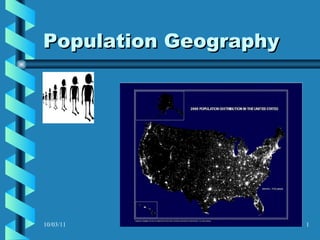
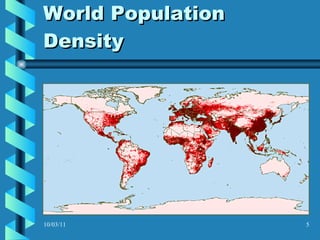
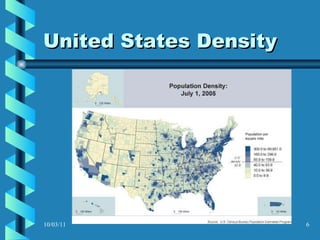
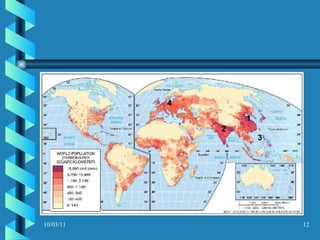
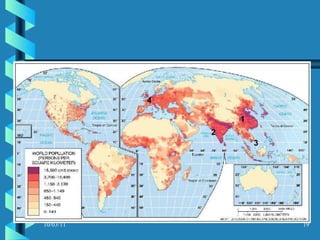
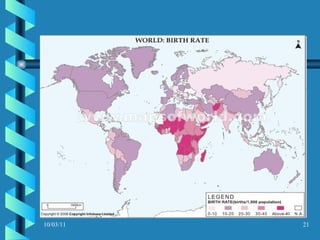
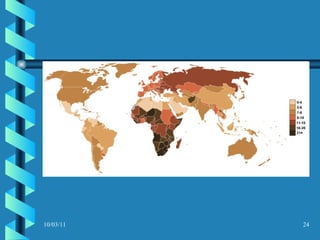
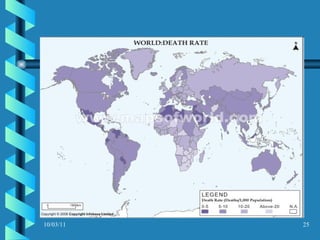
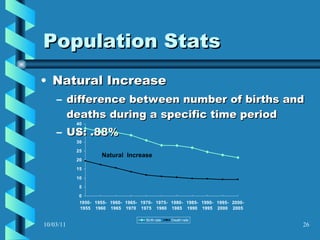
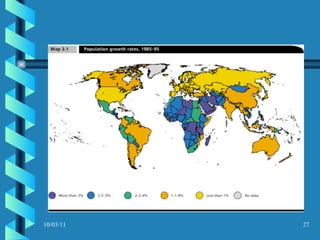
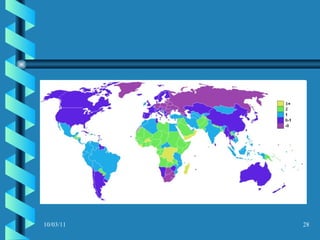
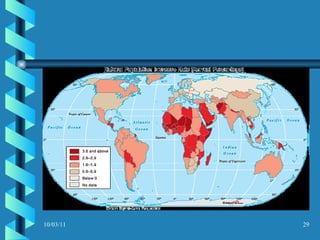
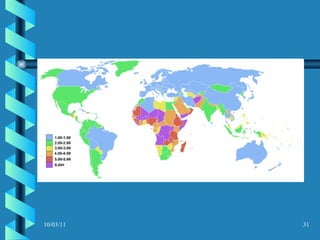
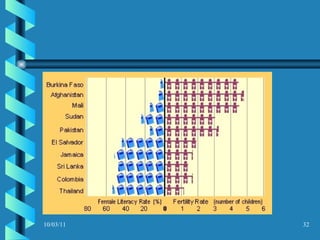
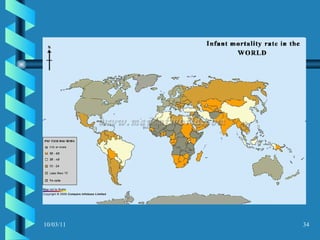
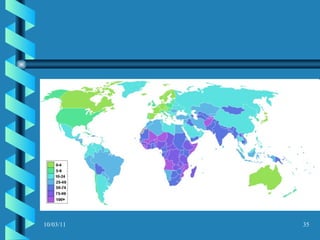
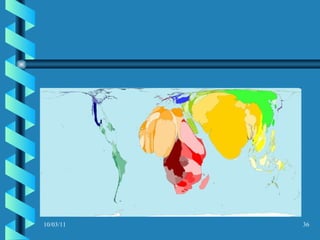
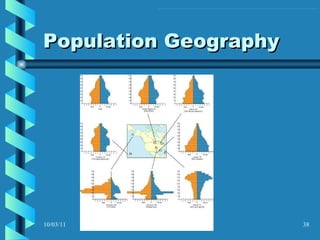
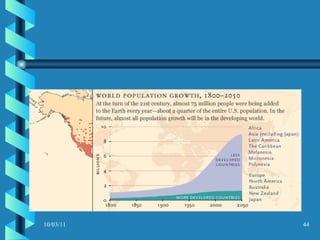
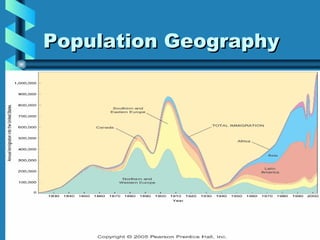
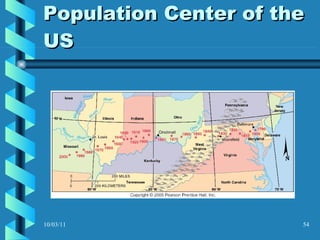
The document discusses key concepts in population geography, including population distribution, density, and growth rates around the world. It notes that over half of the world's population lives in East, South, and Southeast Asia despite these regions making up under 10% of the world's total land area. Birth and death rates vary significantly between regions and are linked to factors like modernization and development. Exponential population growth has led to shorter doubling times in recent decades.