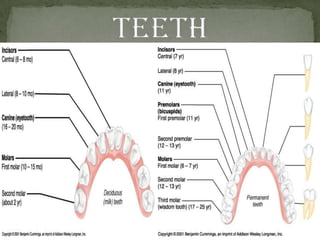
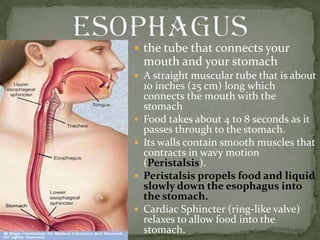
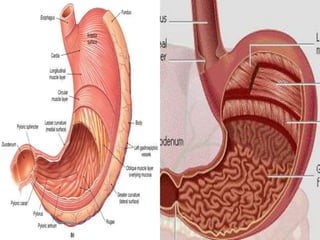
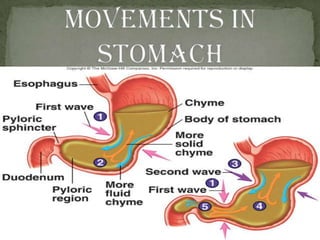
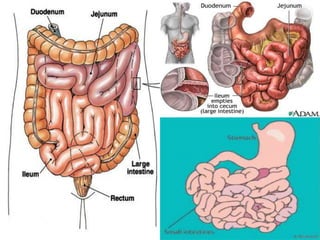
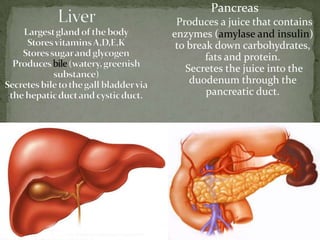
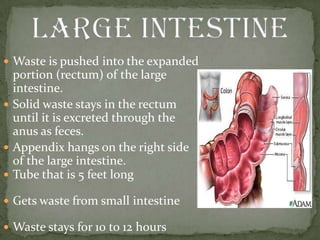
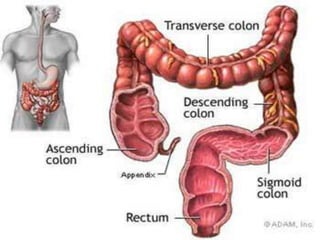
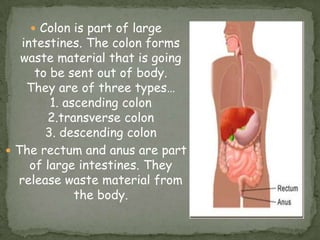
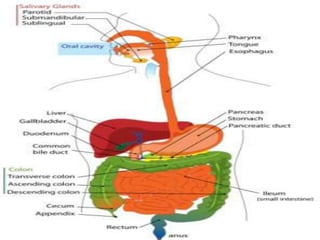
The document outlines the human digestive system, detailing the breakdown of complex biological molecules into simpler components through various organs. It describes the functions of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, pancreas, gall bladder, and large intestine in the digestion and absorption process. Additionally, it explains how enzymes and digestive juices contribute to converting food into usable nutrients and the elimination of waste.