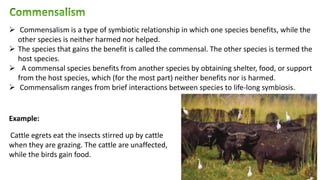
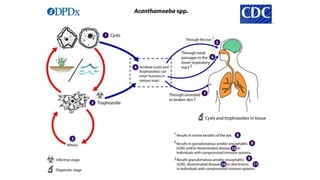
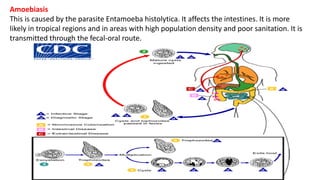
This document discusses various types of biological interactions between organisms including competition, mutualism, commensalism, amensalism, parasitism, and predation. Competition occurs when organisms attempt to use the same limited resources, and can be intraspecific or interspecific. Mutualism benefits both species involved. Commensalism benefits one species without affecting the other. Parasitism benefits one species at the expense of the other. Predation involves a predator consuming another organism, the prey. Examples of each type of interaction are provided.