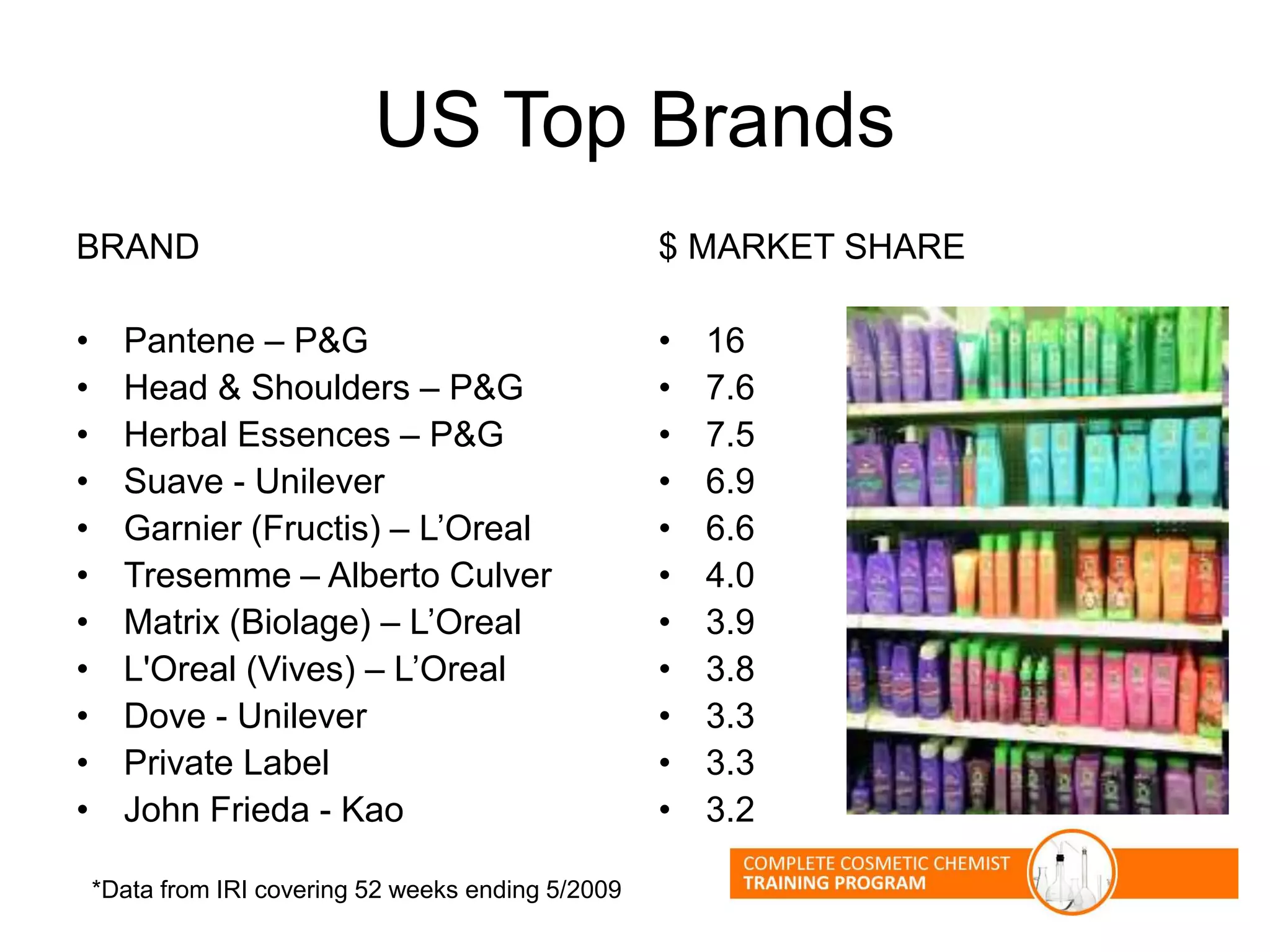
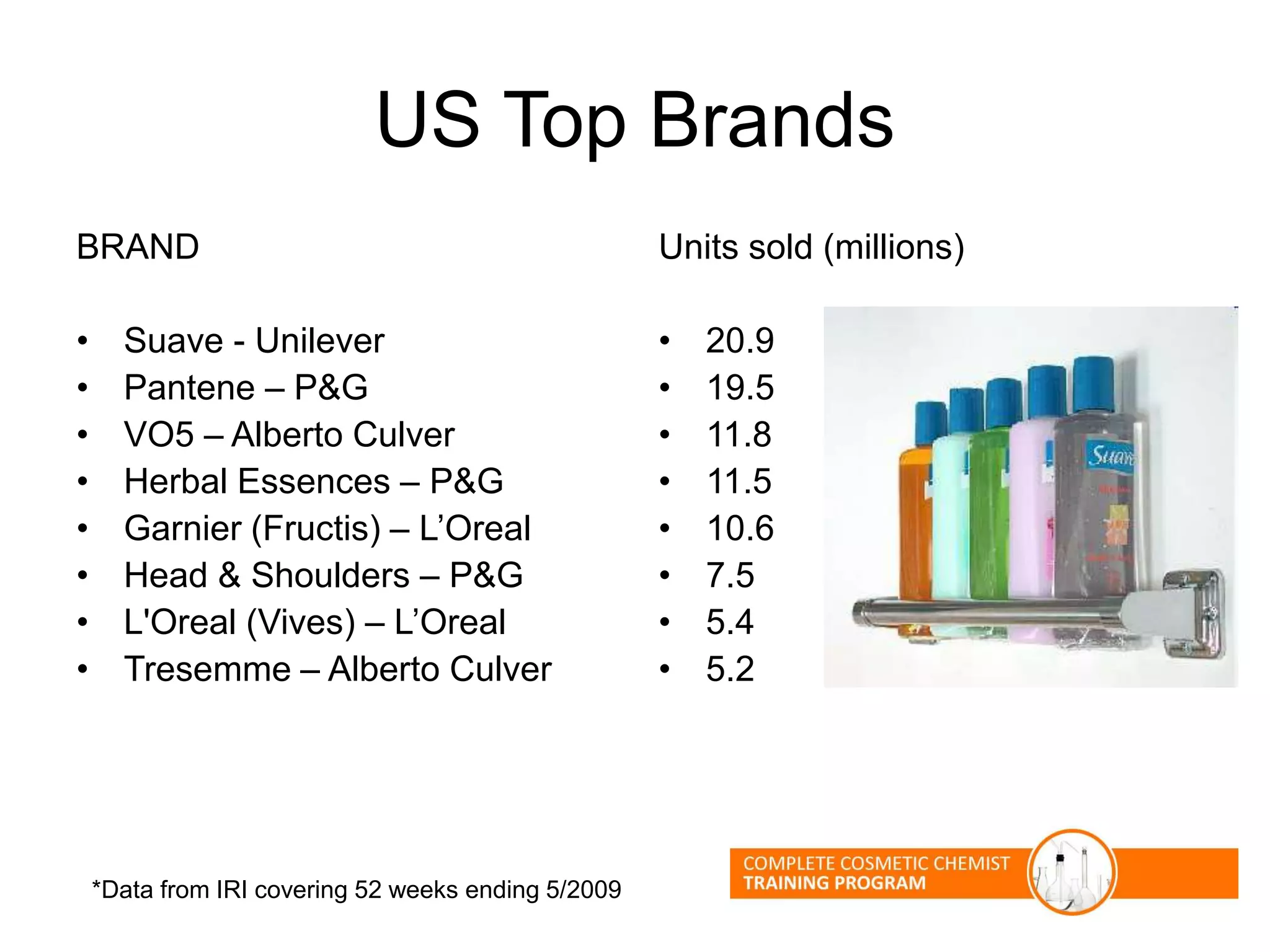
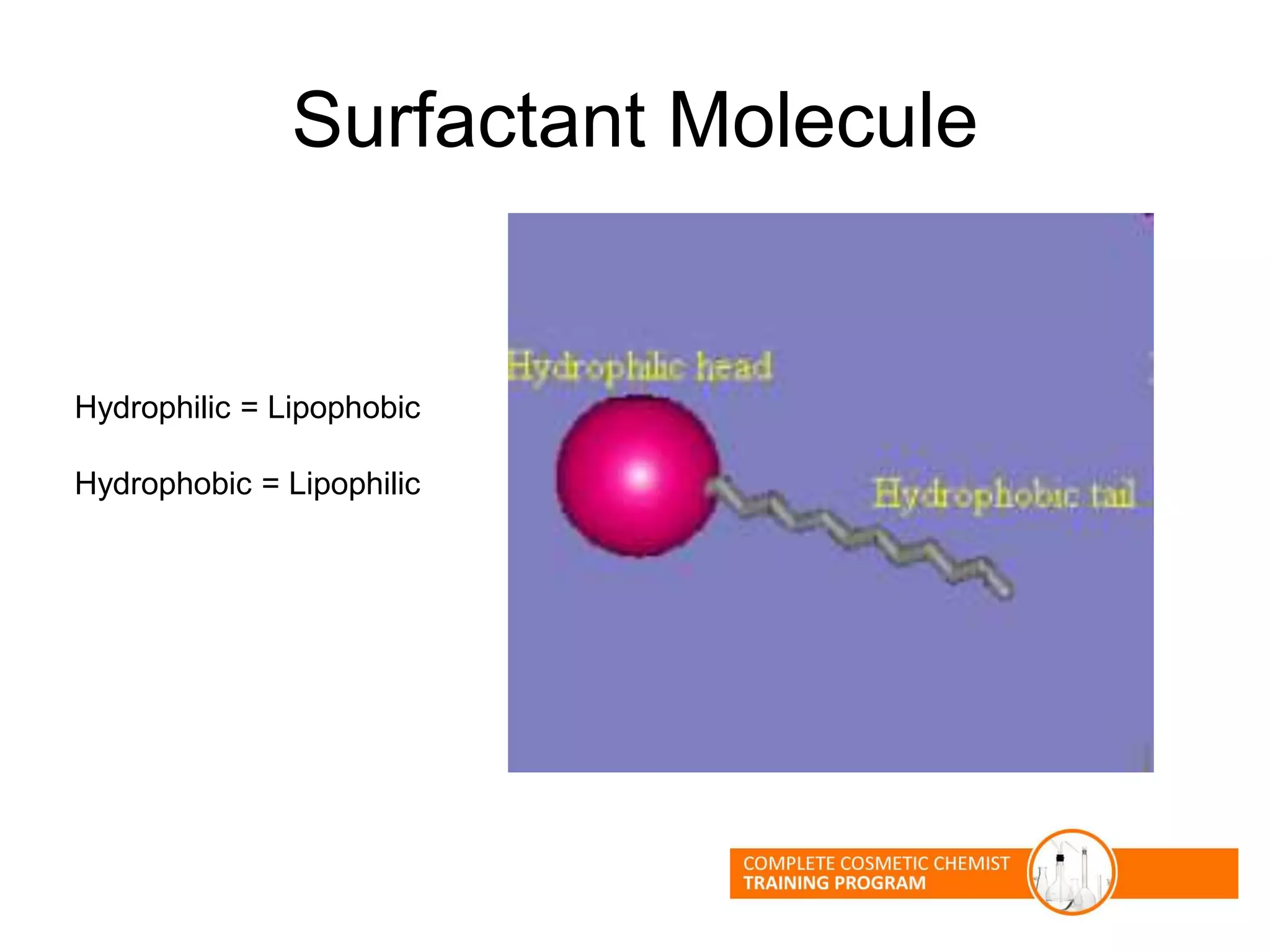
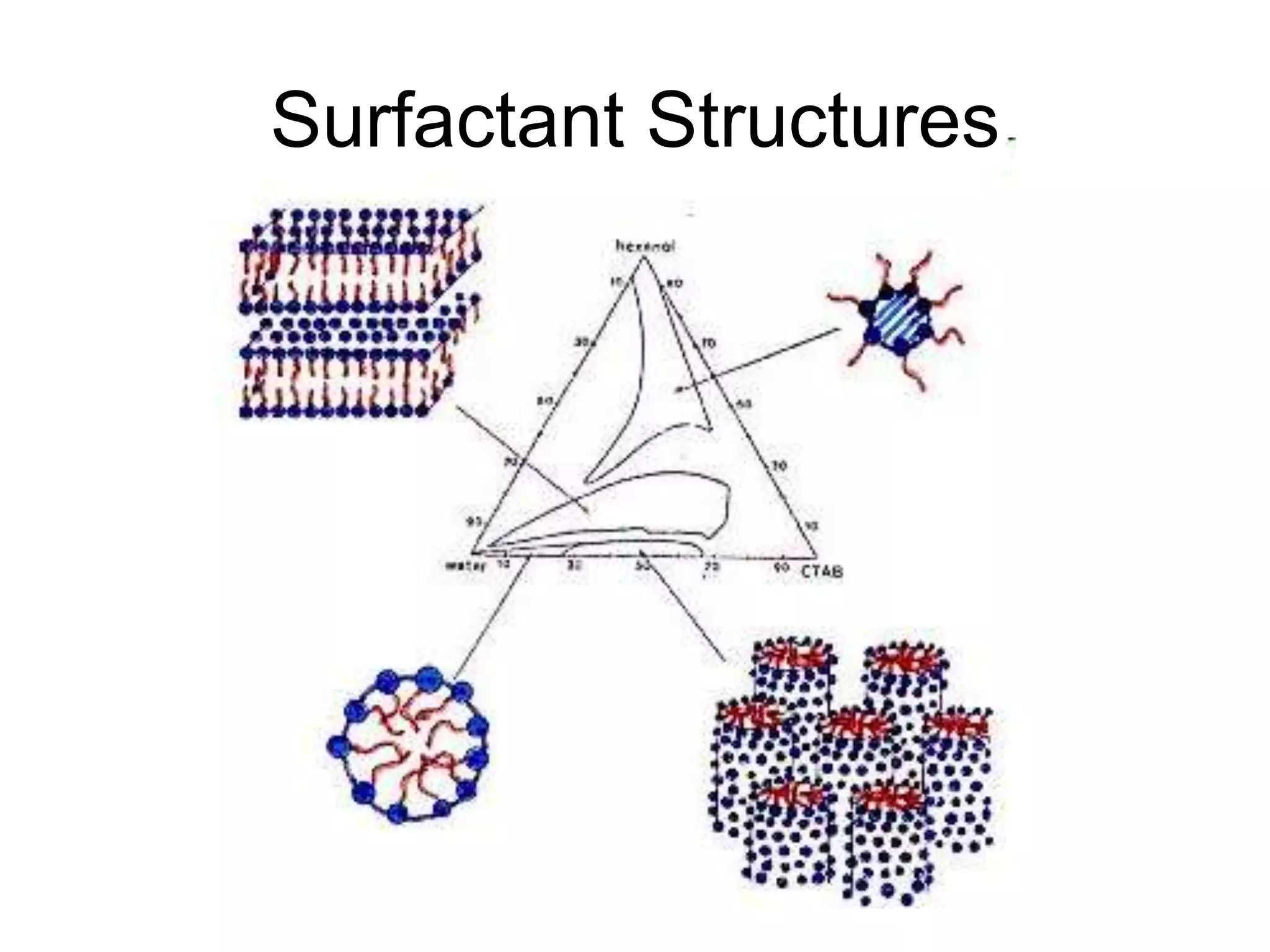
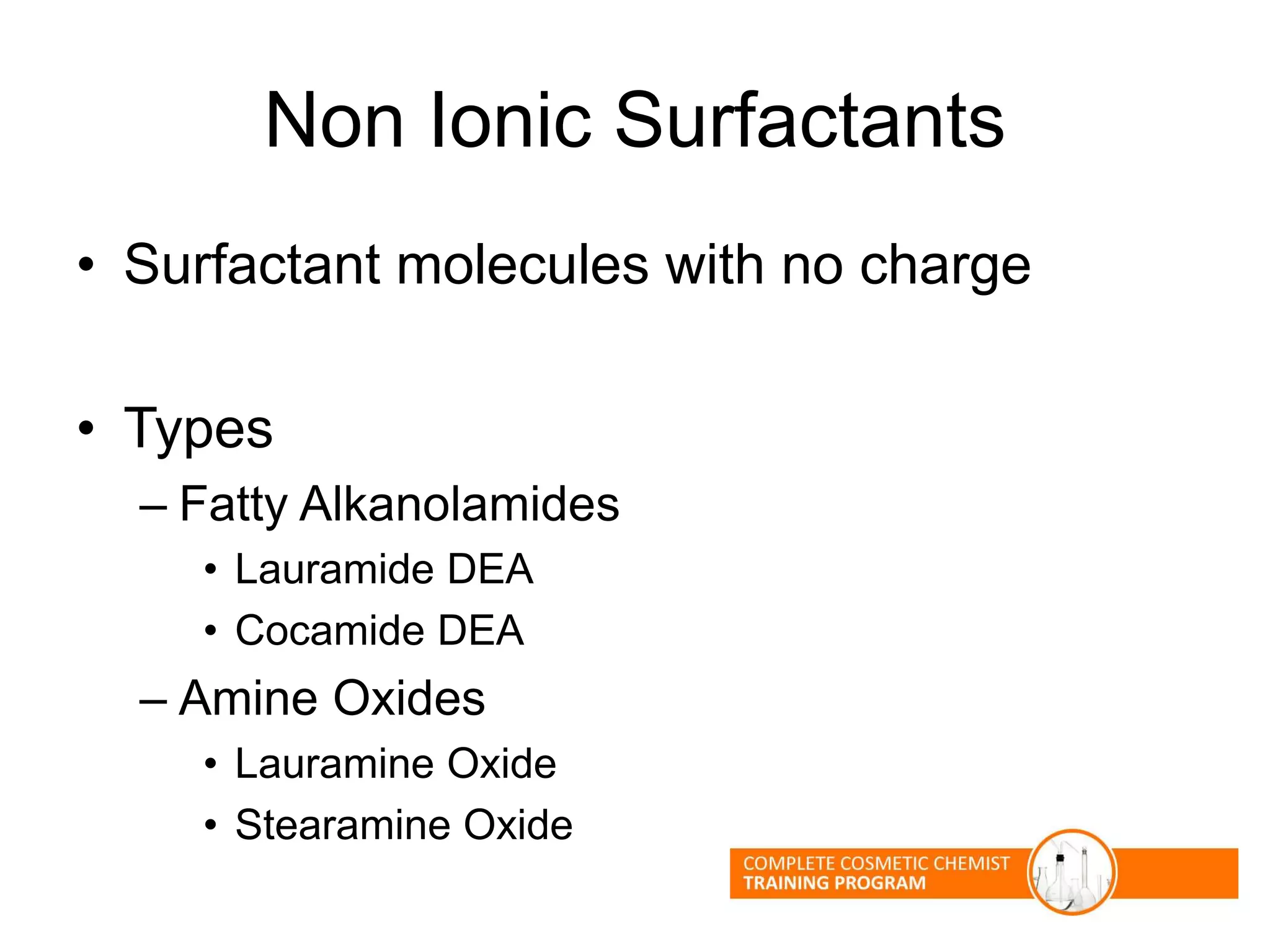
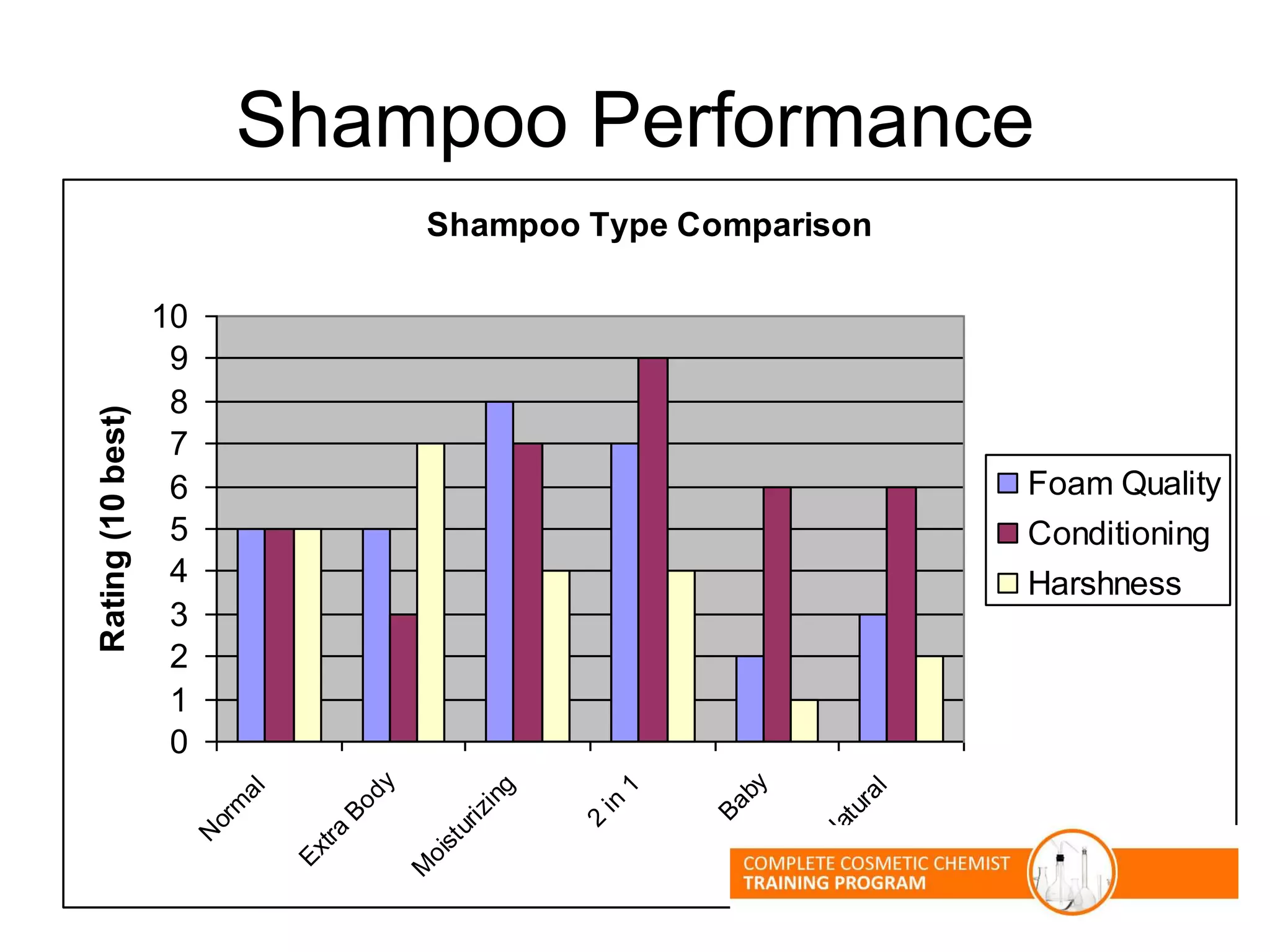
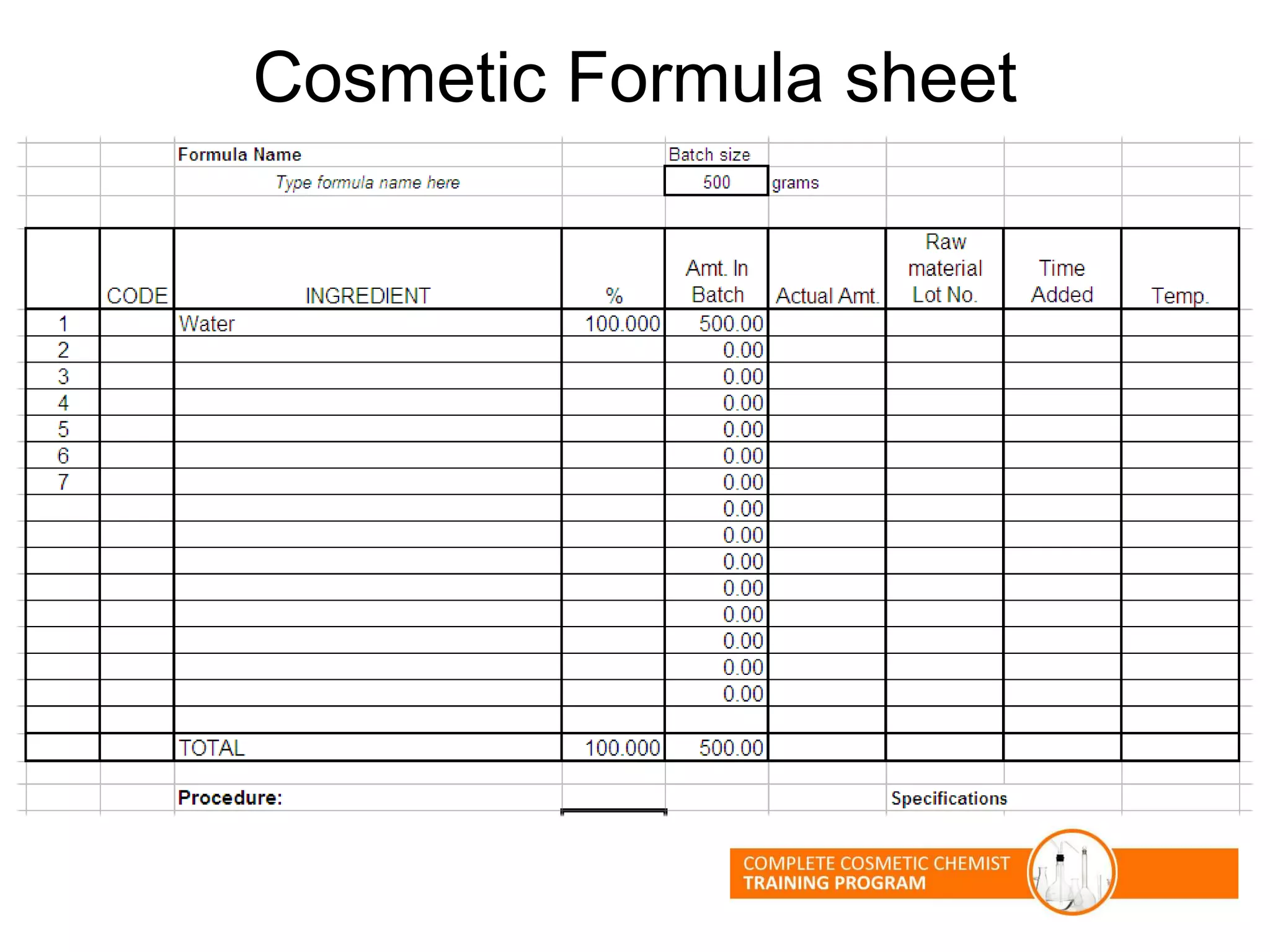
The document provides an overview of shampoo formulation and testing. It discusses the shampoo market size and top brands, consumer problems addressed by shampoos like cleansing and conditioning, and the role of surfactant science in making oils and water compatible for cleaning hair. Key sections cover formulating the 6 main types of shampoos and testing shampoos through use tests, lab tests, and quality control measures to ensure safety and performance.