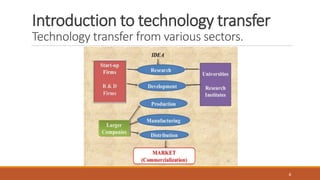
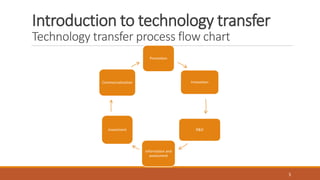
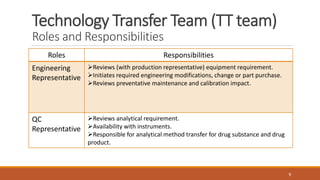
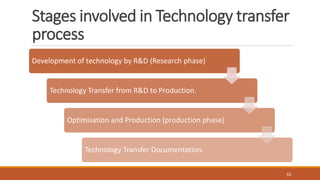
Technology transfer involves the systematic transfer of a technology from research and development to production. It requires a technology transfer team consisting of representatives from R&D, quality assurance, production, engineering and quality control. The technology transfer process involves multiple stages, beginning with development of the technology in R&D. R&D then provides a technology transfer dossier to production with documentation including the master formula, manufacturing instructions, specifications and analytical methods. Successful technology transfer depends on open communication between both the sending and receiving units.