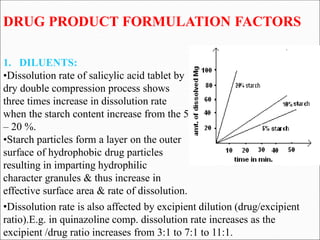
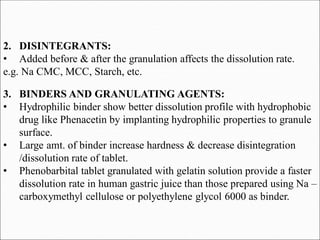
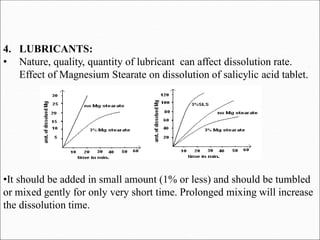
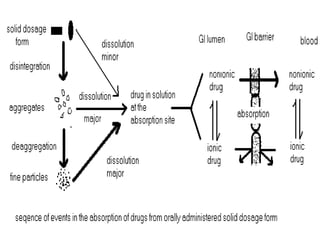
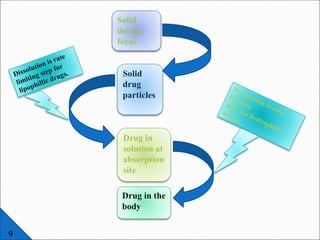
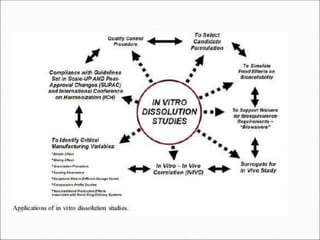
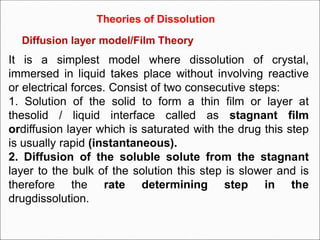
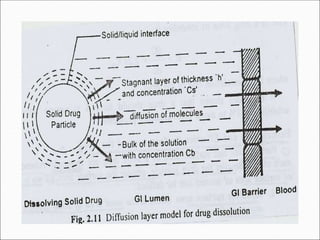
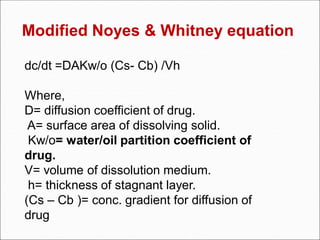
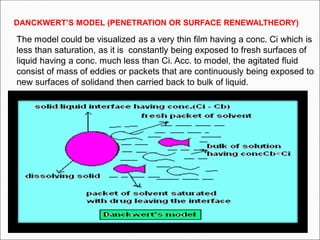
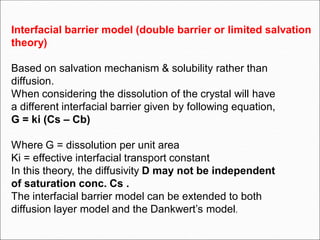
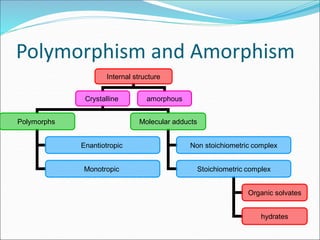
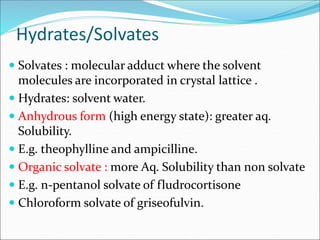
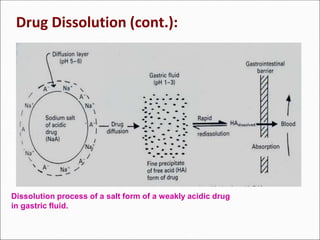
The document discusses dissolution, which is the process by which a solid substance enters the solvent phase to form a solution. Dissolution is important for drug absorption from oral dosage forms and can be the rate-limiting step. Dissolution testing is used for quality control, formulation development, and correlating in vitro dissolution to in vivo bioavailability. Theories of dissolution include diffusion layer models and surface renewal models. Factors that affect dissolution include drug properties, dosage form factors, particle size, polymorphism, salt formation, and lipid solubility.












![ DRUG pKa AND GI pH:
Amount of drug that exists in un-ionized form and in ionized form is
a function of pKa of drug and pH of the fluid at the absorption site,
and it can be determined by Handerson-Hasselbach equation:
For weak acids,
pH = pKa + log [ionized]
[un-ionized]
% Drug ionized = 10pH-pKa x 100
1+10pH-pKa
For weak bases, pH = pKa + log [un-ionized]
[ionized]
% Drug ionized = 10pKa-pH x 100
1+10pKa-pH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissolutionbydr-190210122031/85/Dissolution-by-Dr-Neeraj-Mishra-professor-pharmaceutics-25-320.jpg)
![Lipid solubility of drugs:
- Some drugs are poorly absorbed after oral administration
even though they are non-ionized in small intestine. Low
lipid solubility of them may be the reason.
- The best parameter to correlate between water and lipid
solubility is partition coefficient.
Partition coefficient (p) = [ L] conc / [W] conc
where, [ L] conc is the concentration of the drug in lipid
phase.
[W] conc is the concentration of the drug in aqueous phase.
- The higher p value, the more absorption is observed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissolutionbydr-190210122031/85/Dissolution-by-Dr-Neeraj-Mishra-professor-pharmaceutics-26-320.jpg)