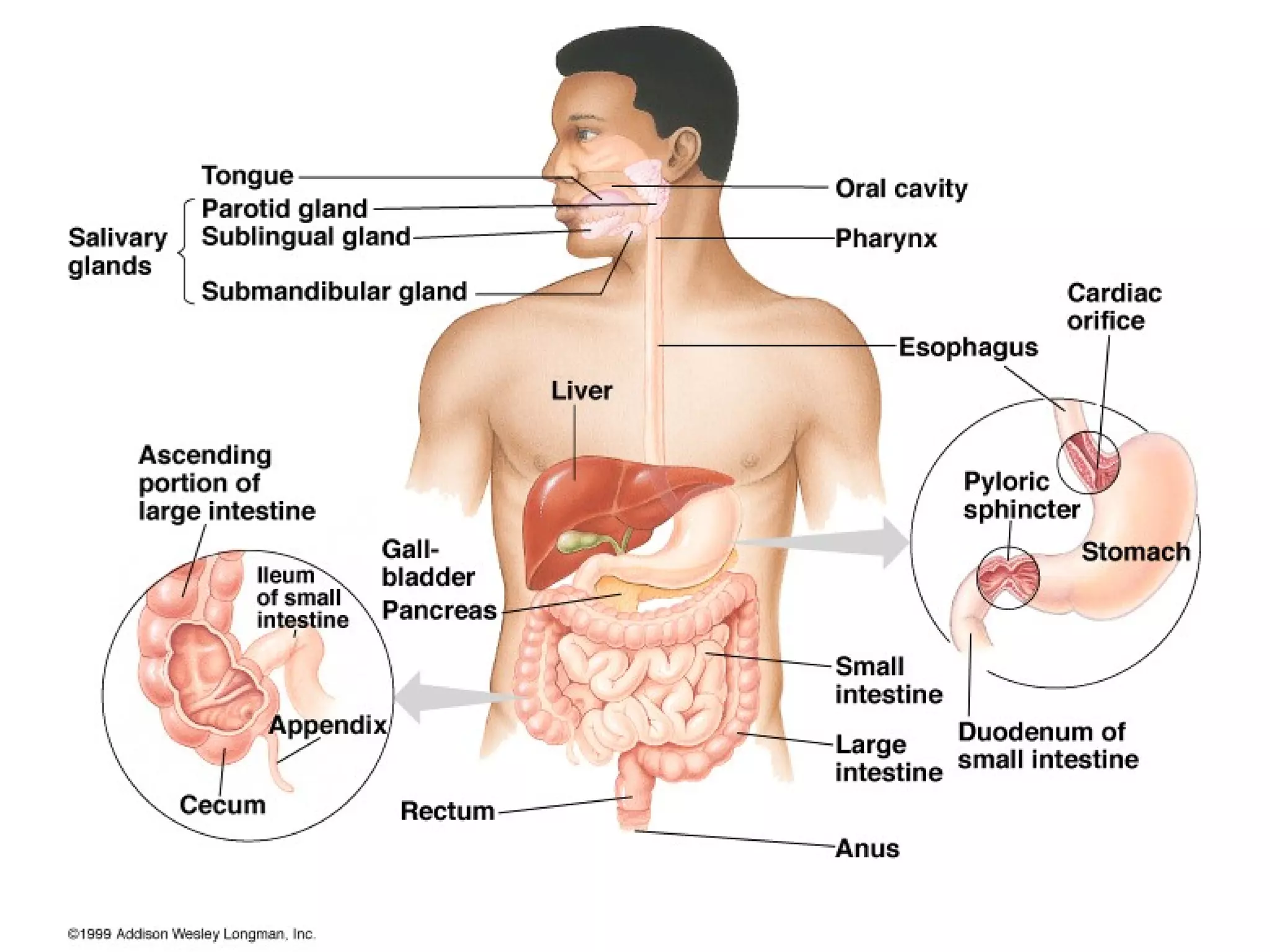
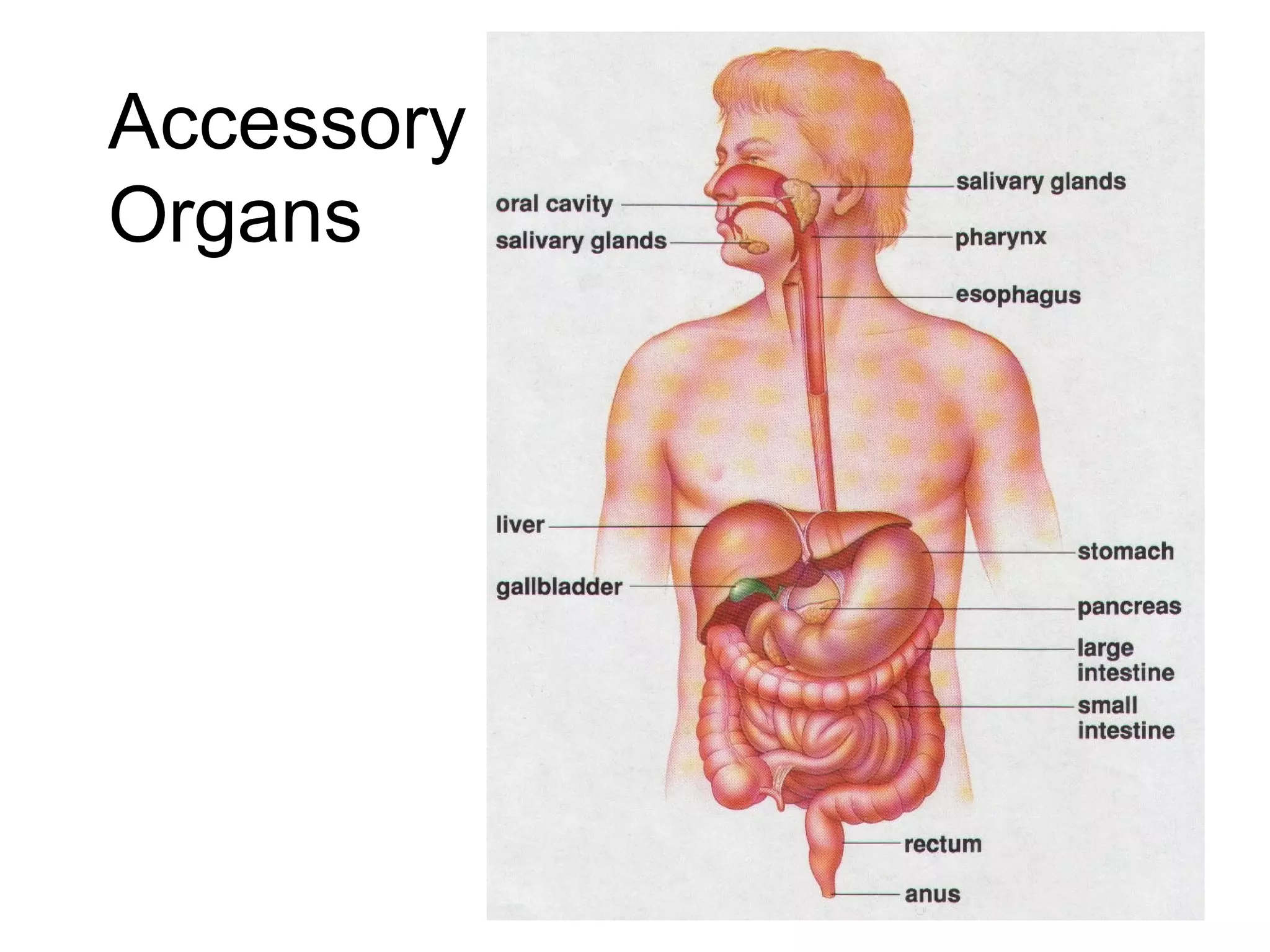
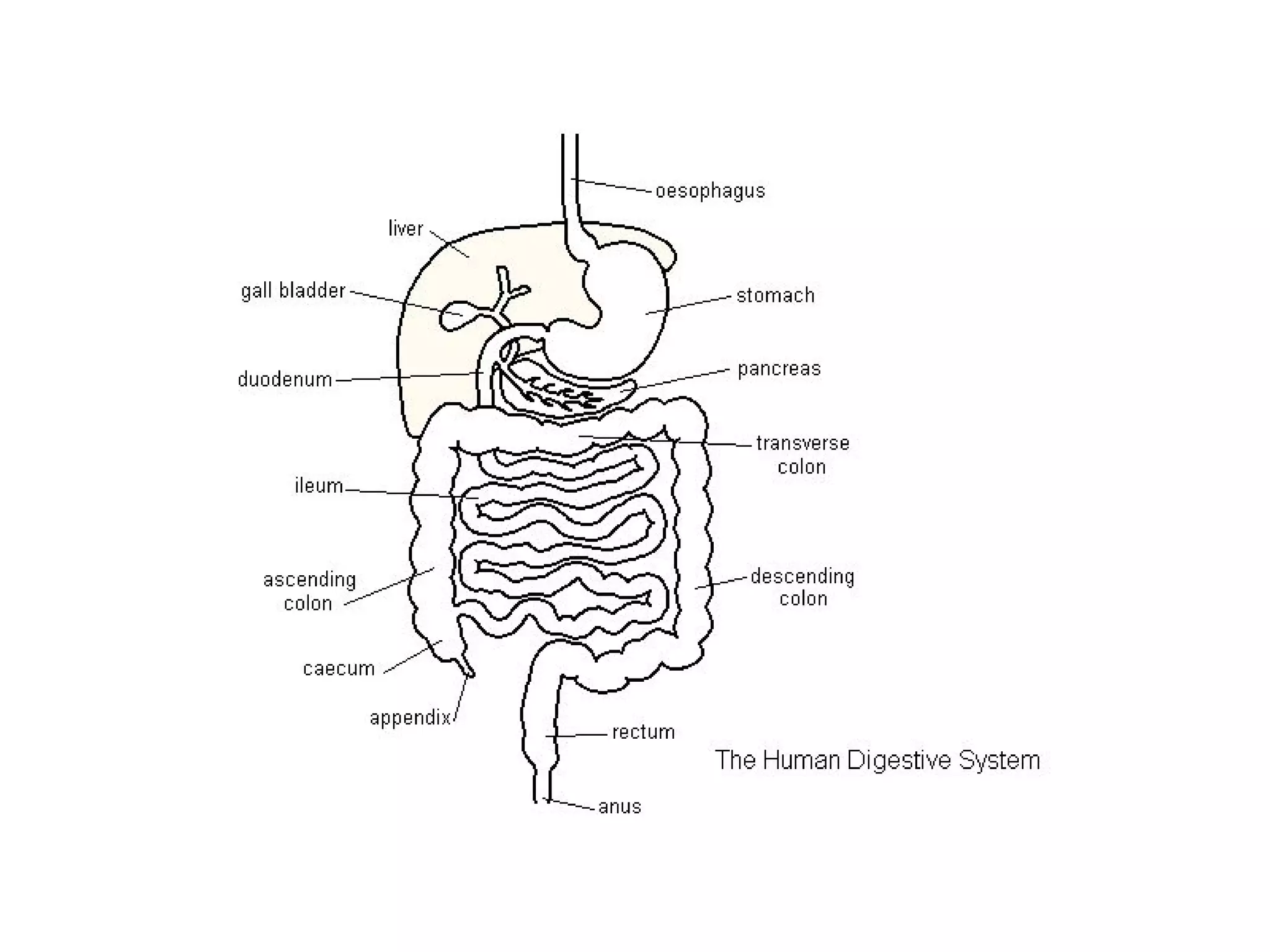
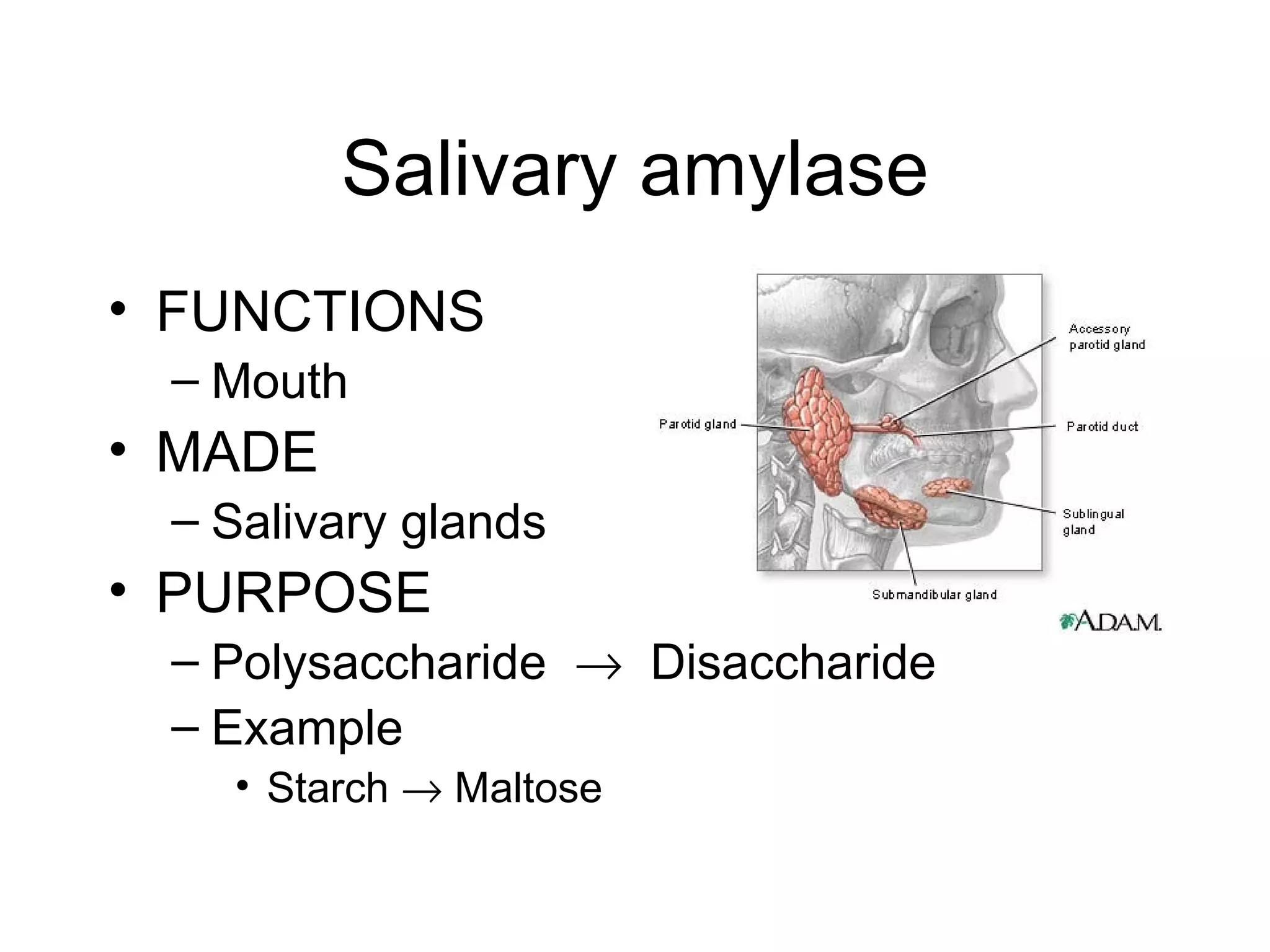
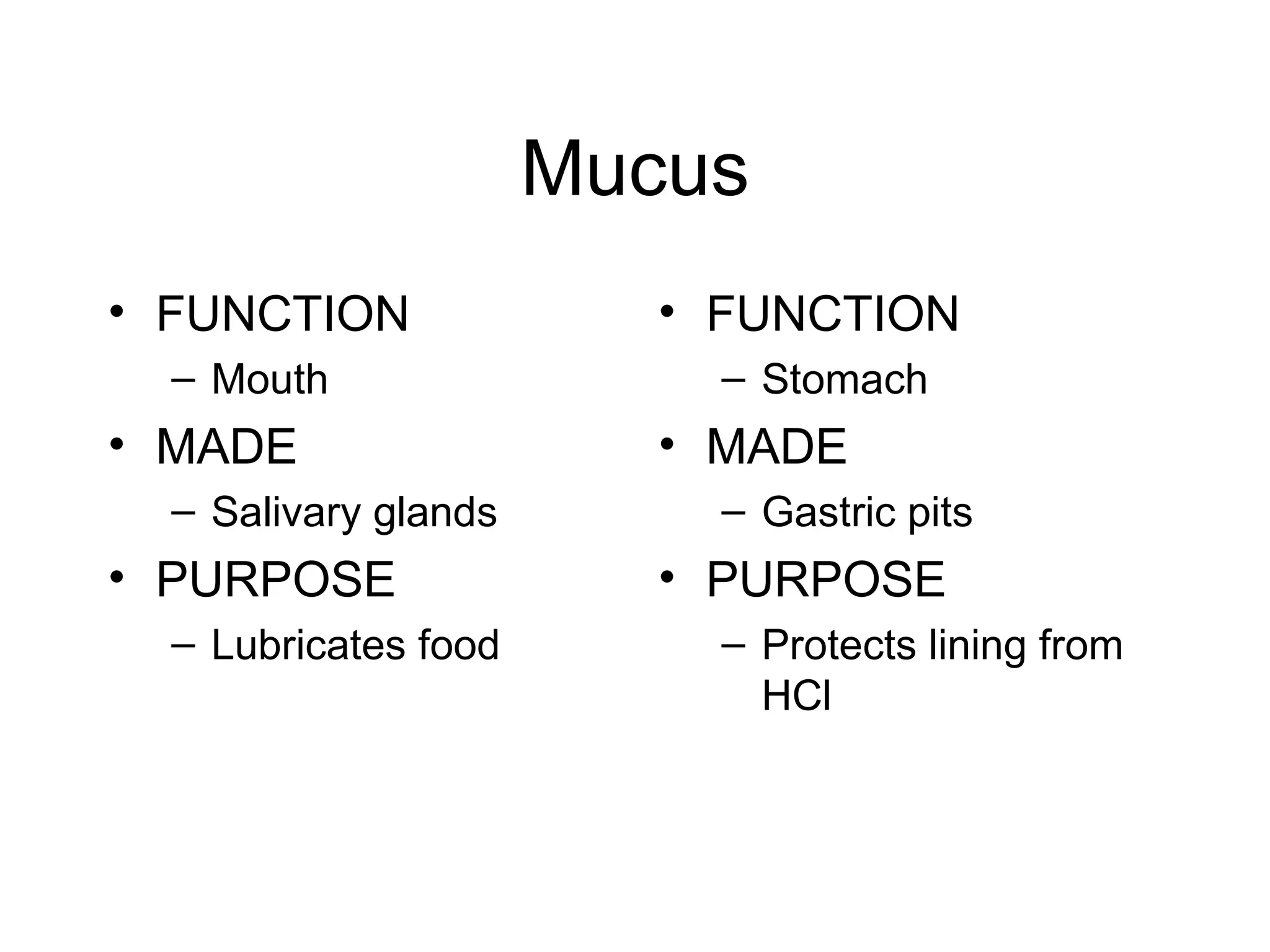
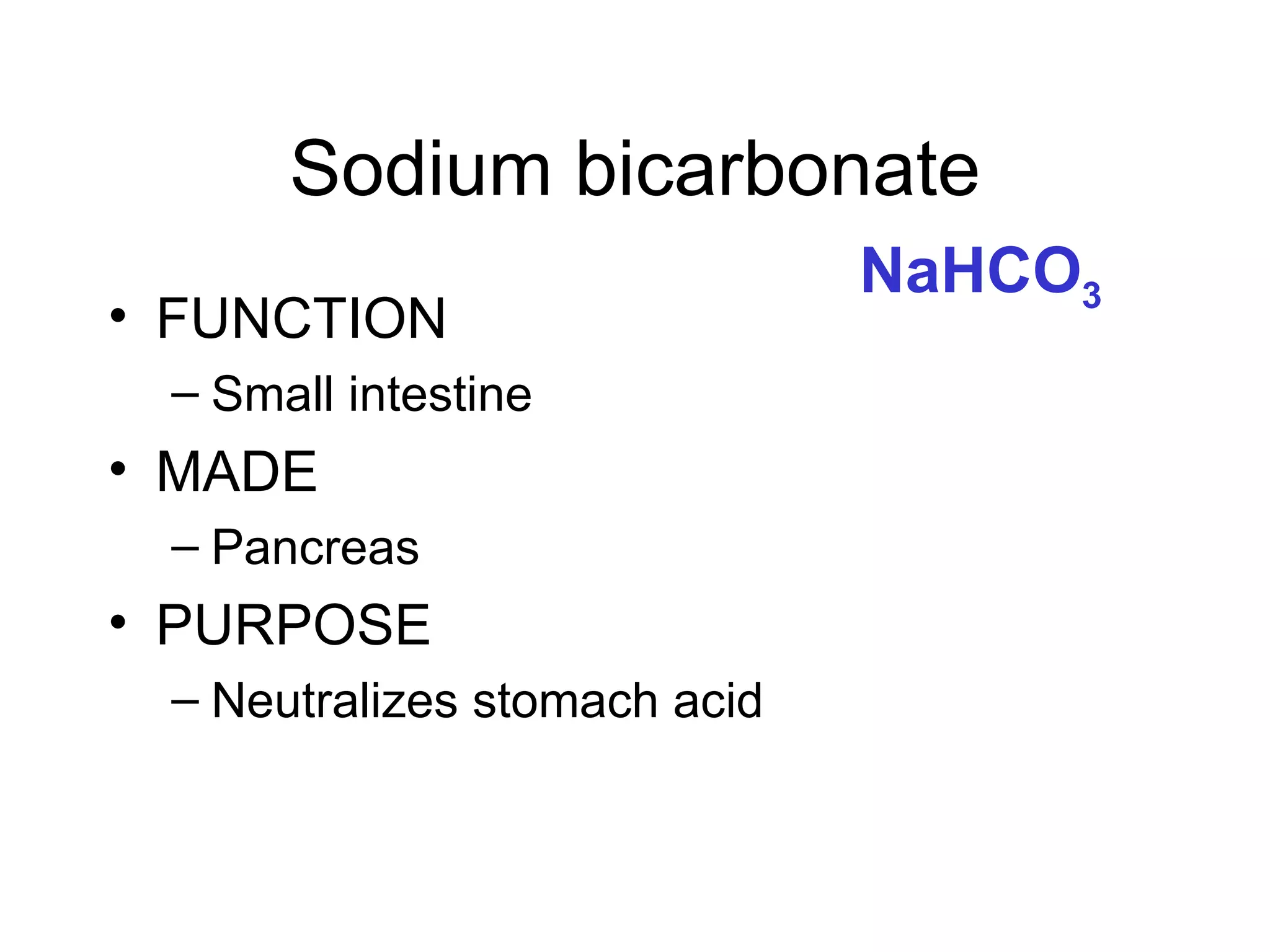
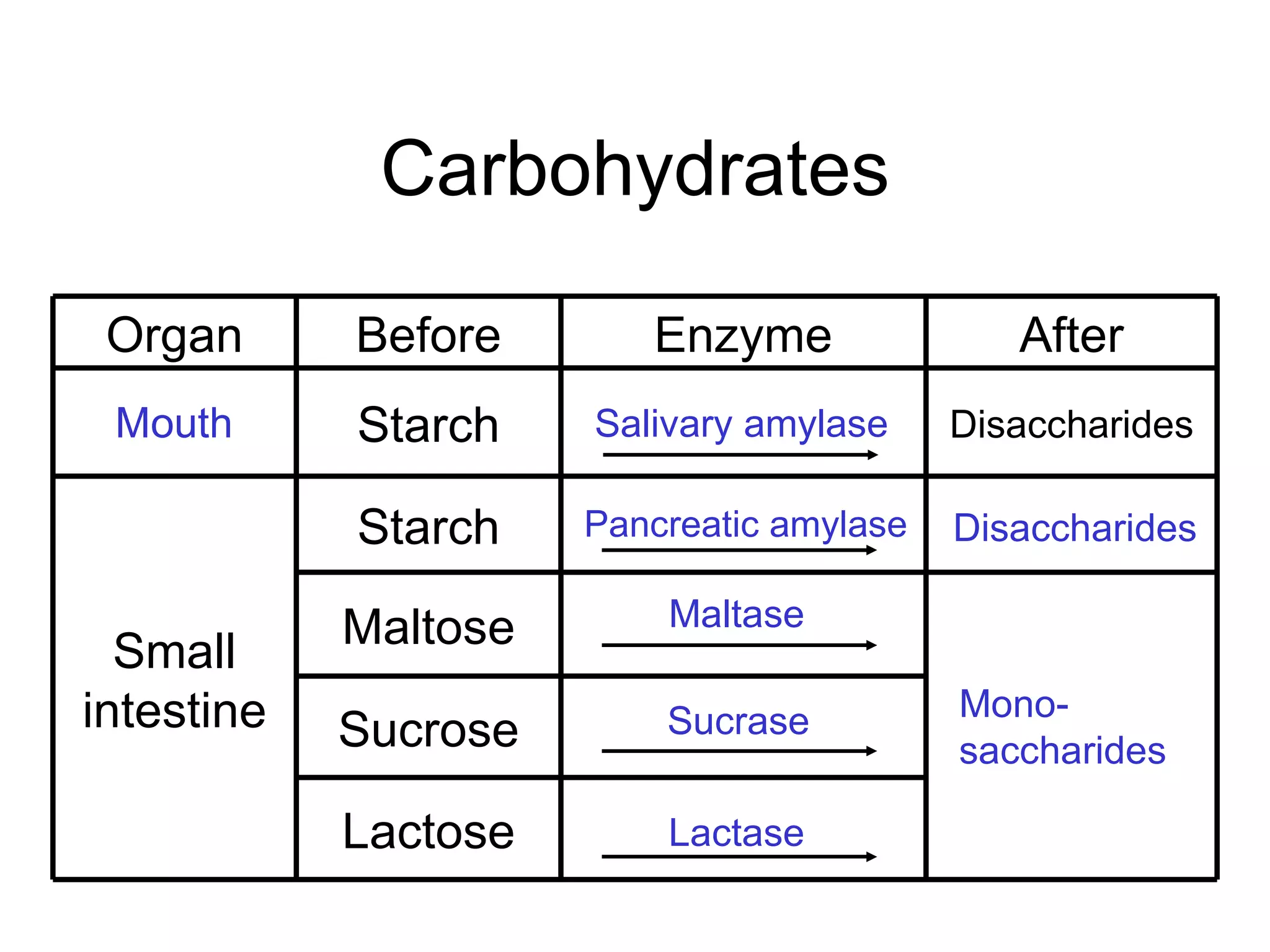
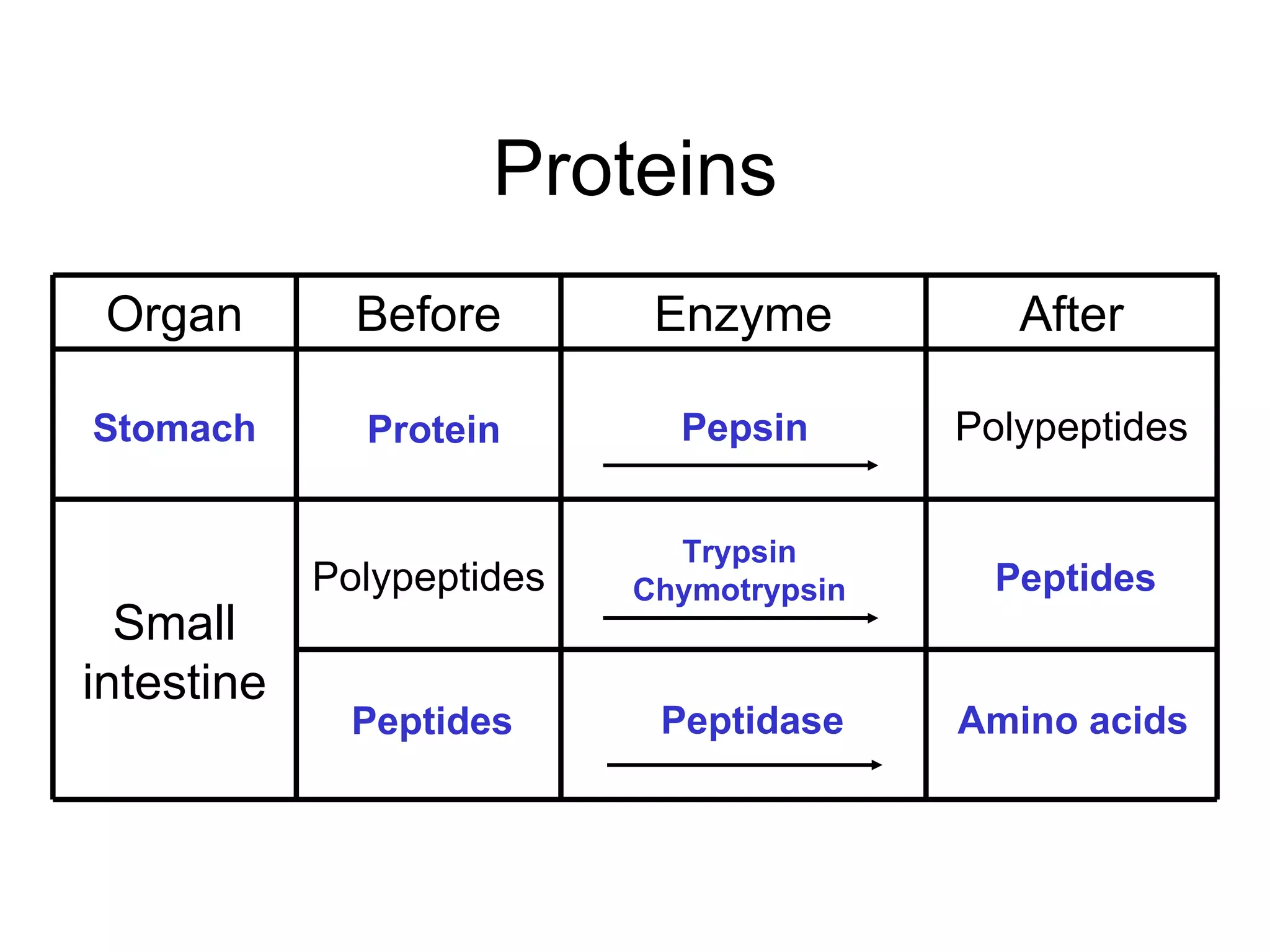
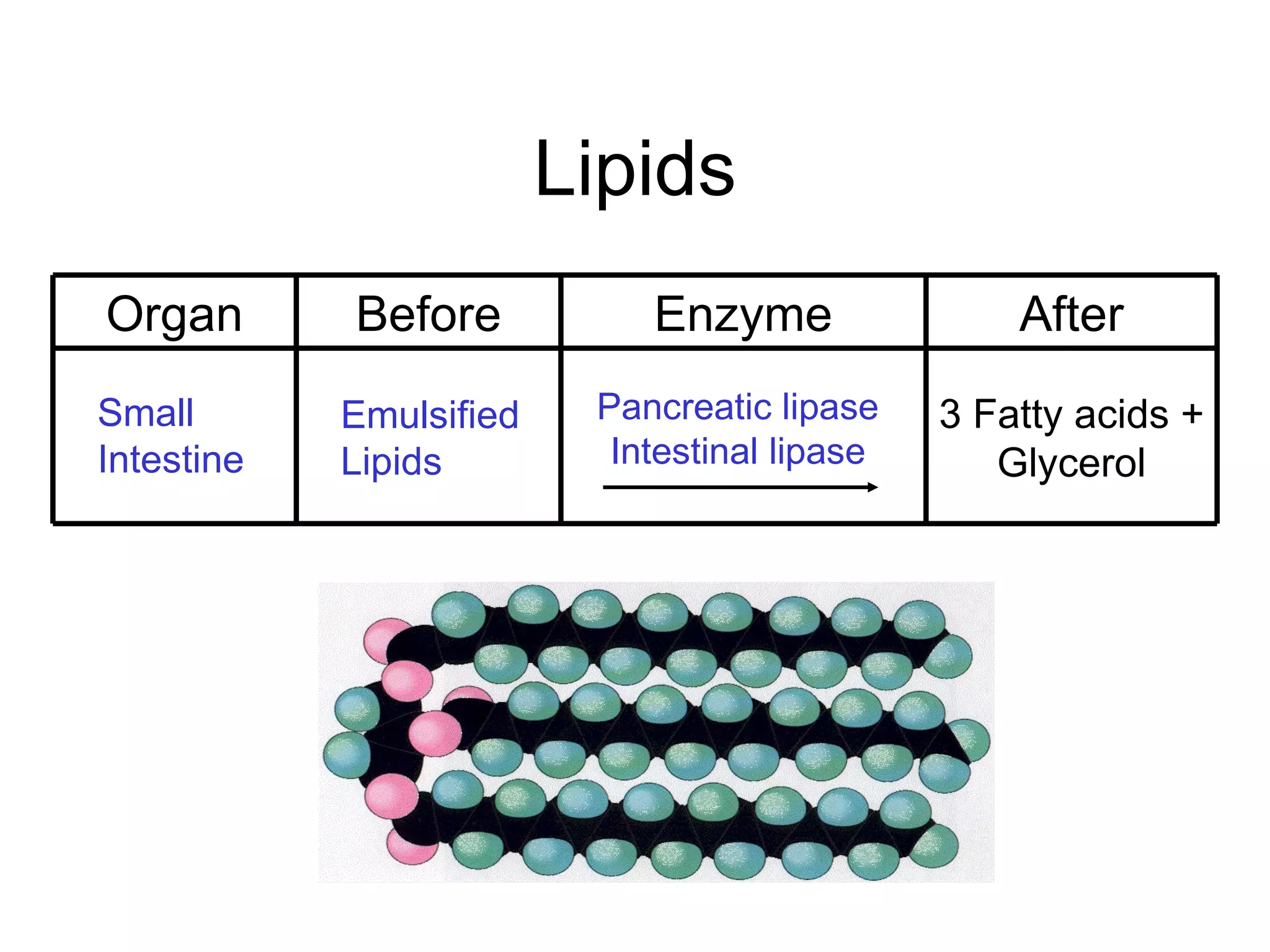
The document summarizes the key components and processes of the human digestive system. It describes how the digestive system breaks down the three main macromolecules (carbohydrates, proteins, lipids) through both physical and chemical digestion using mechanical and enzymatic actions. Various organs and glands secrete enzymes and acids that break down nutrients into smaller components as food moves through the alimentary canal, culminating in the absorption of nutrients and elimination of waste.