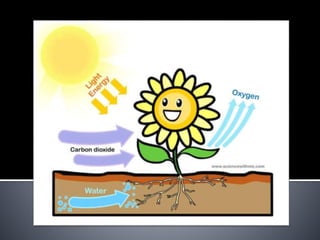
The document outlines the biotic components of an ecosystem, categorizing them as producers, consumers, and decomposers. Producers are autotrophic organisms like plants that use photosynthesis to produce food from inorganic substances. Consumers include heterotrophic organisms like animals that obtain energy and nutrients by consuming producers and other organisms. Consumers are divided into primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers based on trophic level. Decomposers such as fungi and bacteria break down dead organic matter from producers and consumers, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.