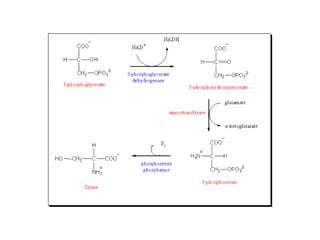
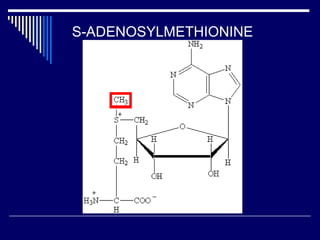
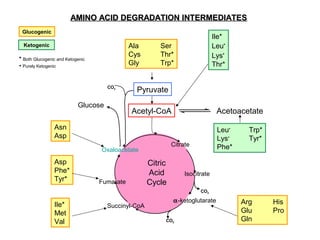
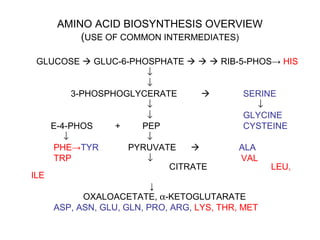
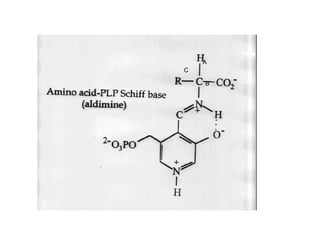
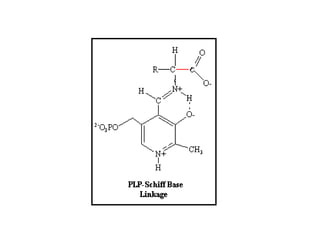
This document discusses amino acid biosynthesis. It begins by explaining how diazotrophs fix atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia. It then describes the glutamate dehydrogenase and glutamine synthetase reactions, which are important in amino acid synthesis. The document notes that preformed alpha-amino nitrogen in the form of glutamate must be considered an essential nutrient. It lists the essential and nonessential amino acids, and explains how nonessential amino acids are synthesized from common metabolic intermediates like pyruvate, oxaloacetate, and alpha-ketoglutarate using transamination reactions. The role of tetrahydrofolate in transferring single carbon units for metabolic precursors is also summarized.











![BACTERIAL GLUTAMINE
SYNTHETASE
BRIEF REVIEW: REGULATING ENZYME
ACTIVITY
NEAR-EQUILIBRIUM (REVERSIBLE)
REACTANTS, PRODUCTS ~ EQUIL. VALUES
ENZYMES ACT QUICKLY TO RESTORE EQUIL.
RATES REGULATED BY [REACT], [PROD]
FAR FROM EQUILIBRIUM (IRREVERSIBLE)
ENZYME SATURATED
NOT ENOUGH ACTIVITY TO ALLOW EQUIL.
RATE INSENSITIVE TO [REACT], [PROD]
“STEADY STATE” (CONSTANT FLUX)
“RATE-DETERMINING STEP”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aminoacidsynthesis-160902171841/85/Amino-acidsynthesis-15-320.jpg)