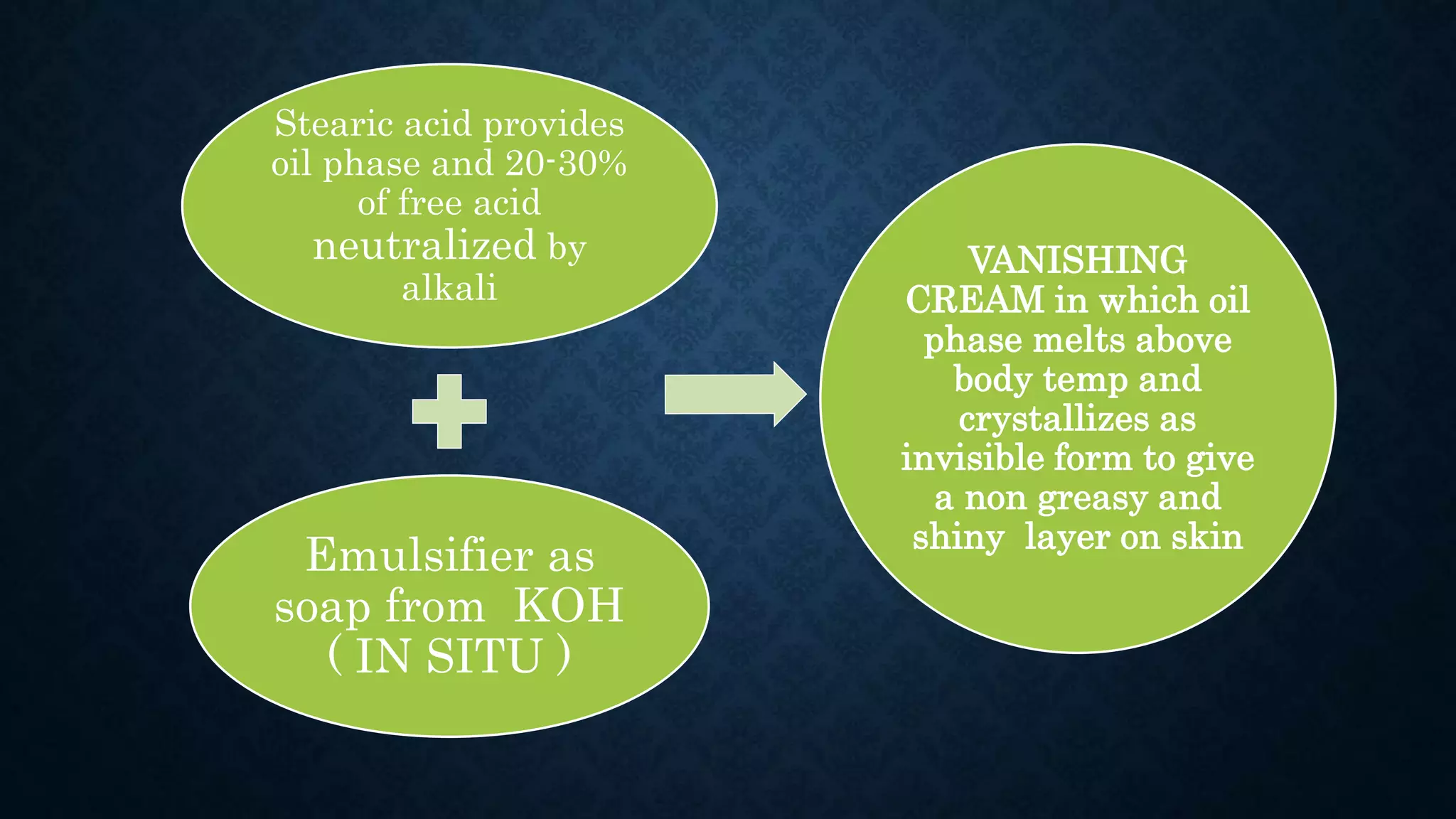
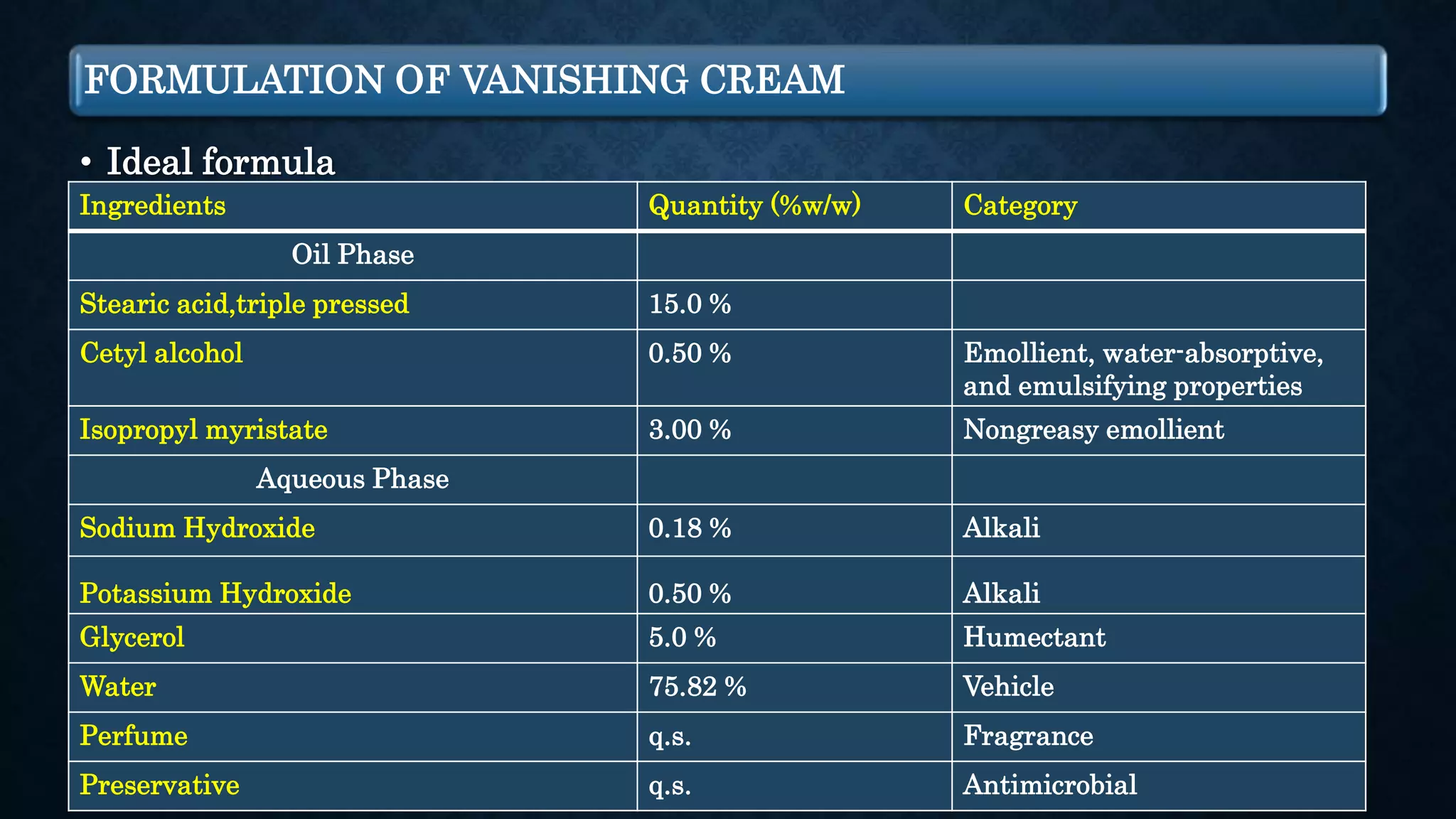
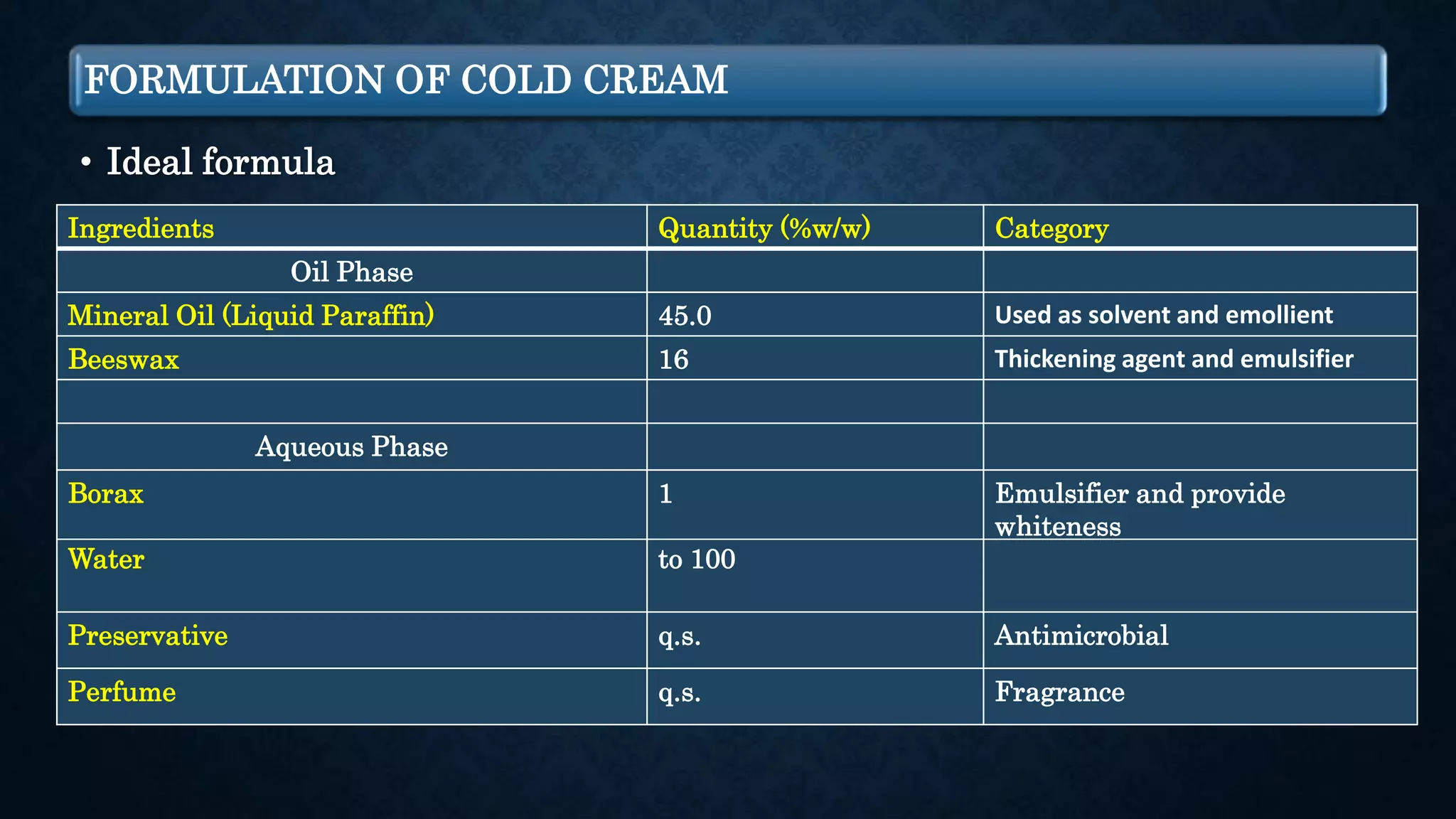
The document discusses two types of creams, cold cream and vanishing cream, detailing their definitions, formulations, and uses. Cold cream is an emulsion of water in oil (w/o) primarily used for moisturizing and cleansing, while vanishing cream is an oil in water emulsion (o/w) that leaves no residue on the skin. Each cream has specific ideal properties, key ingredients, and preparation methods to achieve desired effects and functions.