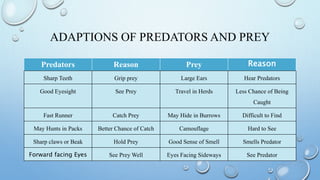
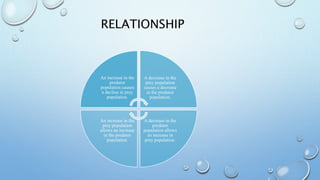
This document discusses predator-prey relationships through three examples. It defines predators as organisms that eat other organisms called prey. Lions hunt in prides and prey on antelopes, zebras and wildebeest. Tsavo lions stampede water buffalo into water to attack the young and weak. Scavengers like vultures, though not direct killers, still rely on the populations of animals lions prey upon. The relationship between predators and prey is interconnected, with increases or decreases in one affecting the other.