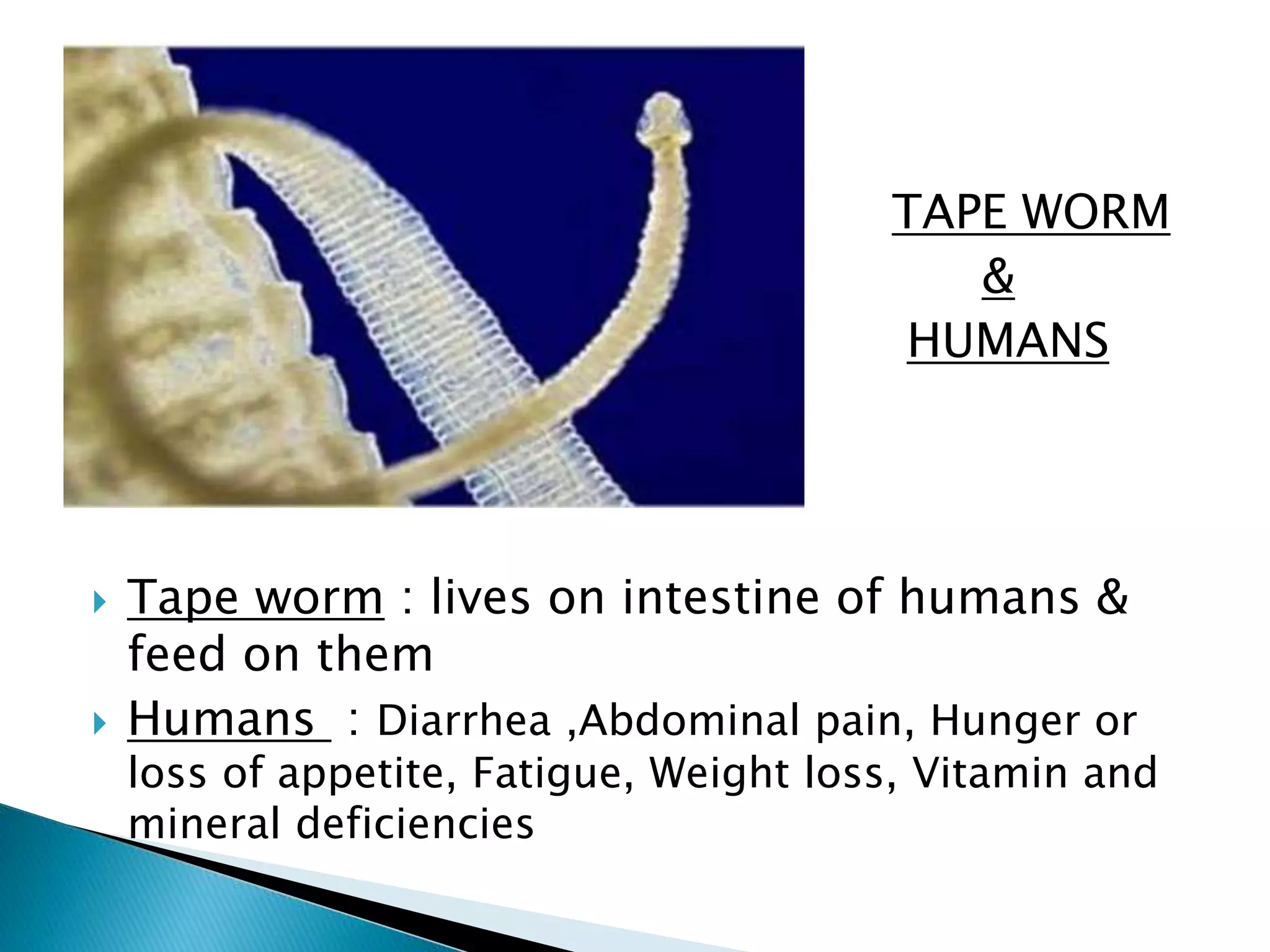
This document discusses the different types of relationships found among organisms. There are two main types of interactions - positive interactions which benefit one or both organisms, and negative interactions which harm one or both organisms. Positive interactions include mutualism, where both organisms benefit each other, and commensalism where one benefits while the other is not harmed. Negative interactions include predation, where one organism is harmed as the other's prey, parasitism where one benefits while harming its host, and competition for resources which can harm individuals. These relationships are an important part of ecosystems, with energy flowing through food chains and webs formed by animal interactions.