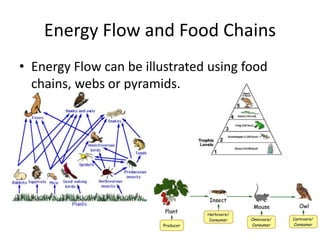
The document discusses energy flow through ecosystems. It explains that:
1) Solar energy is absorbed by plants and used to produce food through photosynthesis.
2) Animals obtain energy by eating plants or other animals. As they are more active, there are typically more plants than animals.
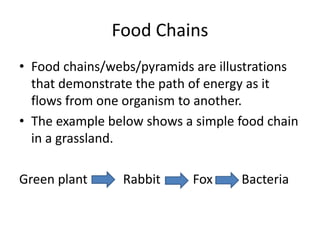
3) When organisms die, decomposers like bacteria break down their bodies and recycle the energy and nutrients.