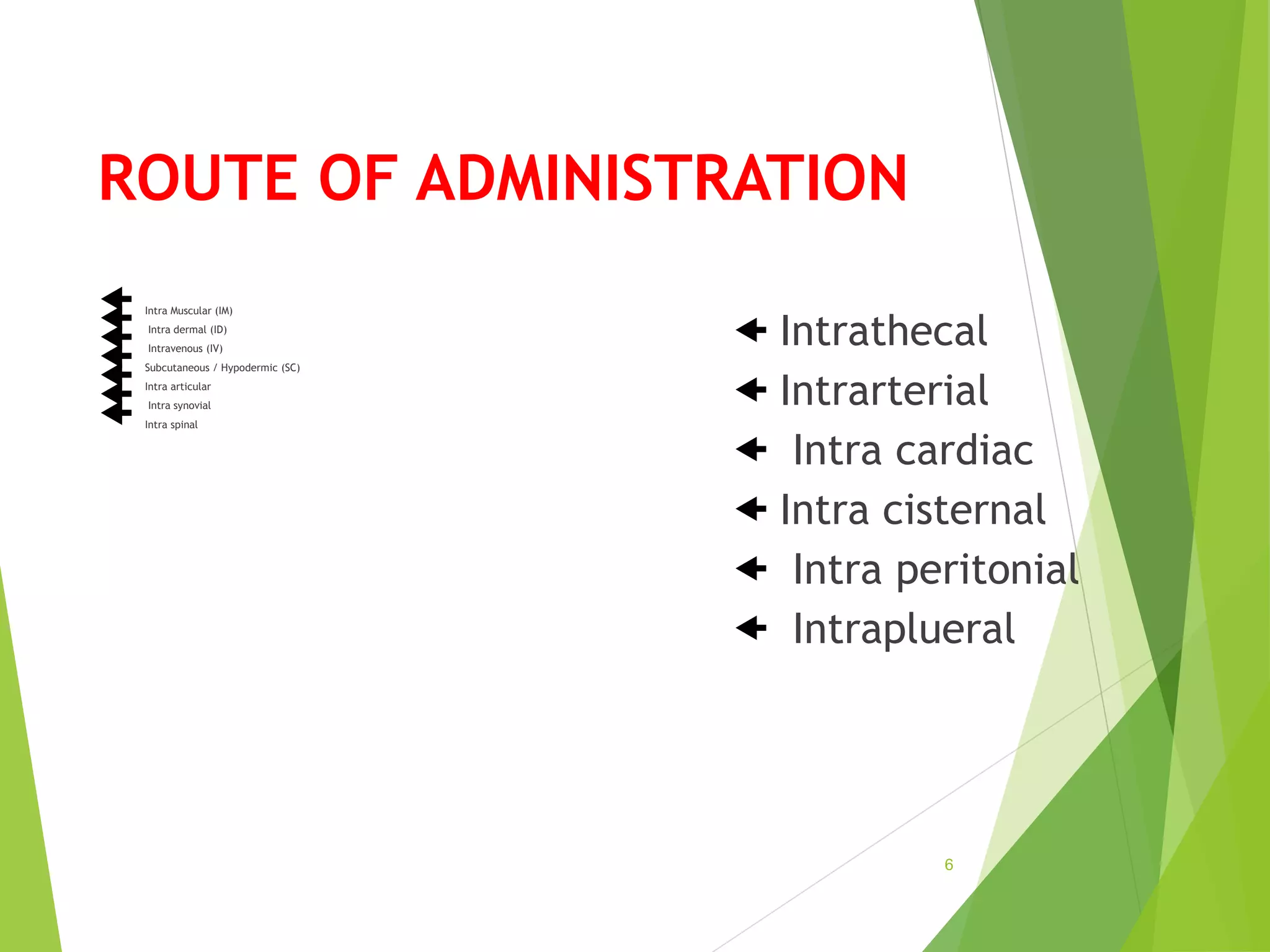
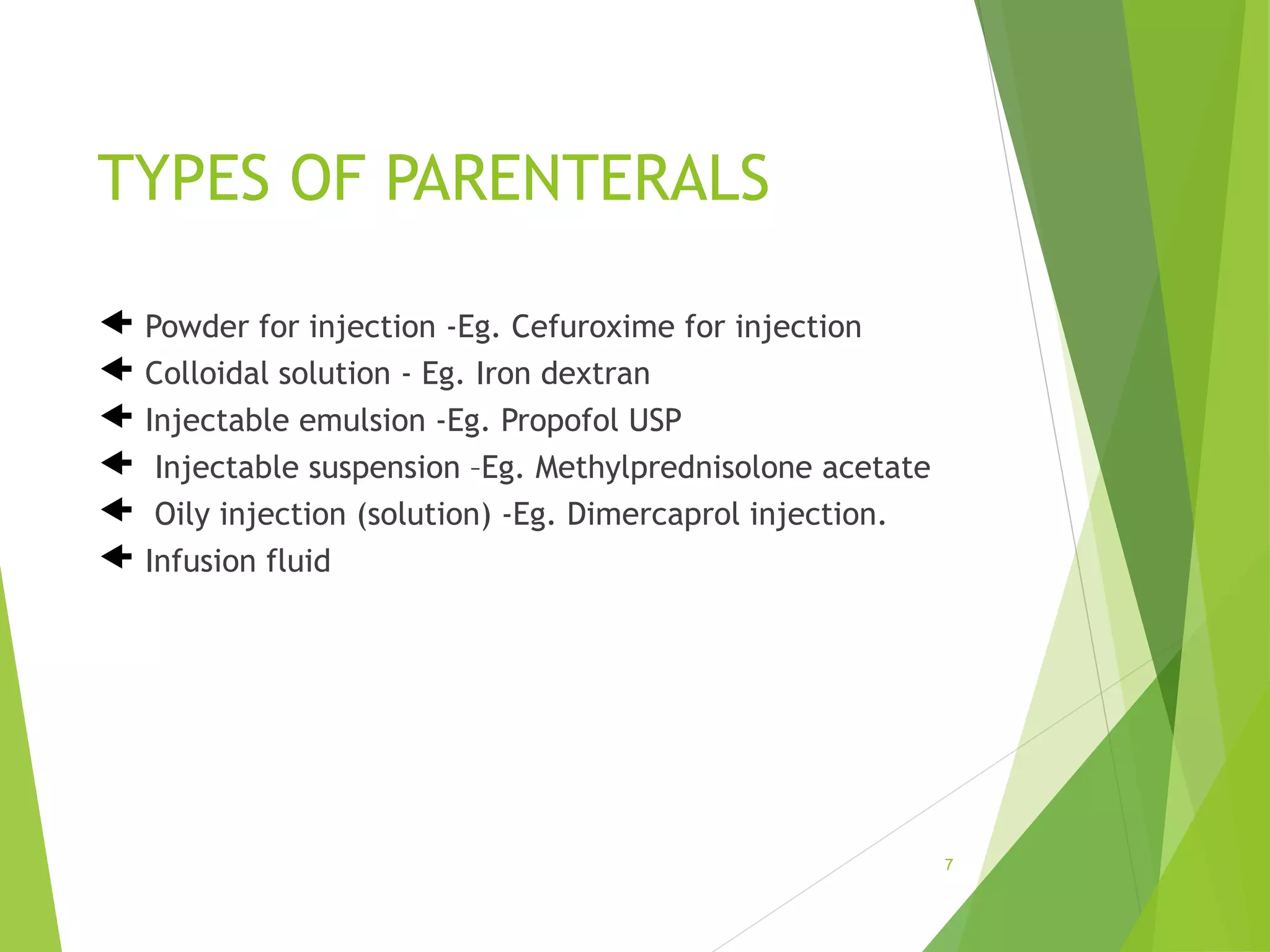
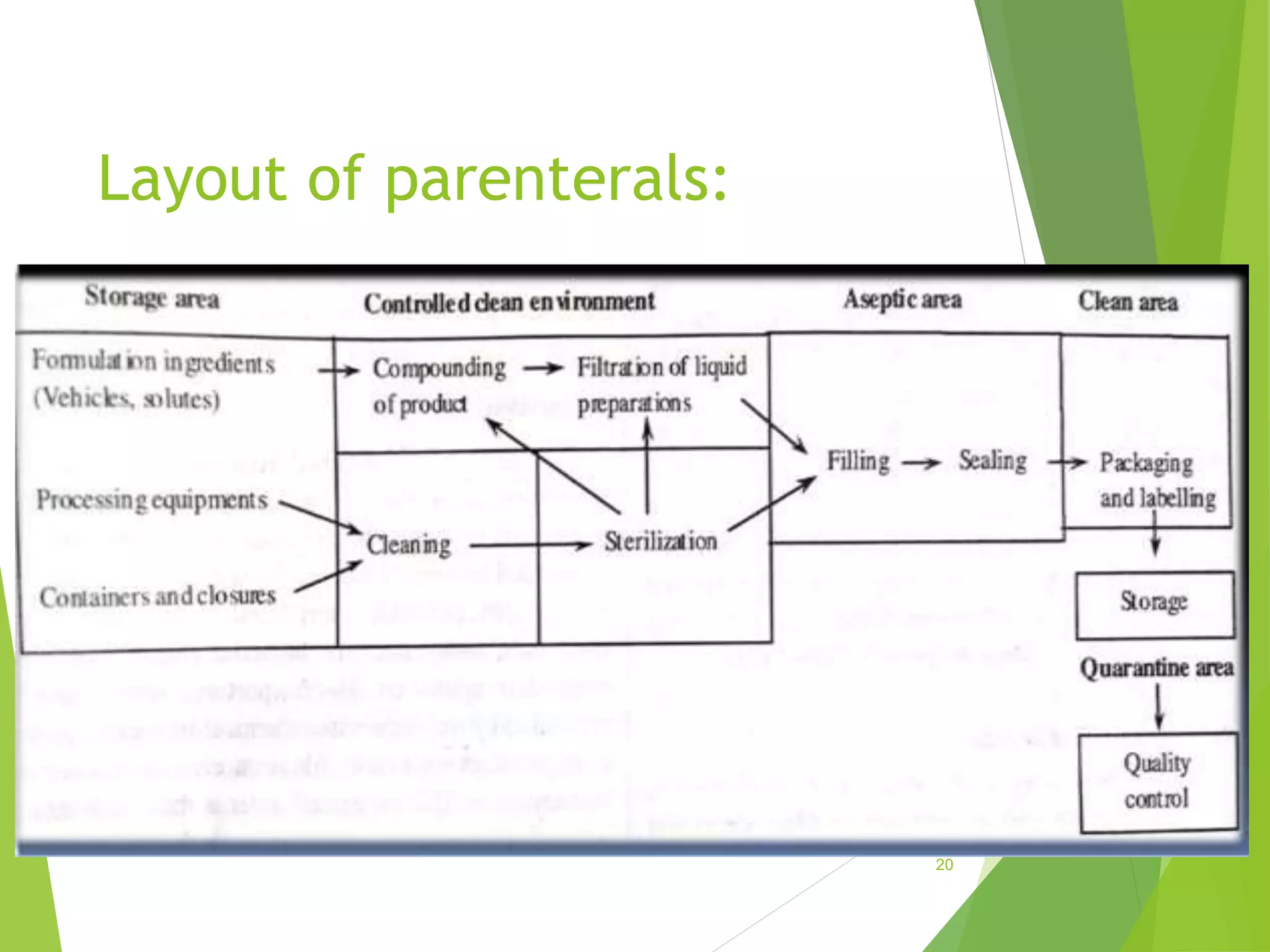
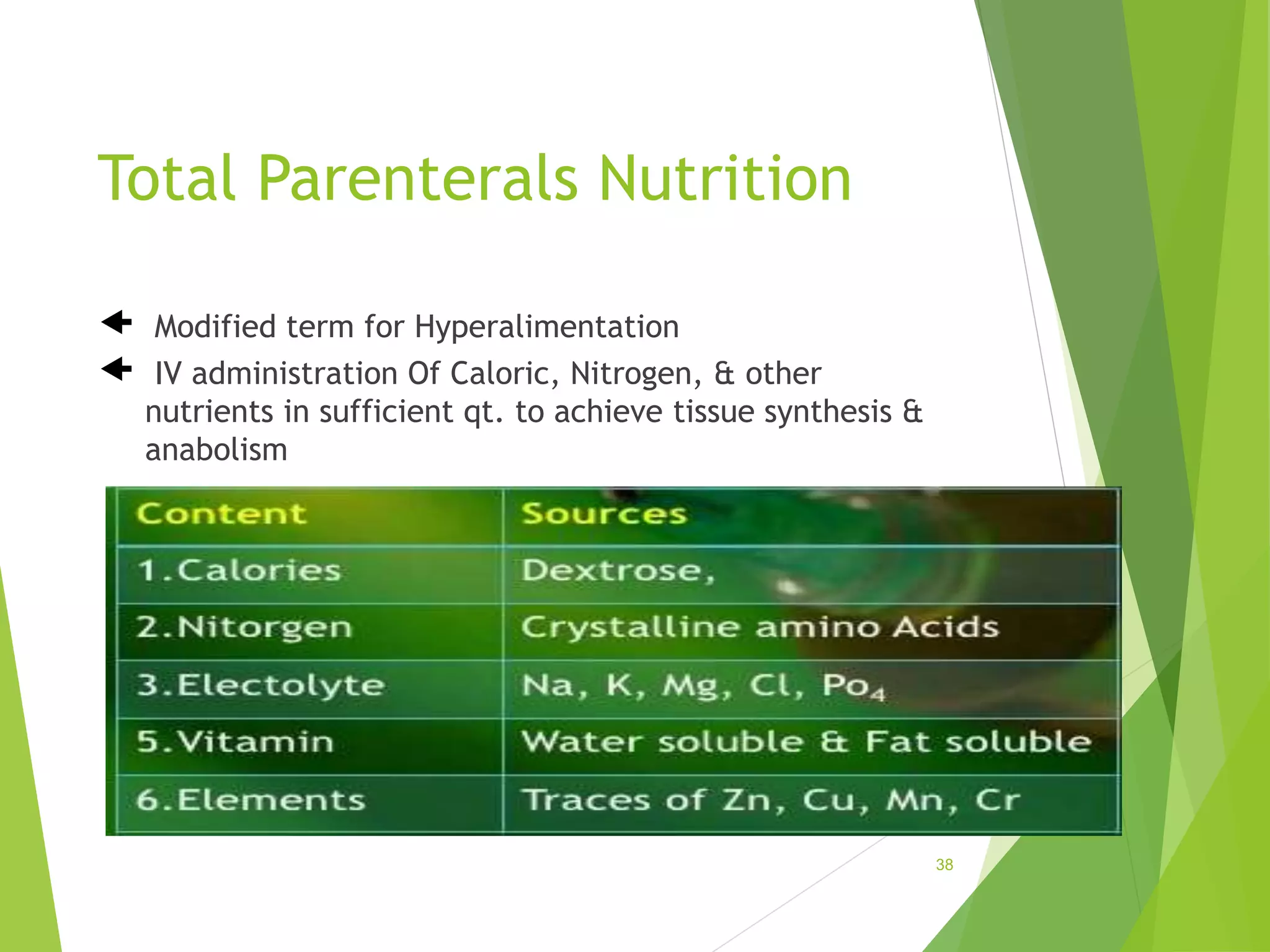
The document discusses parenterals, which are sterile preparations intended for administration through layers of skin or mucous membranes. It defines parenterals and outlines their advantages like 100% bioavailability and ability to administer to unconscious patients. The document also discusses the various routes of parenteral administration, types of parenterals like powders, solutions, and emulsions. It describes the formulation, layout, and quality control testing of parenterals. Specifically, it provides details on the areas involved in parenteral production, types of small and large volume parenterals, and common quality tests like leaker, clarity, pyrogenic, sterility, and content uniformity testing.