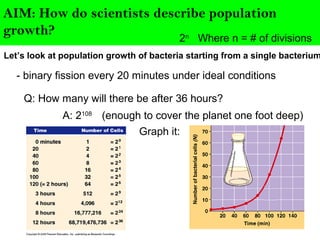
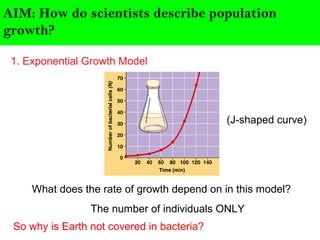
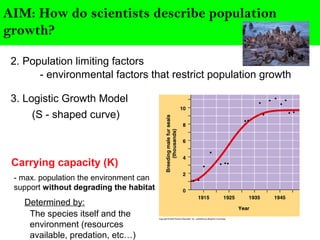
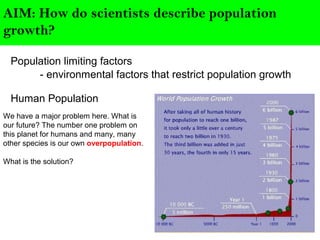
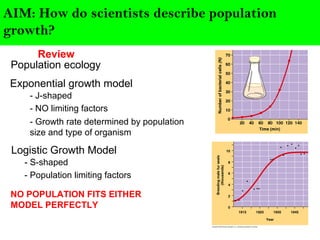
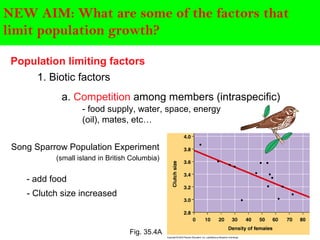
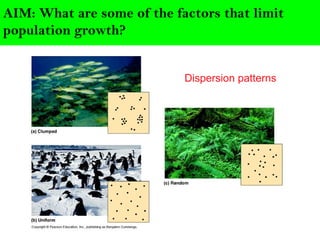
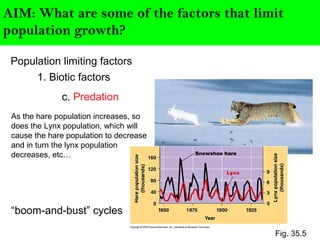
Scientists describe population growth using models like exponential and logistic growth. Exponential growth assumes unlimited resources leading to rapid growth, while logistic growth incorporates limiting factors that slow growth as the population approaches the carrying capacity. Population size is regulated by biotic factors like competition for resources, disease, predation, and physiological stress at high densities, as well as abiotic factors such as climate, weather, and natural disasters. No population perfectly fits either the exponential or logistic growth models due to the complex interplay of these limiting factors.